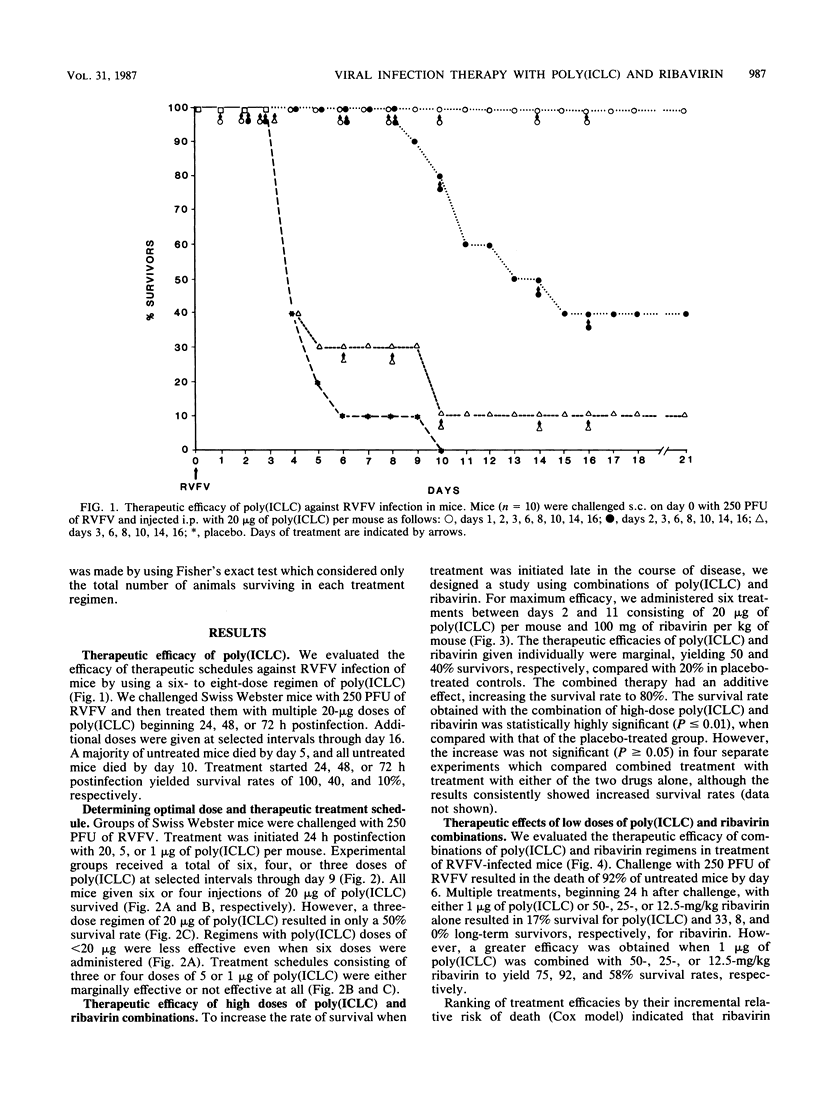
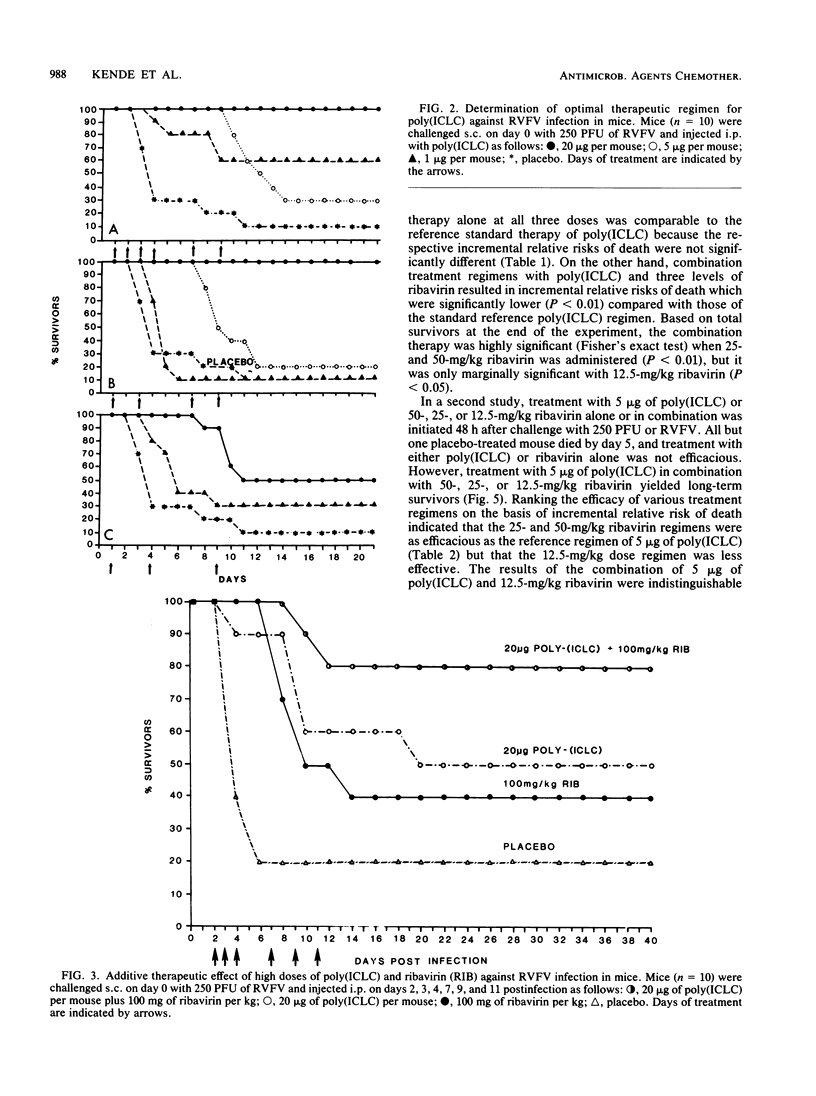
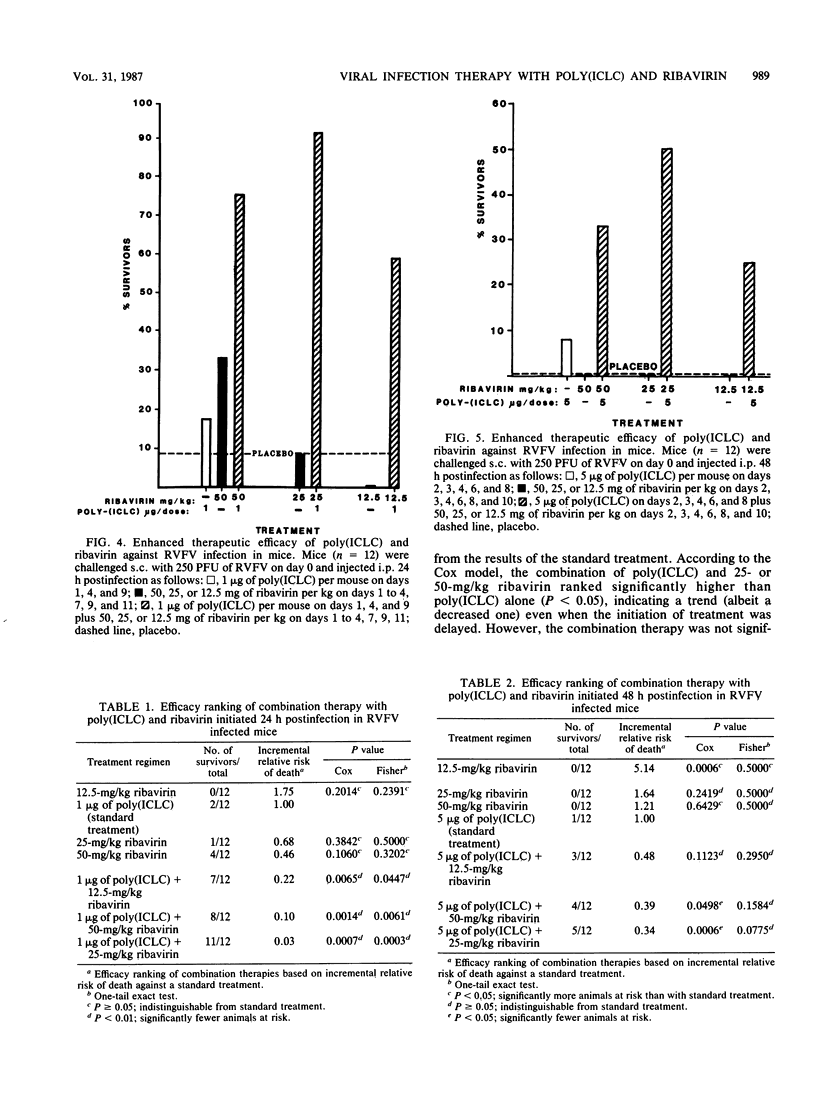
Abstract
The therapeutic efficacy of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid stabilized with poly-L-lysine and carboxymethyl cellulose [poly(ICLC)] given alone or in combination with ribavirin was evaluated in Swiss Webster mice infected with Rift Valley fever virus. Four or more 20-micrograms doses of poly(ICLC) given at various intervals beginning 24 h after infection protected all mice against death. On the other hand, a treatment regimen consisting of only three doses of poly(ICLC) given 24 h postinfection resulted in a 50% survival rate. When initiated 48 h postinfection, an extended treatment regimen with the same dose was required to yield 40% survivors. Lower doses (5 micrograms) of poly(ICLC) per mouse were only marginally effective even when six injections were given between days 1 and 9 postinfection. The combined administration of ribavirin and poly(ICLC) initiated as late as 48 h postinfection was effective even when treatment consisted of doses that were ineffective when either drug was used alone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer G. M., Shaddock J. H., Moore S. A., Yager P. A., Baron S. S., Levy H. B. Successful prophylaxis against rabies in mice and Rhesus monkeys: the interferon system and vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):286–291. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Interferon-induced enzymatic activities and their role in the antriviral state. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90151-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonico P. G., Kende M., Luscri B. J., Huggins J. W. In-vivo activity of antivirals against exotic RNA viral infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Aug;14 (Suppl A):27–41. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_a.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington D. G., Hilmas D. E., Elwell M. R., Whitmire R. E., Stephen E. L. Intranasal infection of monkeys with Japanese encephalitis virus: clinical response and treatment with a nuclease-resistant derivative of poly (I).poly (C). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 1):1191–1198. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. Recent advances in the study of interferon. Pharmacol Rev. 1982 Mar;34(1):119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroath H., Gross H. J., Jungwirth C., Bodo G. RNA methylation in vaccinia virus-infected chick embryo fibroblasts treated with homologous interferon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2441–2454. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehne R. W., Pannier W. L., Stephen E. L. Indirect mouse model for the evaluation of potential antiviral compounds: results with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):683–687. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin S. Interferon in acute viral infections. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;140(1):2–4. doi: 10.1007/BF00661894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., London W., Fuccillo D. A., Baron S., Rice J. Prophylactic control of simian hemorrhagic fever in monkeys by an interferon inducer, polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid-poly-L-lysine. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A256–A259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlin D. E., Bever C. T., Salazar A. M., Levy H. B. A preliminary trial of poly(I,C)-LC in multiple sclerosis. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Oct;4(5):544–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M. The Rift Valley fever epizootic in Egypt 1977-78. 1. Description of the epizzotic and virological studies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):618–623. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Sidwell R. W., Robins R. K. Antiviral mechanisms of action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. L., Hilmas D. E., Levy H. B., Spertzel R. O. Protective and toxic effects of a nuclease-resistant derivative of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid on Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis. 1979 Mar;139(3):267–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen E. L., Sammons M. L., Pannier W. L., Baron S., Spertzel R. O., Levy H. B. Effect of a nuclease-resistant derivative of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid complex on yellow fever in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):122–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


