Abstract
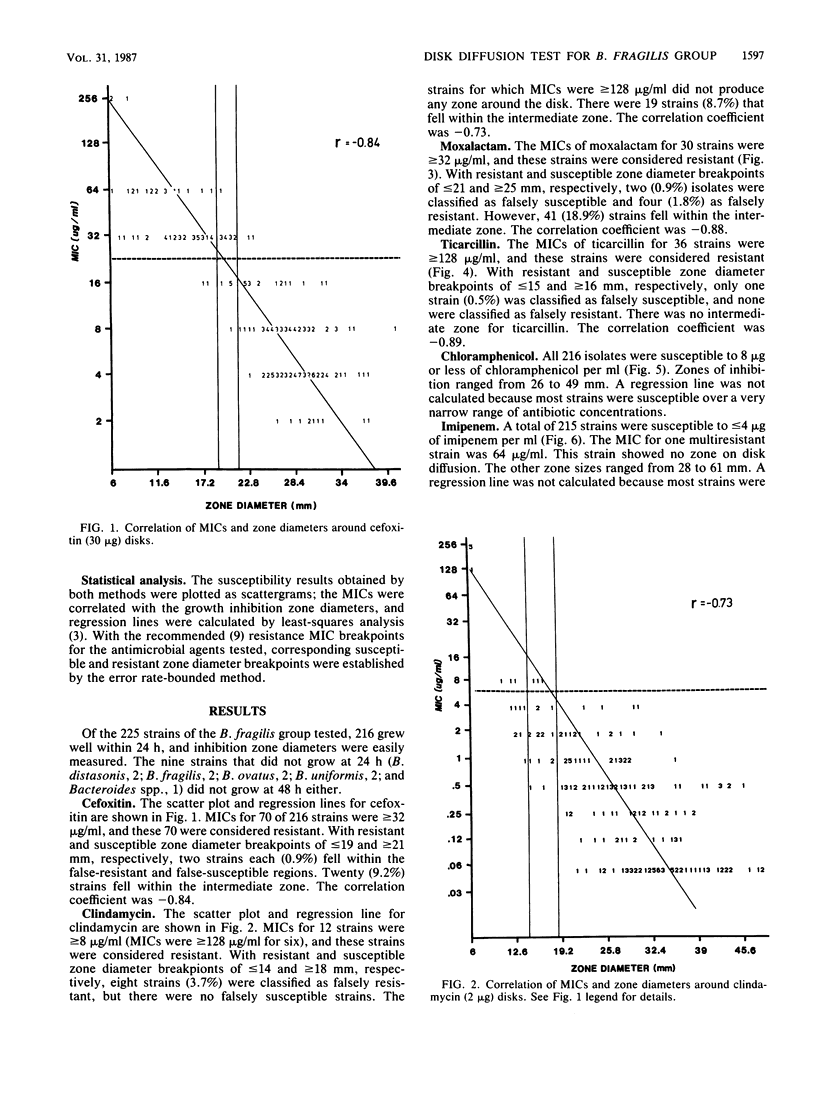
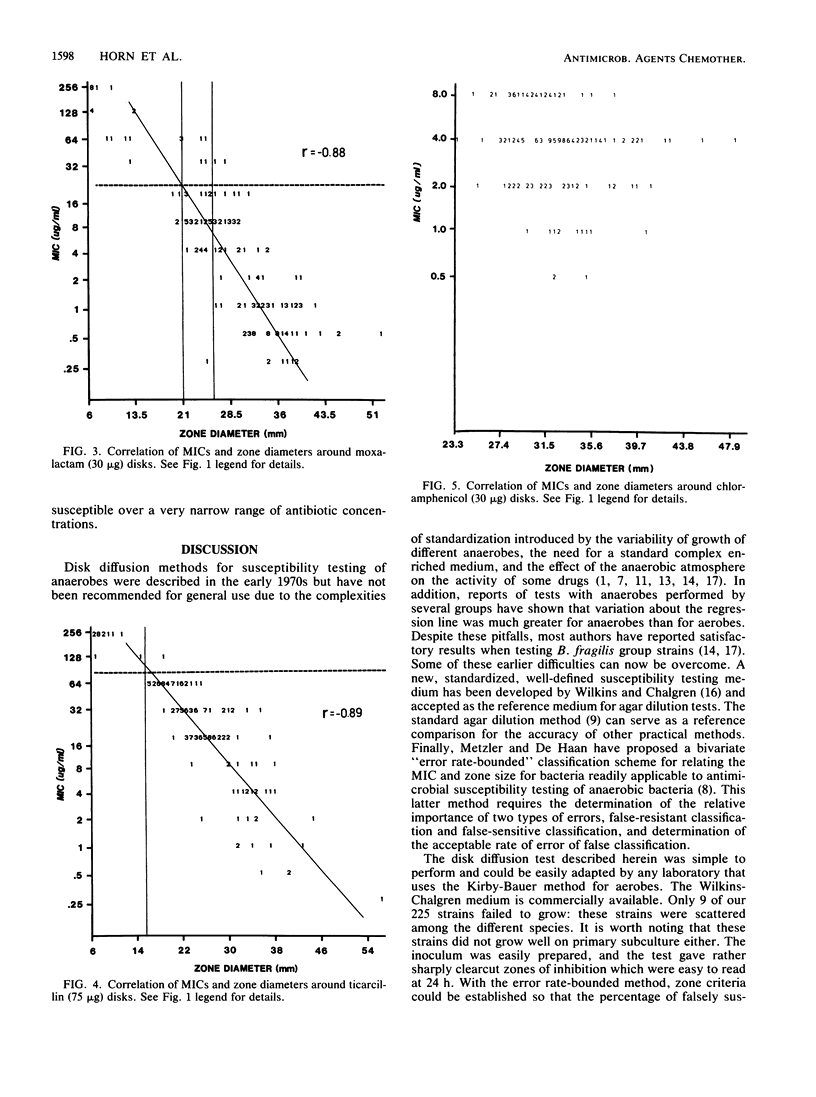
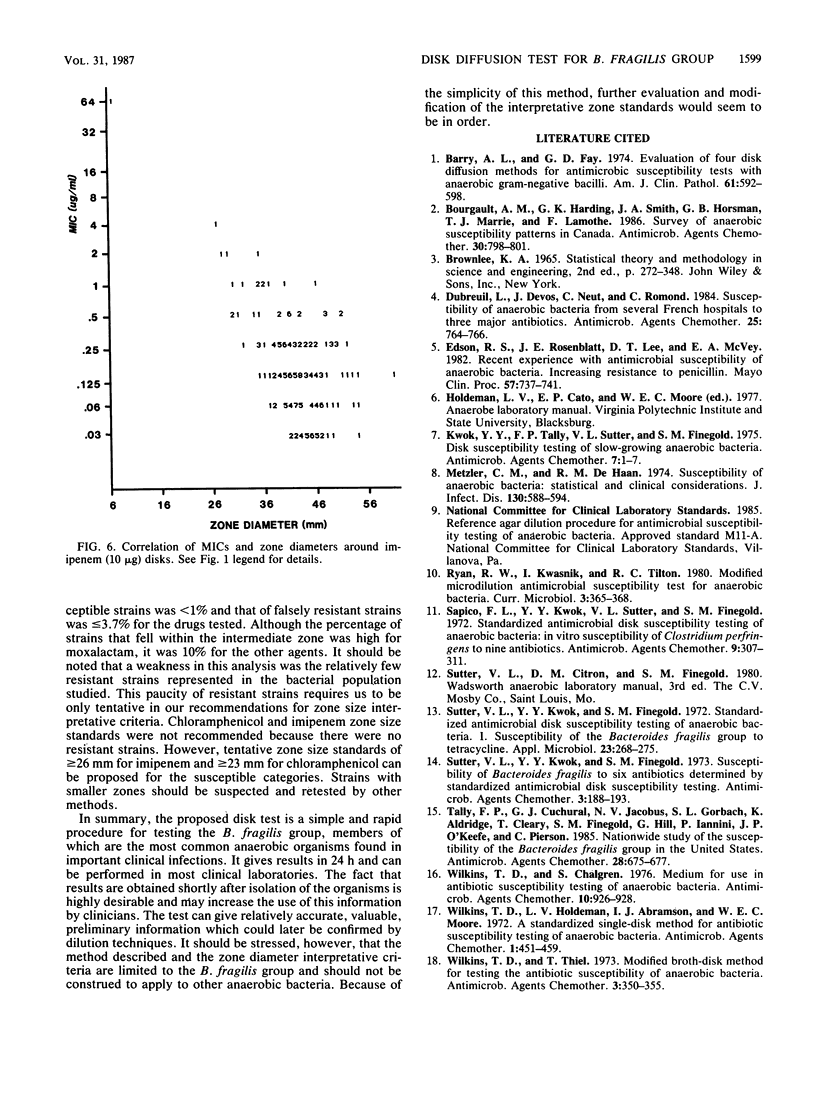
The susceptibilities of 225 isolates of the Bacteroides fragilis group to six antibiotics were determined by a new disk diffusion test in Wilkins-Chalgren agar and by the standard agar dilution method. For disk diffusion, the bacteria were directly suspended in saline and immediately swabbed onto 15-cm agar plates. Disks of cefoxitin (30 micrograms), chloramphenicol (30 micrograms), clindamycin (2 micrograms), moxalactam (30 micrograms), imipenem (10 micrograms), and ticarcillin (75 micrograms) were applied, and the plates were incubated at 37 degrees C in an anaerobic atmosphere. Zone sizes were measured at 24 h. The results of disk diffusion and agar dilution were compared by regression analysis by the method of least squares and by the error rate-bounded method. Zones were easily measured for 216 strains (96%). The correlation between the MICs and diameters of inhibition for cefoxitin, clindamycin, moxalactam, and ticarcillin was generally good. A correlation could not be established for chloramphenicol and imipenem, as there were too few resistant strains. With the recommended resistance breakpoints, the following susceptible and resistant zone diameter breakpoints could be established: cefoxitin, less than or equal to 19 and greater than or equal to 21 mm; clindamycin, less than or equal to 14 and greater than or equal to 18 mm; moxalactam, less than or equal to 21 and greater than or equal to 25 mm; and ticarcillin, less than or equal to 15 and greater than or equal to 16 mm. By applying these zone criteria, the percentage of false-susceptible strains was less than 1% and of false-resistant strains was less than 4% for the drugs tested.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Fay G. D. Evaluation of four disk diffusion methods for antimicrobic susceptibility tests with anaerobic gram-negative bacilli. Am J Clin Pathol. 1974 May;61(5):592–598. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/61.5.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgault A. M., Harding G. K., Smith J. A., Horsman G. B., Marrie T. J., Lamothe F. Survey of anaerobic susceptibility patterns in Canada. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):798–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil L., Devos J., Neut C., Romond C. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria from several French hospitals to three major antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):764–766. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson R. S., Rosenblatt J. E., Lee D. T., McVey E. A., 3rd Recent experience with antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria: increasing resistance to penicillin. Mayo Clin Proc. 1982 Dec;57(12):737–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. M., DeHaan R. M. Susceptibility tests of anaerobic bacteria: statistical and clinical considerations. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):588–594. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y. Y., Finegold S. M. Standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. I. Susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to tetracycline. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):268–275. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.268-275.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Kwok Y., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis to six antibiotics determined by standardized antimicrobial disc susceptibility testing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):188–193. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr, Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P. Nationwide study of the susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):675–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikins T. D., Holdeman L. V., Abramson I. J., Moore W. E. Standardized single-disc method for antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):451–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Chalgren S. Medium for use in antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):926–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Thiel T. Modified broth-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):350–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


