Abstract
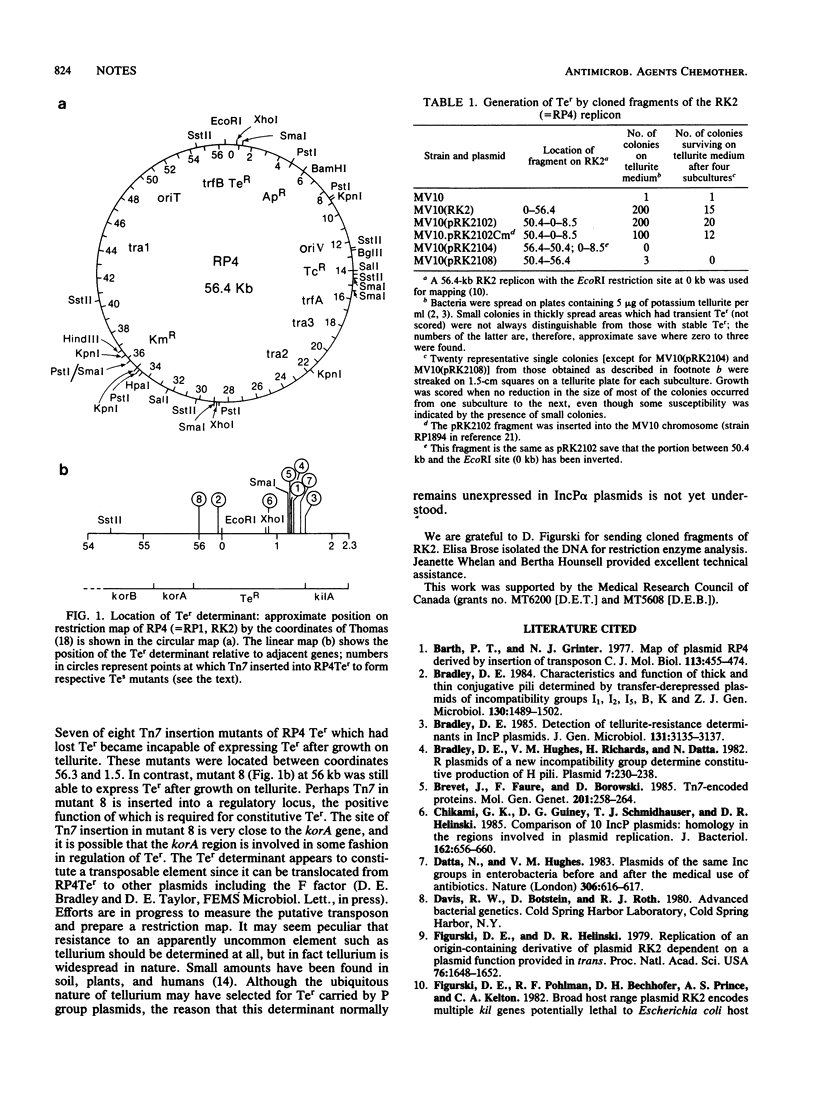
The tellurite resistance (Ter) determinant of RP4 is not normally expressed unless variants are selected on medium containing tellurite. The determinant was mapped in the variant plasmid RP4Ter by Tn7 insertion mutagenesis. Based on a 56.4-kilobase (kb) replicon, it covered the region from 56 kb, across the EcoRI site at 0 kb, to 1.5 kb.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Map of plasmid RP4 derived by insertion of transposon C. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul 5;113(3):455–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Characteristics and function of thick and thin conjugative pili determined by transfer-derepressed plasmids of incompatibility groups I1, I2, I5, B, K and Z. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jun;130(6):1489–1502. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-6-1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Detection of tellurite-resistance determinants in IncP plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Nov;131(11):3135–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-11-3135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Hughes V. M., Richards H., Datta N. R plasmids of a new incompatibility group determine constitutive production of H pili. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brevet J., Faure F., Borowski D. Tn7-encoded proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(2):258–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00425668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikami G. K., Guiney D. G., Schmidhauser T. J., Helinski D. R. Comparison of 10 IncP plasmids: homology in the regions involved in plasmid replication. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):656–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.656-660.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hughes V. M. Plasmids of the same Inc groups in Enterobacteria before and after the medical use of antibiotics. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):616–617. doi: 10.1038/306616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Pohlman R. F., Bechhofer D. H., Prince A. S., Kelton C. A. Broad host range plasmid RK2 encodes multiple kil genes potentially lethal to Escherichia coli host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial drugs and toxic metal ions in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):361–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.361-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanka E., Lurz R., Fürste J. P. Molecular cloning and mapping of SphI restriction fragments of plasmid RP4. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Jacoby G. A. Plasmid-determined resistance to tellurium compounds. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):276–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.276-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Summers A. O. Association of tellurium resistance and bacteriophage inhibition conferred by R plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1430–1433. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1430-1433.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E. Transfer-defective and tetracycline-sensitive mutants of the incompatibility group HI plasmid R27 generated by insertion of transposon 7. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M. Molecular genetics of broad host range plasmid RK2. Plasmid. 1981 Jan;5(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel R., Hedges R. W., Maenhaut R., Leemans J., Engler G., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Heteroduplex analysis of P-plasmid evolution: the role of insertion and deletion of transposable elements. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):390–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00325900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley M., Taylor D. E. Identification of DNA homologies among H incompatibility group plasmids by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern transfer hybridization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):194–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Bechhofer D. H., Figurski D. H. Gene regulation in plasmid RK2: positive control by korA in the expression of korC. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.247-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


