Abstract
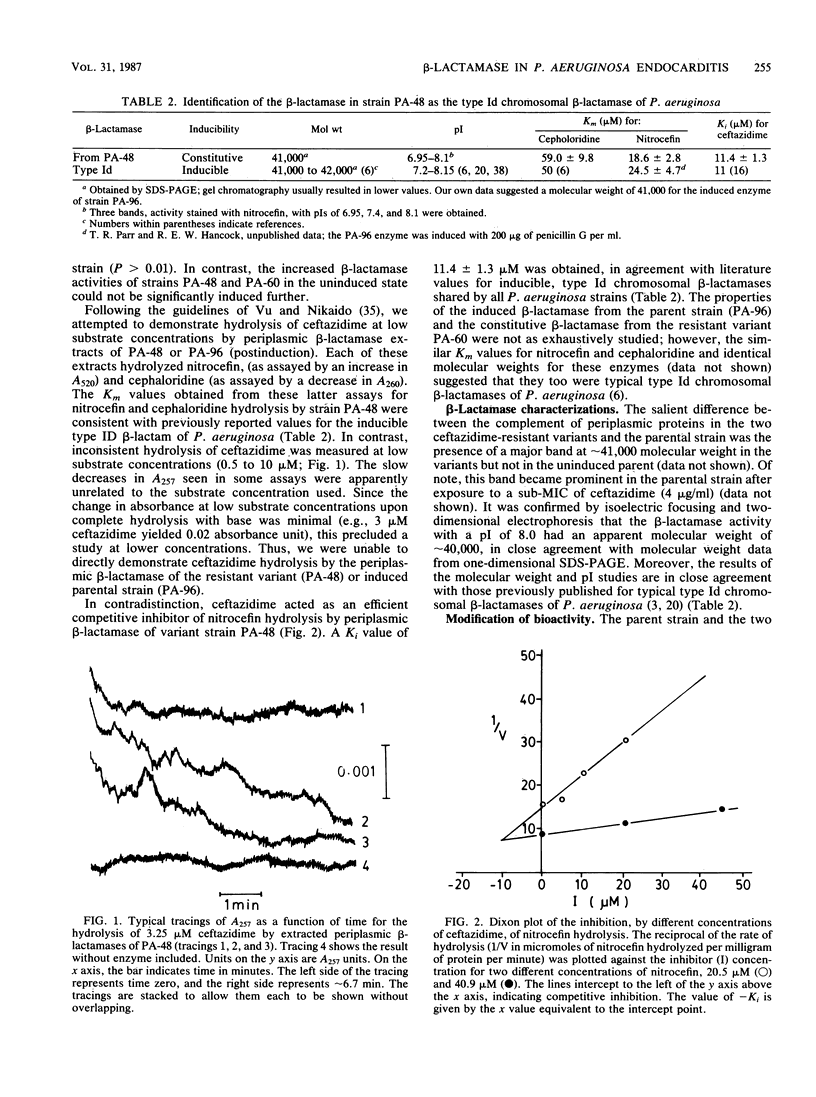
Two ceftazidime-resistant variants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA-48, PA-60), obtained from cardiac vegetations of rabbits with endocarditis receiving ceftazidime therapy, were studied for mechanisms of resistance. Both resistant variants were stably derepressed for the type Id beta-lactamase, which was ceftazidime inducible in the parental strain (PA-96) used to initially infect the rabbits. There was no evidence of ceftazidime bioinactivation by the resistant strains, and their outer membrane permeabilities were comparable to those of the parental strain. No alterations were observed in patterns of outer membrane proteins or membrane lipopolysaccharides in the resistant variants as compared with the parental strain. Penicillin-binding protein patterns of the resistant variants revealed the absence of penicillin-binding protein 4 in both, with acquisition of a new protein of higher apparent molecular weight in PA-60. Calculation of the rate of appearance of ceftazidime in the periplasm at sub-MICs suggested that slow enzymatic hydrolysis of the beta-lactam, rather than nonhydrolytic trapping, was the major explanation for the induced resistance in vivo in strains PA-48 and PA-60.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus B. L., Carey A. M., Caron D. A., Kropinski A. M., Hancock R. E. Outer membrane permeability in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of a wild-type with an antibiotic-supersusceptible mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Feb;21(2):299–309. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Norman D., Kim K. S. Efficacy of amikacin and ceftazidime in experimental aortic valve endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):781–785. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D. Two-dimensional CNBr peptide patterns of collagen types I, II and III. Coll Relat Res. 1981;1(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(80)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Kwan S., Godfrey A. J. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants with altered control of chromosomal beta-lactamase to piperacillin, ceftazidime, and cefsulodin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):382–384. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. L., Mendelman P. M., Levy J., Stull T. L., Smith A. L. A permeability barrier as a mechanism of chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):46–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Hatlelid L., Bryan L. E. Correlation between lipopolysaccharide structure and permeability resistance in beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootz T. D., Sanders C. C., Goering R. V. Resistance to cefamandole: derepression of beta-lactamases by cefoxitin and mutation in Enterobacter cloacae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jul;146(1):34–42. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T., Kageyama M. Purification and properties of a binding protein for branched-chain amino acids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1055–1063. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1055-1063.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keim G. R., Sibley P. L., Hines F. A., Miller M. M., Peterson A. E., Yoon Y. H. Parenteral toxicological profile of the monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic SQ 26,776 in mice, rats and dogs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8 (Suppl E):141–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.suppl_e.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Shannon K., Eykyn S., Phillips I. Reduced sensitivity to beta-lactam antibiotics arising during ceftazidime treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12(4):363–370. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.4.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu Y., Murakami K., Nishikawa T. Penetration of moxalactam into its target proteins in Escherichia coli K-12: comparison of a highly moxalactam resistant mutant with its parent strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):613–619. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Williams J. D., Davy K. W. Cephalosporin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with special reference to the proposed trapping of antibiotics by beta-lactamase. Chemioterapia. 1985 Feb;4(1):28–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Williams R. J., Williams J. D. Comparison of the beta-lactamase stability and the in-vitro activity of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, cefsulodin, ceftazidime, moxalactam and ceftriaxone against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):323–331. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane permeability: isolation of a porin protein F-deficient mutant. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):281–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.281-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Song S. A., Shaltiel L., Nurminen M. Outer membrane of Salmonella XIV. Reduced transmembrane diffusion rates in porin-deficient mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Fukasawa M., Komatsu T., Mitsuhashi S., Matsuhashi M. Mutation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing simultaneous defects in penicillin-binding protein 5 and in enzyme activities of penicillin release and D-alanine carboxypeptidase. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):849–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.849-851.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative studies of penicillin-binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L. C., Penn R. G., Sanders C. C., Goering R. V., Giger D. K. Emergence of resistance to beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics during moxalactam therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes M. P., Lerner A. M. Current problems in the treatment of infective endocarditis due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):314–321. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance during therapy with the newer beta-lactam antibiotics: role of inducible beta-lactamases and implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):639–648. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Angehrn P. Trapping of nonhydrolyzable cephalosporins by cephalosporinases in Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a possible resistance mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Livermore D. M., Lindridge M. A., Said A. A., Williams J. D. Mechanisms of beta-lactam resistance in British isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Jun;17(3):283–293. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-3-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Busuttil R. W., Kurtz T. O., Young L. S. Moxalactam therapy for bacterial infections. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Nov;141(12):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Sawai T., Ono H., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Biochemical properties of a cephalosporin beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;17(2):141–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Permeability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane to hydrophilic solutes. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):636–642. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.636-642.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]