Abstract
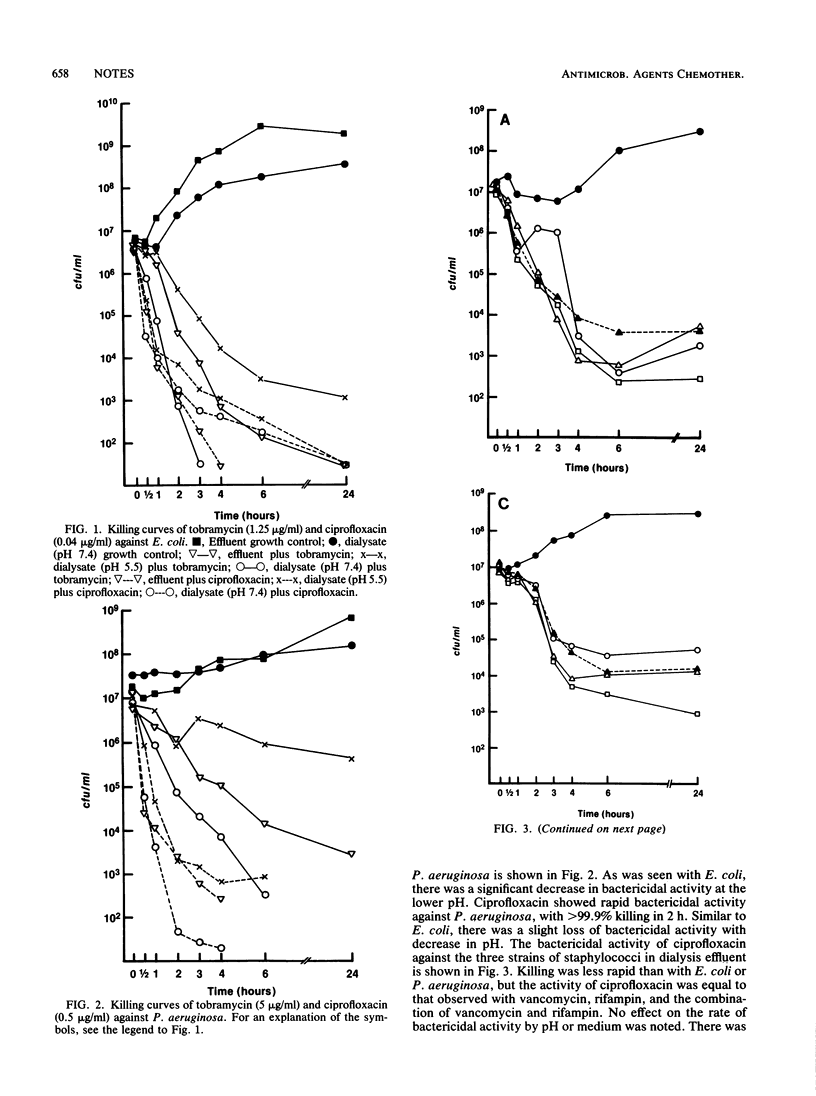
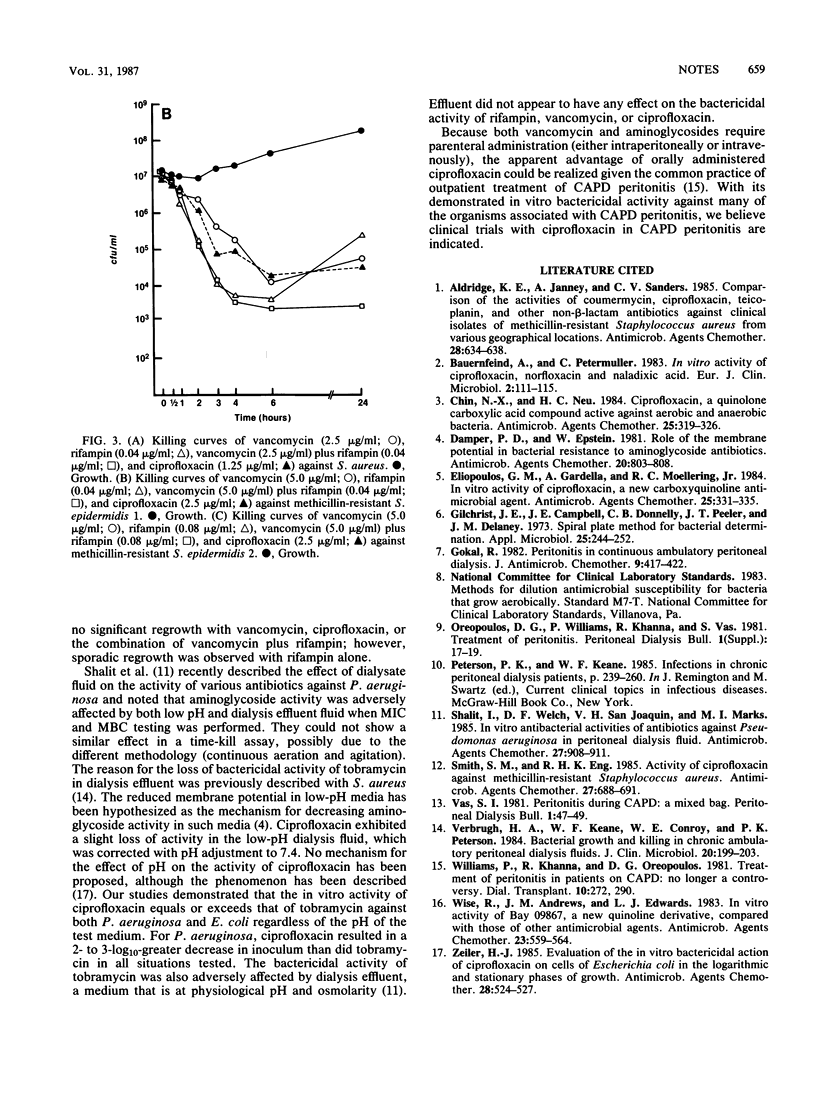
Ciprofloxacin is active in vitro against most bacteria that cause peritonitis associated with peritoneal dialysis. We compared the effects of pH (5.5 and 7.4) and medium (dialysis fluid) on the bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin, tobramycin, vancomycin plus rifampin, and rifampin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and three strains of staphylococci. The bactericidal activity of ciprofloxacin was not significantly affected by pH or medium, in contrast to the activity of tobramycin, which was decreased by low pH.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge K. E., Janney A., Sanders C. V. Comparison of the activities of coumermycin, ciprofloxacin, teicoplanin, and other non-beta-lactam antibiotics against clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from various geographical locations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):634–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damper P. D., Epstein W. Role of the membrane potential in bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Dec;20(6):803–808. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.6.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist J. E., Campbell J. E., Donnelly C. B., Peeler J. T., Delaney J. M. Spiral plate method for bacterial determination. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):244–252. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.244-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gokal R. Peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jun;9(6):417–420. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalit I., Welch D. F., San Joaquin V. H., Marks M. I. In vitro antibacterial activities of antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in peritoneal dialysis fluid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):908–911. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H. Activity of ciprofloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):688–691. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Keane W. F., Conroy W. E., Peterson P. K. Bacterial growth and killing in chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis fluids. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):199–203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.199-203.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J. Evaluation of the in vitro bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin on cells of Escherichia coli in the logarithmic and stationary phases of growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):524–527. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


