Abstract
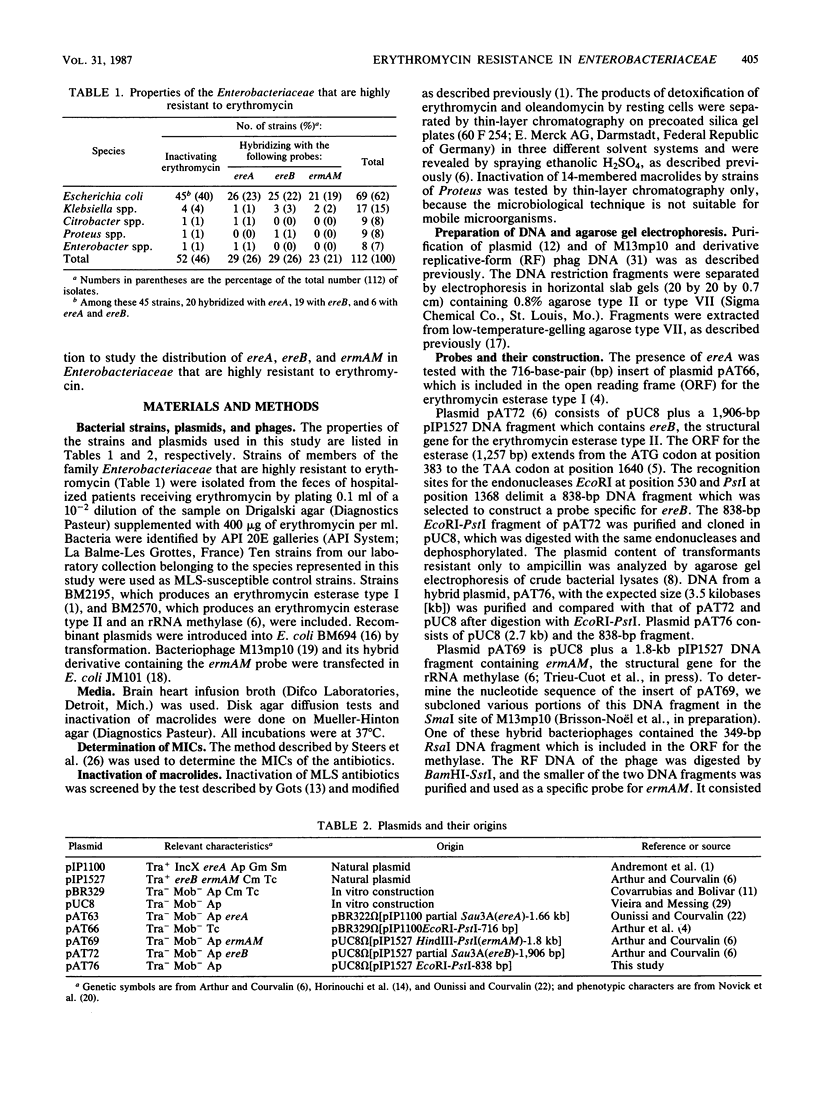
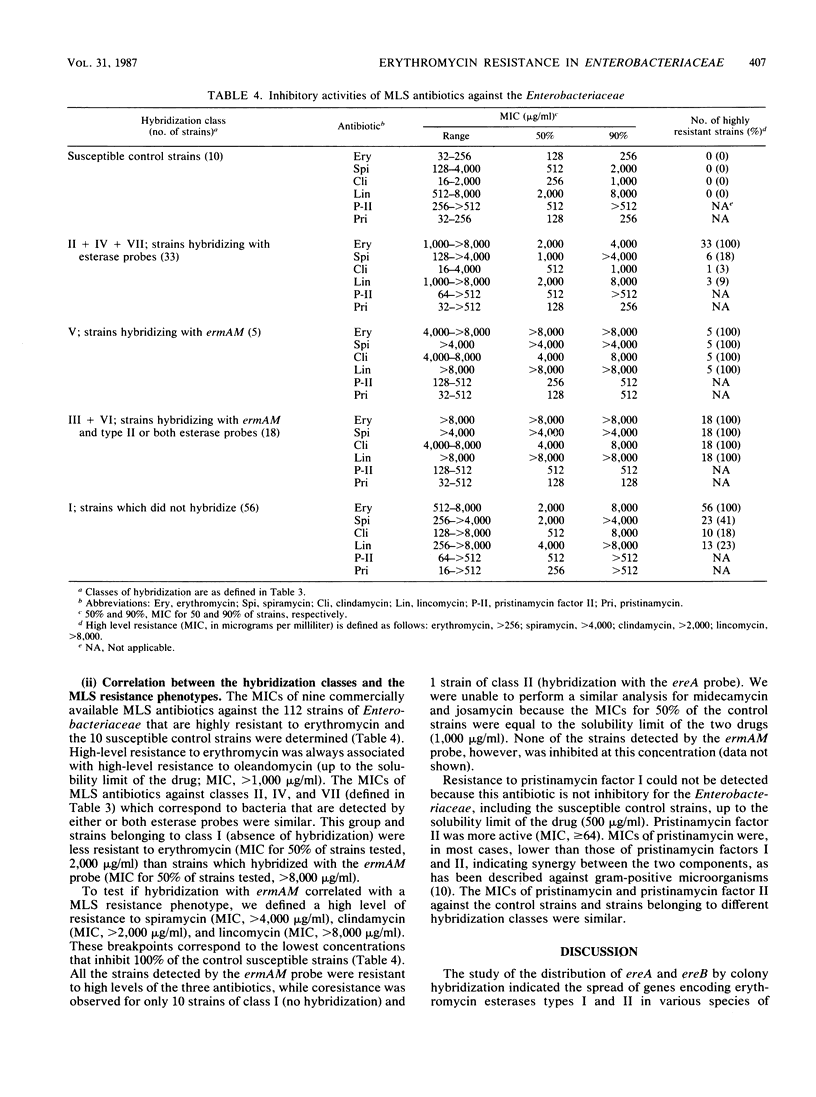
The distribution of nucleotide sequences related to ereA, ereB, and ermAM was studied by colony hybridization in 112 strains of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae that are highly resistant to erythromycin. The ereA and ereB genes encoding erythromycin esterases type I and II, respectively, were detected in strains inactivating the 14-membered macrolides erythromycin and oleandomycin. Because all 52 strains resisting these antibiotics by inactivation were detected by ereA (n = 23), ereB (n = 23), or both probes (n = 6), only two classes of genes accounted for this resistance phenotype. The ermAM gene encoding a streptococcal rRNA methylase was detected in 21 strains of Escherichia coli and two strains of Klebsiella spp. Determination of the MICs of macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin (MLS) antibiotics demonstrated a correlation between hybridization with ermAM and the so-called MLS resistance phenotype. The presence of 11 strains coresistant to MLS antibiotics that did not hybridize to the ermAM probe suggests that, as in gram-positive organisms, MLS resistance in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae involves more than one class of rRNA methylase. Numerous strains (n = 18) were found to produce both an erythromycin esterase type II and an rRNA methylase. Physical linkage between ereB and ermAM may be responsible for the codissemination of the genes. Despite their exogenous origin, ereB and ermAM are already disseminated in various genera of the Enterobacteriaceae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andremont A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated high-level resistance to erythromycin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):515–518. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae highly resistant to erythromycin in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Tancrede C. Reduction of the aerobic Gram negative bacterial flora of the gastro-intestinal tract and prevention of traveller's diarrhea using oral erythromycin. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Nov-Dec;132 B(3):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Andremont A., Courvalin P. Heterogeneity of genes conferring high-level resistance to erythromycin by inactivation in enterobacteria. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Mar-Apr;137A(2):125–134. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Autissier D., Courvalin P. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the ereB gene encoding the erythromycin esterase type II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 25;14(12):4987–4999. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.12.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur M., Courvalin P. Contribution of two different mechanisms to erythromycin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):694–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy P., Autissier D., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Enzymic hydrolysis of erythromycin by a strain of Escherichia coli. A new mechanism of resistance. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Dec;37(12):1692–1696. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Courvalin P. Synergie des composants des antibiotiques du groupe de la streptogramine. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1971 Jun-Jul;19(11):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. VI. Plasmid pBR329, a new derivative of pBR328 lacking the 482-base-pair inverted duplication. Gene. 1982 Jan;17(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots J. S. THE DETECTION OF PENICILLINASE-PRODUCING PROPERTIES OF MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1945 Sep 21;102(2647):309–309. doi: 10.1126/science.102.2647.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horinouchi S., Byeon W. H., Weisblum B. A complex attenuator regulates inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides, and streptogramin type B antibiotics in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1252–1262. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1252-1262.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Casadaban M. J. Transposition of the gram-positive transposon Tn917 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):711–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.711-712.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Translocation of sequences encoding antibiotic resistance from the chromosome to a receptor plasmid in Salmonella ordonez. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):390–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00293927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ounissi H., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the gene ereA encoding the erythromycin esterase in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;35(3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Lorian V., Gerstein D., Loder P. B., Finland M. Enhancing effect on alkalinization of the medium on the activity of erythromycin against gram-negative bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1288–1292. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1288-1292.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. H., Clewell D. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B-resistance transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):782–796. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.782-796.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4653–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakker-Varia S., Ranzini A. C., Dubin D. T. Ribosomal RNA methylation in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli: effect of the "MLS" (erythromycin resistance) methylase. Plasmid. 1985 Sep;14(2):152–161. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B. Inducible resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramin type B antibiotics: the resistance phenotype, its biological diversity, and structural elements that regulate expression--a review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16 (Suppl A):63–90. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.suppl_a.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Boeke J. D. The filamentous phage (Ff) as vectors for recombinant DNA--a review. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




