Abstract
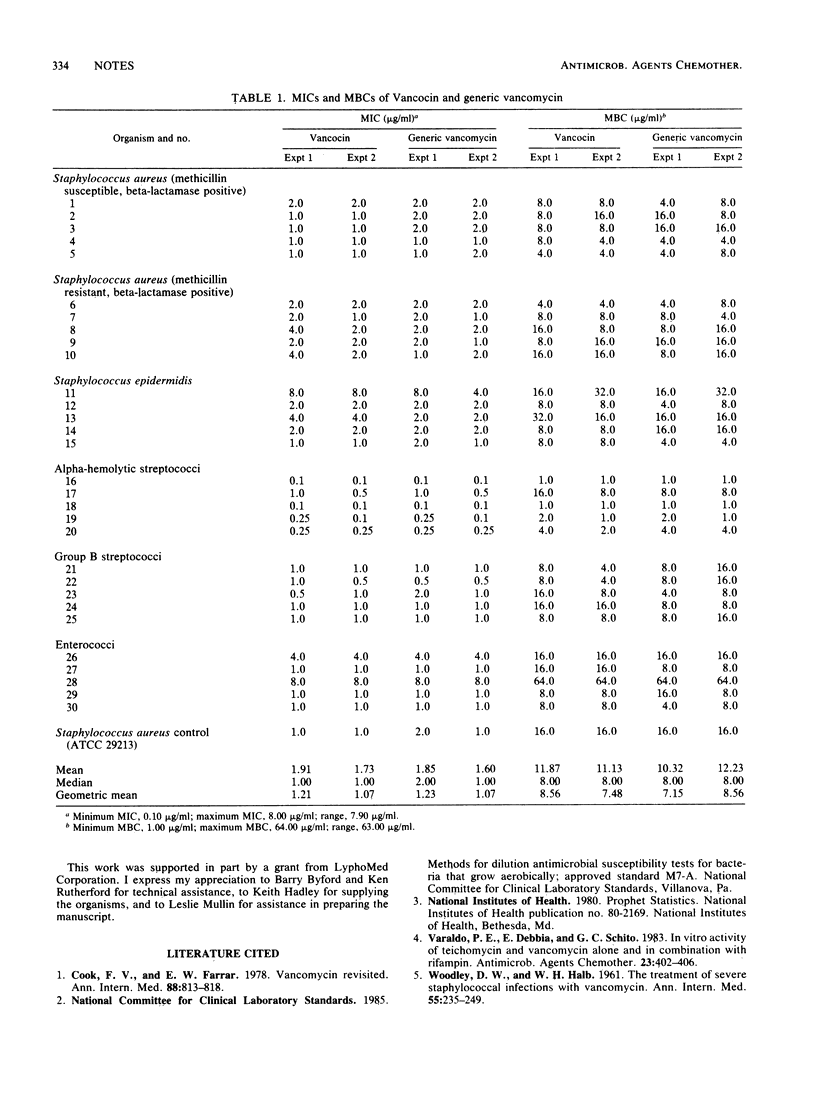
The in vitro antibacterial activity of generic vancomycin was compared with that of Vancocin (vancomycin hydrochloride; Eli Lilly & Co.) using macrotube dilution testing and subculture. There were no significant differences in MICs or MBCs of the two drugs when tested against a variety of recently isolated hospital pathogens.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgers M., De Brabander M., Van Den Bossche H., Van Cutsem J. Promotion of pseudomycelium formation of Candida albicans in culture: a morphological study of the effects of miconazole and ketoconazole. Postgrad Med J. 1979 Sep;55(647):687–691. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.55.647.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Schwartz D. R., Vertut-Croquin A., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Involvement of oxidative damage in erythrocyte lysis induced by amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):172–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Elberg S. Influence of extracellular K+ or Mg2+ on the stages of the antifungal effects of amphotericin B and filipin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):593–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook F. V., Farrar W. E., Jr Vancomycin revisited. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jun;88(6):813–818. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-6-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Drutz D. J., Zajic J. E. Factors governing adherence of Candida species to plastic surfaces. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.97-101.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisch P. A., Calderone R. A. Adherence of Candida albicans to a fibrin-platelet matrix formed in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.650-656.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niimi M., Kamiyama A., Tokunaga M., Tokunaga J., Nakayama H. Germ tube-forming cells of Candida albicans are more susceptible to clotrimazole-induced killing than yeast cells. Sabouraudia. 1985 Feb;23(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent K. M., Couchot K. R. Effects of sublethal concentrations of amphotericin B on Candida albicans. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):665–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rast D. M., Bartnicki-Garcia S. Effects of amphotericin B, nystatin, and other polyene antibiotics on chitin synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1233–1236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Bedell G. W., Brummel M. Zinc and regulation of growth and phenotype in the infectious yeast Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1139–1147. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1139-1147.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staebell M., Soll D. R. Temporal and spatial differences in cell wall expansion during bud and mycelium formation in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1467–1480. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varaldo P. E., Debbia E., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Mar;23(3):402–406. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.3.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODLEY D. W., HALL W. H. The treatment of severe staphylococcal infections with vancomycin. Ann Intern Med. 1961 Aug;55:235–249. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood N. C., Nugent K. M. Inhibitory effects of chlorpromazine on Candida species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):692–694. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


