Abstract
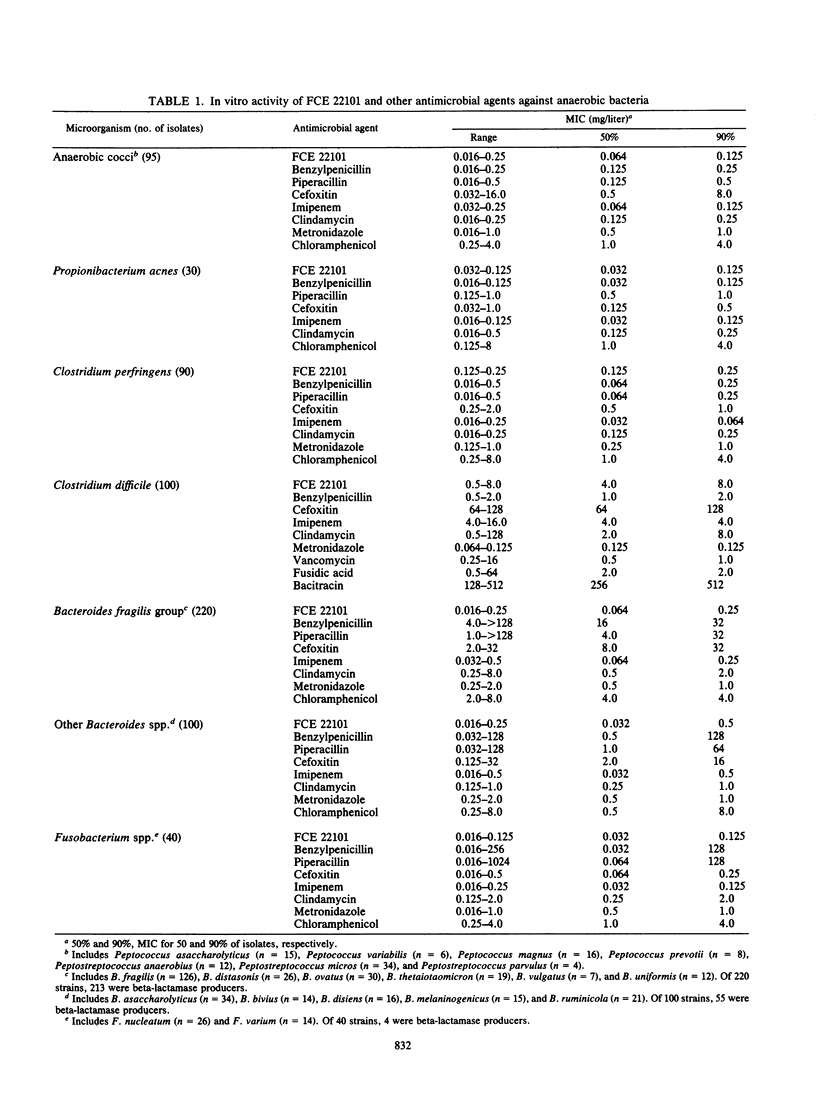
The activity of FCE 22101 against 675 strains of anaerobic bacteria was determined by an agar dilution method. Its activity was compared with those of benzylpenicillin, piperacillin, cefoxitin, imipenem, clindamycin, metronidazole, chloramphenicol, vancomycin, fusidic acid, and bacitracin. FCE 22101 and imipenem (MIC, less than or equal to 0.5 mg/liter) were the most active agents against the anaerobic strains tested, except against Clostridium difficile strains. On the basis of these results, FCE 22101 appears to be a promising antimicrobial agent for treatment of anaerobic infections, and further clinical investigations are indicated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dornbusch K., Nord C. E., Olsson-Liljeqvist B. Antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria with special reference to Bacteroides fragilis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1979;(19):17–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Chin N. X., Labthavikul P. The in-vitro activity of a novel penem FCE 22101 compared to other beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Sep;16(3):305–313. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordbring F., Nord C. E. Aspects on antibacterial treatment of anaerobic infections. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1982;35:59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


