Abstract
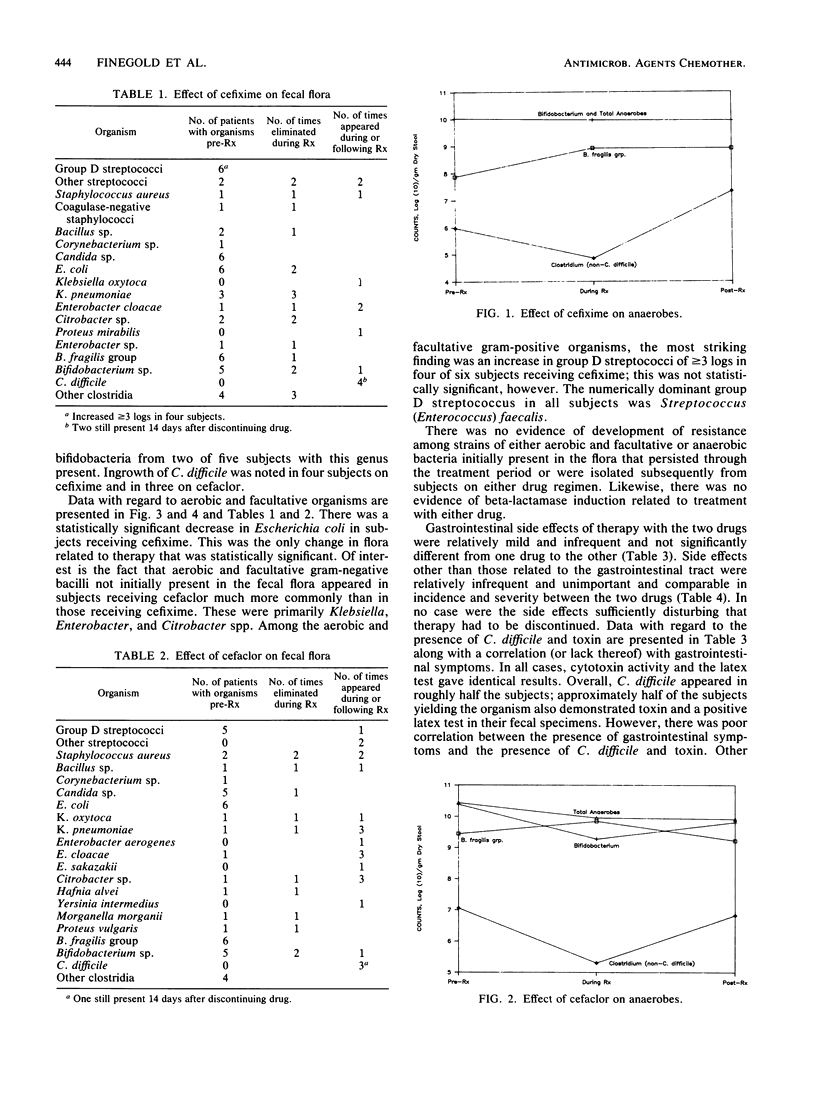
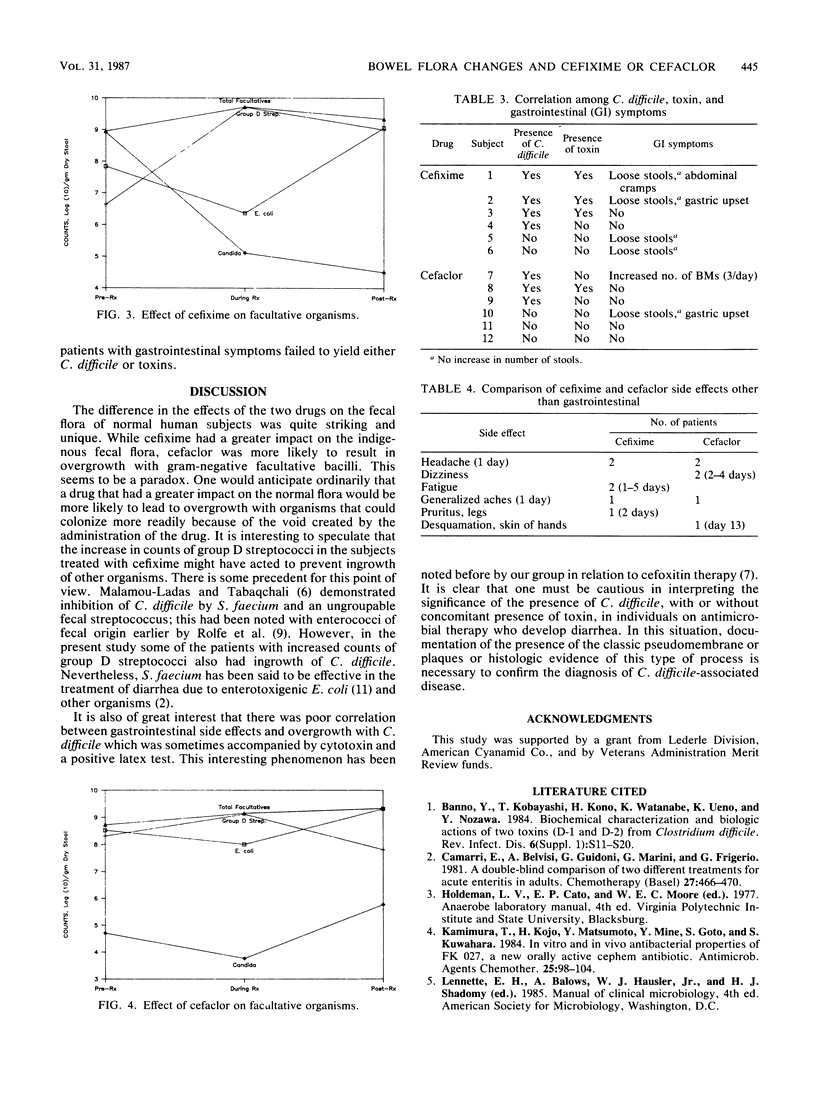
Twelve healthy young male subjects received either cefixime, a new oral cephalosporin (CL 284,635), or cefaclor (six subjects on each drug) orally for 2 weeks. In the case of cefixime, single daily doses of 400 mg were taken; with cefaclor, the dosage was 250 mg three times daily. Modest changes in the fecal flora were noted in both drug groups, but the changes were of different types. In the case of cefixime, there was more of an impact on the indigenous flora, and in the case of cefaclor, there was more ingrowth of new flora. With cefixime, Enterobacteriaceae were usually decreased (the decrease in Escherichia coli count was statistically significant), as were counts of clostridia and sometimes Bifidobacterium spp.; the Bacteroides fragilis group was eliminated in one subject. Coincident with these decreases, four subjects had increases in counts of group D streptococci of 3 logs or more. There was new appearance of Clostridium difficile in four subjects and of Staphylococcus aureus in one; four new strains of Enterobacteriaceae appeared. With cefaclor, there was no decrease of E. coli counts; two subjects had elimination of Bifidobacterium spp. There was little change in counts of group D streptococci. On the other hand, there were 13 new strains of Enterobacteriaceae, two of S. aureus, and three of C. difficile.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banno Y., Kobayashi T., Kono H., Watanabe K., Ueno K., Nozawa Y. Biochemical characterization and biologic actions of two toxins (D-1 and D-2) from Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S11–S20. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camarri E., Belvisi A., Guidoni G., Marini G., Frigerio G. A double-blind comparison of two different treatments for acute enteritis in adults. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(6):466–470. doi: 10.1159/000238017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura T., Kojo H., Matsumoto Y., Mine Y., Goto S., Kuwahara S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial properties of FK 027, a new orally active cephem antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jan;25(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamou-Ladas H., Tabaqchali S. Inhibition of Clostridium difficile by faecal streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):569–574. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Citron D., Gabay E., Kirby B. D., George W. L., Finegold S. M. Alterations in human fecal flora, including ingrowth of Clostridium difficile, related to cefoxitin therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Sep;26(3):343–346. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.3.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe R. D., Helebian S., Finegold S. M. Bacterial interference between Clostridium difficile and normal fecal flora. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):470–475. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Streptococcus faecium M 74 in control of diarrhoea induced by a human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain in an infant rabbit model. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984 Aug;257(3):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


