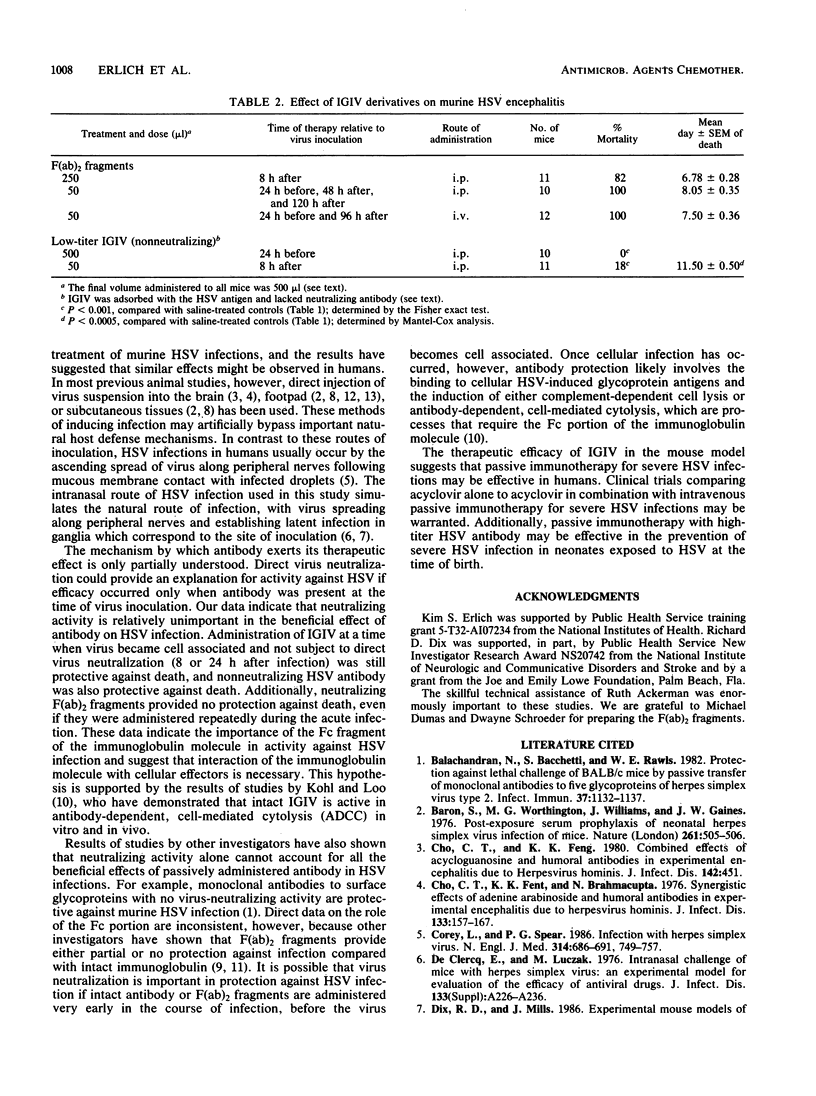
Abstract
Pooled human immunoglobulin suitable for intravenous administration (IGIV) was evaluated in the prophylaxis and treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 encephalitis in a murine model. Four-week-old BALB/c mice received a single intraperitoneal injection of IGIV or saline 24 h before or up to 24 h after intranasal infection with 10(4.6) PFU of HSV type 1. Treatment with IGIV was protective against death, and the protective effects were dose and time dependent. Treatment with IGIV blocked the production of HSV antibody by infected mice and reduced the number of trigeminal ganglia containing latent virus. Removal of neutralizing antibody from the IGIV pool did not eliminate the protective effect, whereas F(ab)2 fragments of IGIV, which had virus-neutralizing activity that was identical to that of native IGIV, conferred no protection against death. Pooled human IGIV was effective for the prevention and treatment of HSV encephalitis in mice. Antibody-mediated protection required the Fc portion of the immunoglobulin molecule but did not require the direct neutralization of virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S., Worthington M. G., Williams J., Gaines J. W. Postexposure serum prophylaxis of neonatal herpes simplex virus infection of mice. Nature. 1976 Jun 10;261(5560):505–506. doi: 10.1038/261505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho C. T., Feng K. K., Brahmacupta N. Synergistic antiviral effects of adenine arabinoside and humoral antibodies in experimental encephalitis due to Herpesvirus hominis. J Infect Dis. 1976 Feb;133(2):157–167. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho C. T., Feng K. K. Combined effects of acycloguanosine and humoral antibodies in experimental encephalitis due to Herpesvirus hominis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Sep;142(3):451–451. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Spear P. G. Infections with herpes simplex viruses (2). N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 20;314(12):749–757. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603203141205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Luczak M. Intranasal challenge of mice with herpes simplex virus: an experimental model for evaluation of the efficacy of antiviral drugs. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A226–A236. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiades J. A., Montgomery J., Hughes T. K., Jensen D., Baron S. Determinants of protection by human immune globulin against experimental herpes neonatorum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jul;170(3):291–297. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida I., Nagafuchi S., Hayashi Y., Kino Y., Mori R., Oda H., Ohtomo N., Tashiro A. Mechanism of antibody-mediated protection against herpes simplex virus infection in athymic nude mice: requirement of Fc portion of antibody. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(6):497–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Loo L. S. Protection of neonatal mice against herpes simplex virus infection: probable in vivo antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):370–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurz K. H., Berger M. Intrauterine contraceptive devices for diabetics. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):707–707. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90725-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R. IgG-mediated viral clearance in experimental infection with herpes simplex virus type 1: role for neutralization and Fc-dependent functions but not C' cytolysis and C5 chemotaxis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):464–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKendall R. R., Klassen T., Baringer J. R. Host defenses in herpes simplex infections of the nervous system: effect of antibody on disease and viral spread. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):305–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.305-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes J. E., Rosemond-Hornbeak H. Antibody-mediated recovery from subcutaneous herpes simplex virus type 2 infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):489–495. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.489-495.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B. Complement fixation by the F(ab')2-fragment of pepsin-treated rabbit antibody. Immunology. 1971 May;20(5):649–658. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Alford C. A., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Luby J. P., Aoki F. Y., Hanley D., Nahmias A. J., Soong S. J. Vidarabine versus acyclovir therapy in herpes simplex encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 16;314(3):144–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601163140303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Nahmias A. J., Soong S. J., Galasso G. G., Fleming C. L., Alford C. A. Vidarabine therapy of neonatal herpes simplex virus infection. Pediatrics. 1980 Oct;66(4):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Hayashi Y., Tang L. L., Mori R. Effects of combined use of acyclovir and antibody in athymic nude mice inoculated intracutaneously with herpes simplex virus. Antiviral Res. 1985 Apr;5(2):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


