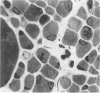
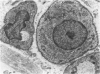
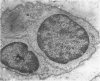
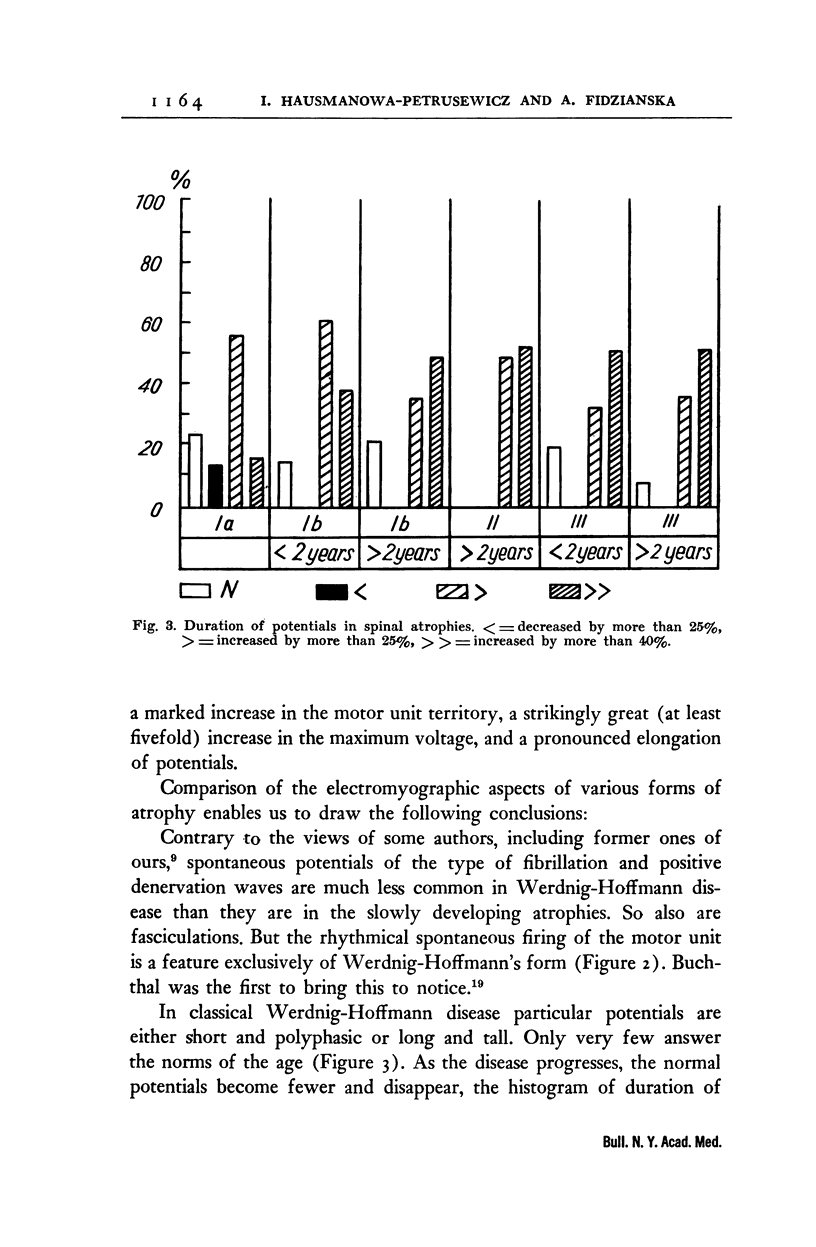
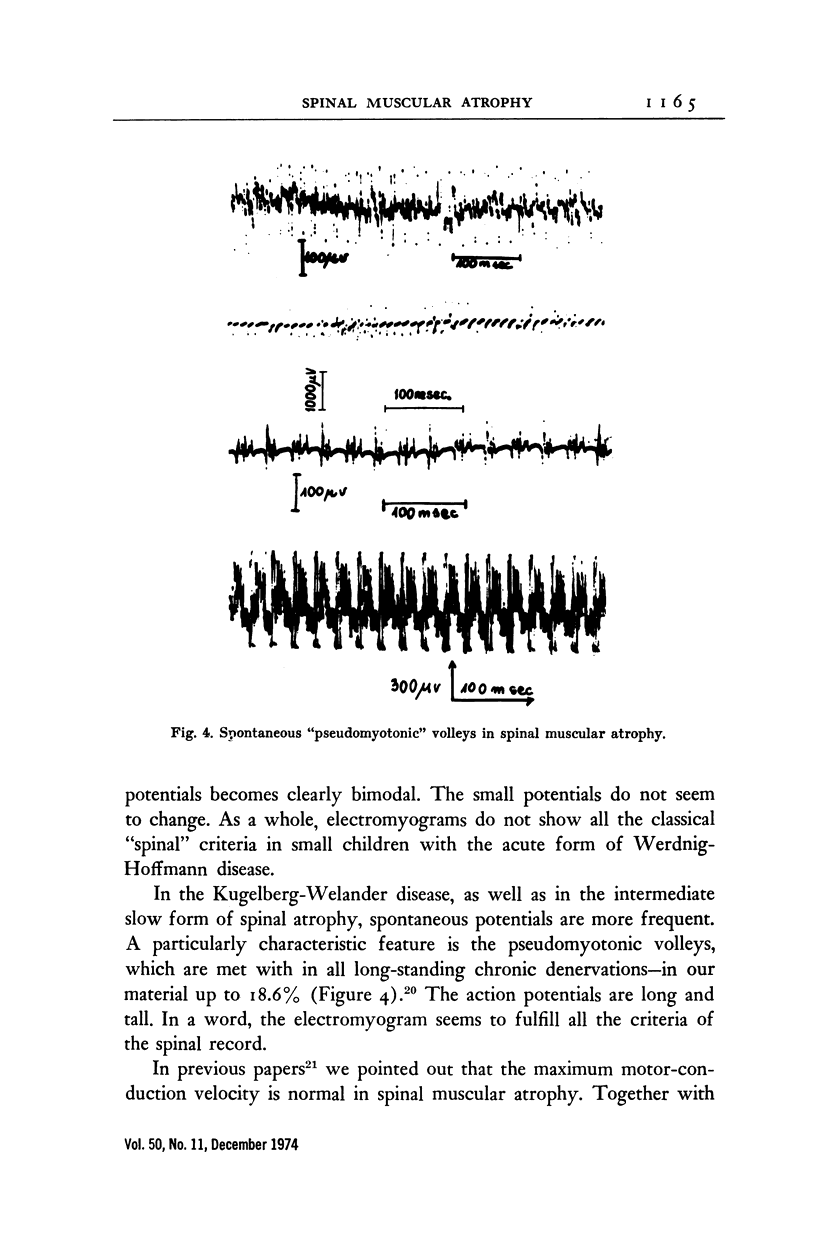
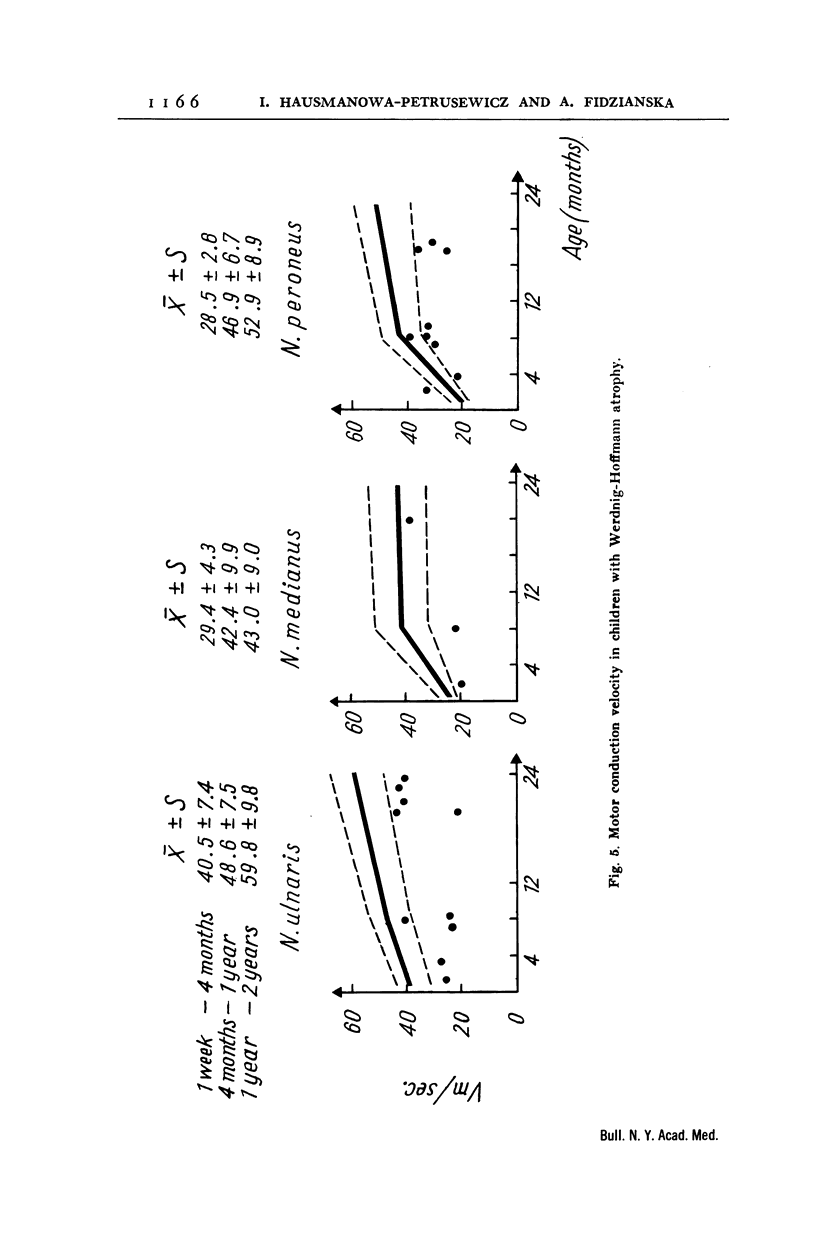
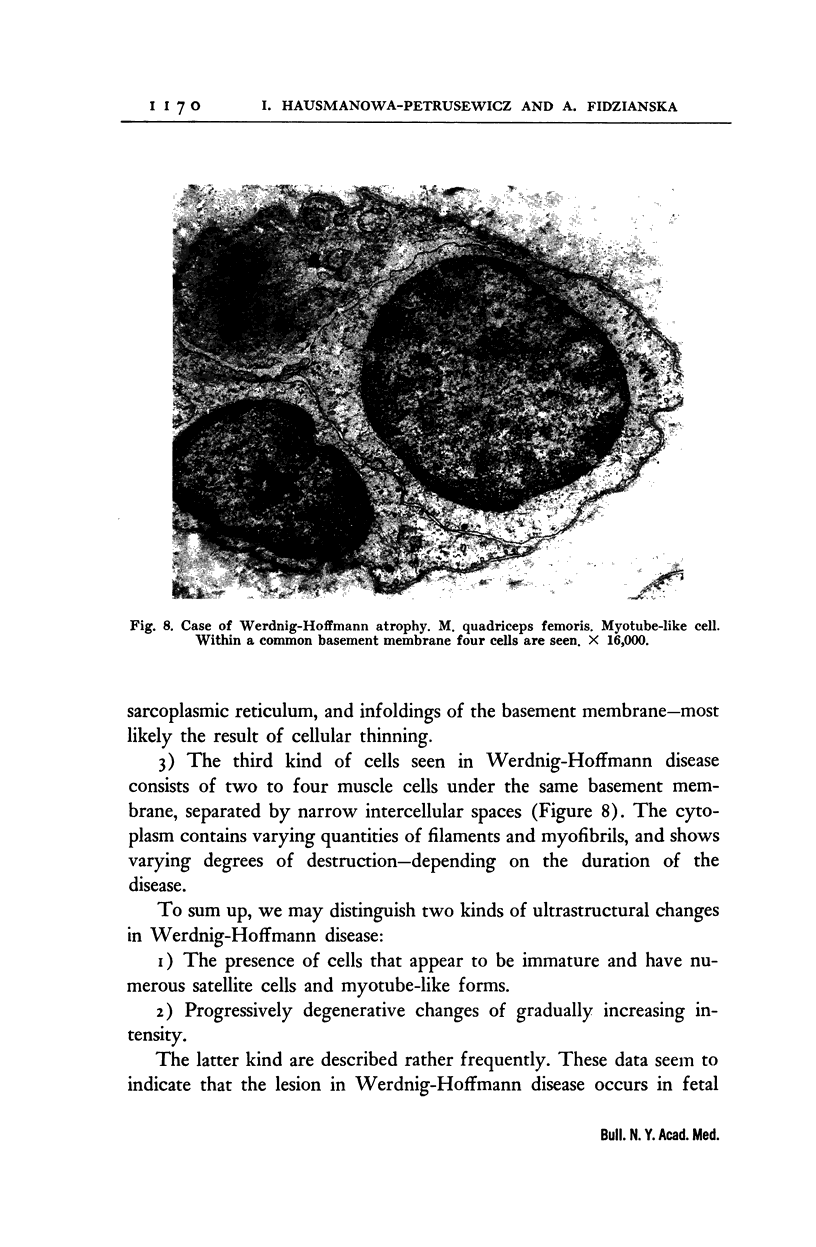
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchthal F., Olsen P. Z. Electromyography and muscle biopsy in infantile spinal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1970;93(1):15–30. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWITZ V. INFANTILE MUSCULAR ATROPHY. A PROSPECTIVE STUDY WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO A SLOWLY PROGRESSIVE VARIETY. Brain. 1964 Dec;87:707–718. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.4.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried K., Emery A. E. Spinal muscular atrophy type II. A separate genetic and clinical entity from type I (Werdnig-Hoffmann disease) and type 3 (Kugelberg-Welander disease). Clin Genet. 1971;2(4):203–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner-Medwin D., Hudgson P., Walton J. N. Benign spinal muscular atrophy arising in childhood and adolescence. J Neurol Sci. 1967 Jul-Aug;5(1):121–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(67)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmanowa-Pétrusewicz I., Prot J., Sawicka E. Le problème des formes infantiles et juvéniles de l'atrophie musculaire spinale. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1966 Apr;114(4):295–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hetnarska L., Prot J., Sawicka E. Creatine phospholinase activity in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Mar-Apr;6(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOHLFART G., FEX J., ELIASSON S. Hereditary proximal spinal muscular atrophy, a clinical entity simulating progressive muscular dystrophy. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1955;30(1-2):395–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]