MEDICAL SCIENCES. For the article “Germ-line mutations in p27Kip1 cause a multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome in rats and humans,” by Natalia S. Pellegata Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez Heide Siggelkow Elenore Samson Karin Bink Heinz Höfler Falko Fend Jochen Graw and Michael J. Atkinson, which appeared in issue 42, October 17, 2006, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (103:15558–15563; first published October 9, 2006; 10.1073/pnas.0603877103), the authors note that in Fig. 3B, patient II-1 was incorrectly identified as having parathyroid cancer (PC). The corrected figure and legend appear below. These errors do not affect the conclusions of the article.
Fig. 3.
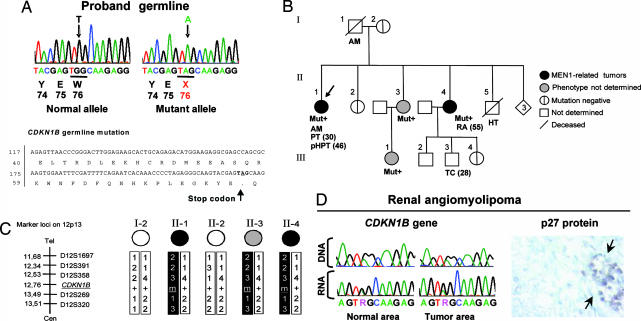
Identification of a germ-line mutation in CDKN1B in a suspected MEN1 patient and segregation analyses. (A) A PCR fragment corresponding to part of the CDKN1B exon 1 was obtained from the proband and cloned, and both alleles were sequenced separately. (Upper) The germ-line of the proband showed a heterozygous nonsense mutation at codon 76 (c. 692G→A). (Lower) Shown is the position of the mutation in the CDKN1B gene and p27 protein. (B) Proband family pedigree. Generation numbers are represented by Roman numerals; individuals are represented by Arabic numerals. The proband is II-1, indicated by the arrow. Mut+, mutation-positive individual; AM, acromegaly; PT, pituitary adenoma; pHPT, primary hyperparathyroidism; RA, renal angiomyolipoma; HT, hypertension; TC, testicular cancer. Age of onset is given in parentheses. (C) Haplotype analysis. The microsatellite markers on chromosome 12, and their positions, are indicated on the right. The affected haplotype is indicated in black. (D) Analysis of the tumor tissue of individual II-4. (Left) Sequencing chromatograms showing the 692G→A mutation in both normal and tumor tissue DNA and RNA. (Right) Immunohistochemical staining with an anti-p27 antibody shows lack of p27 protein in the tumor tissue. The arrows indicate infiltrating lymphocytes used as positive control for p27 staining. (Immunoperoxidase original magnification: ×640.)