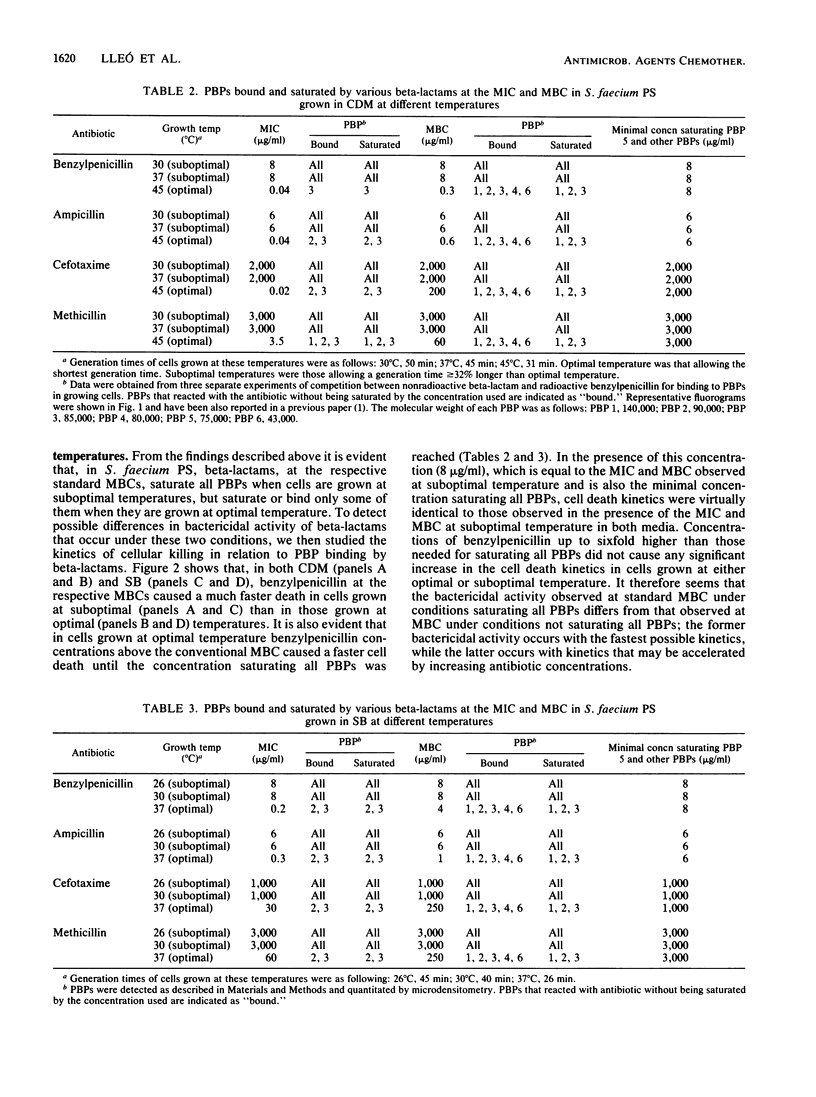
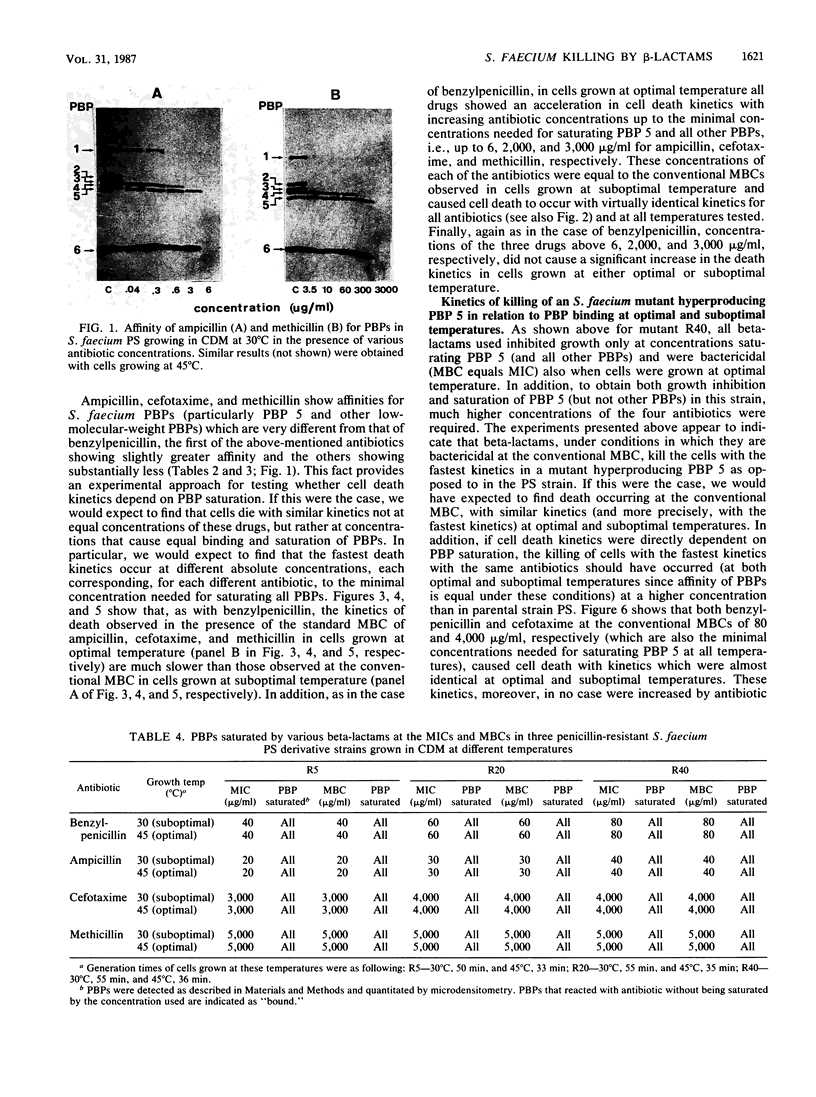
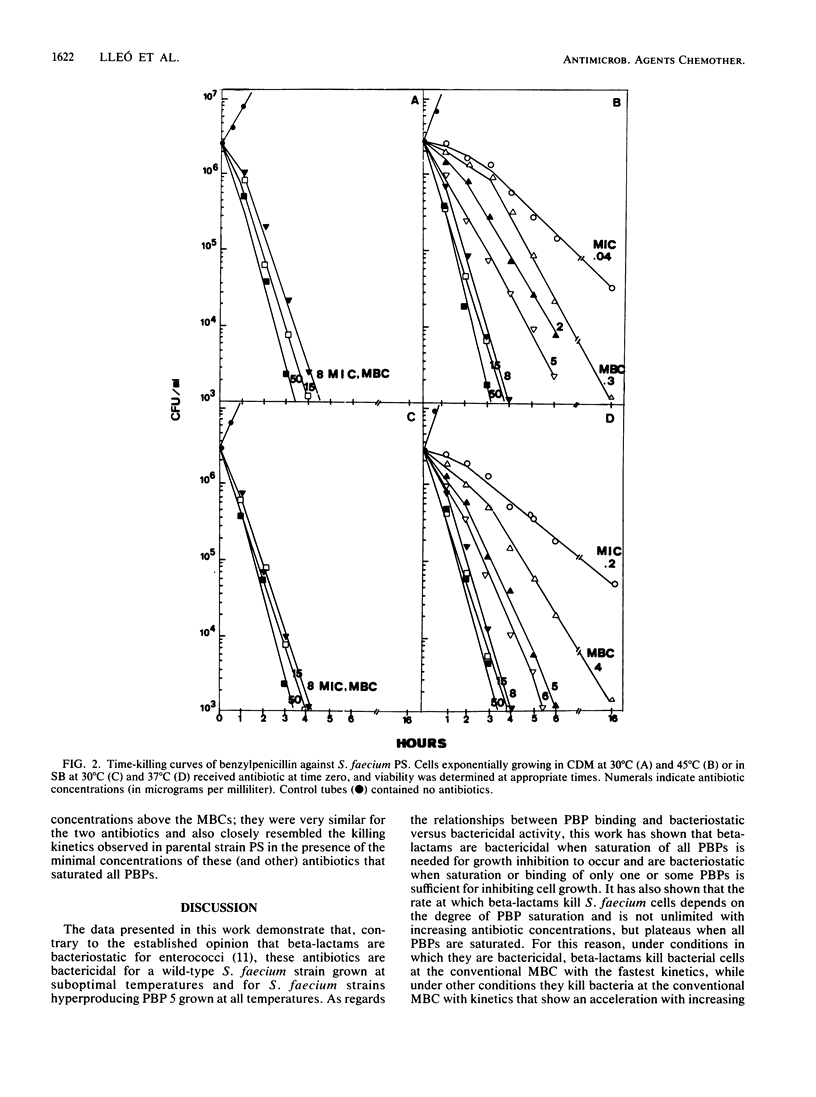
Abstract
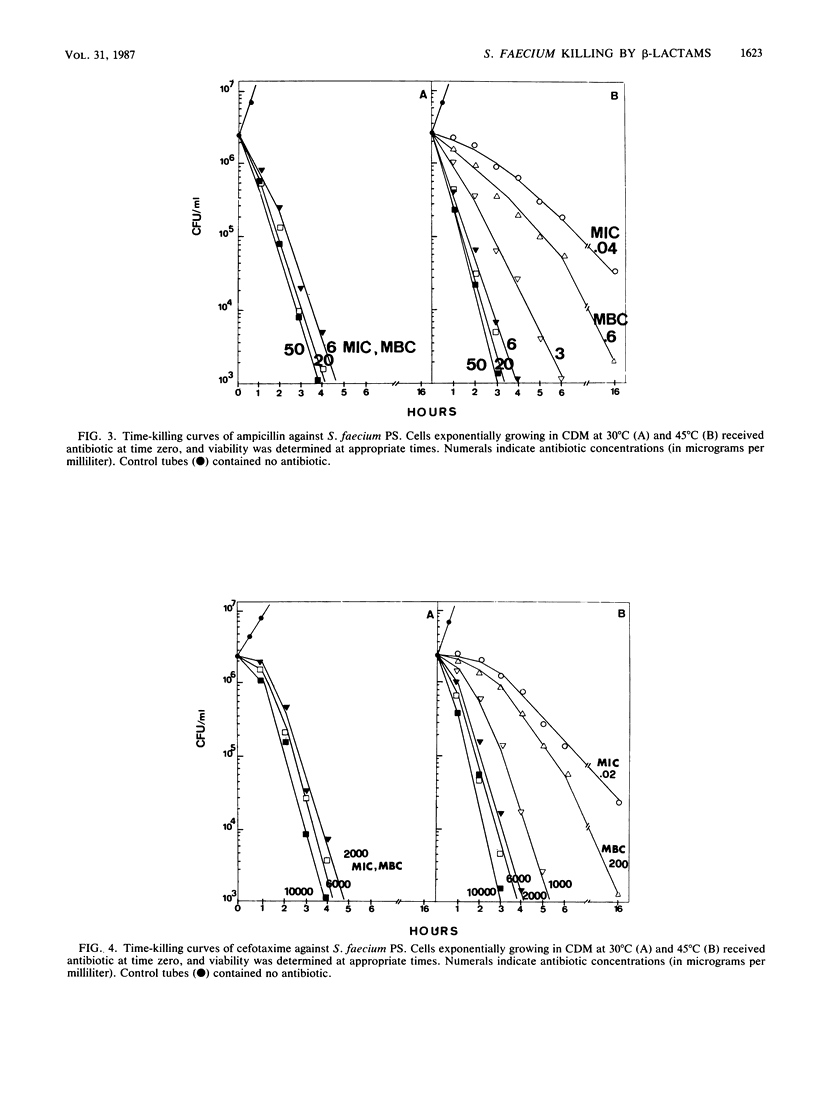
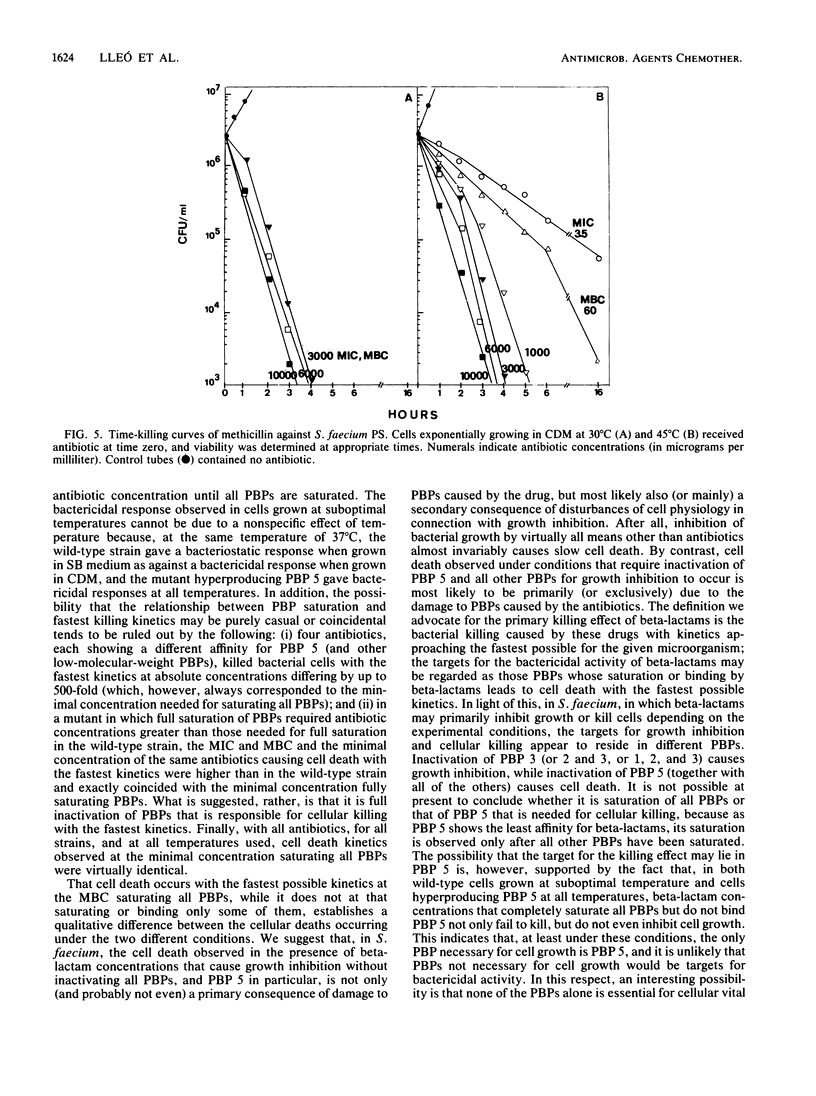
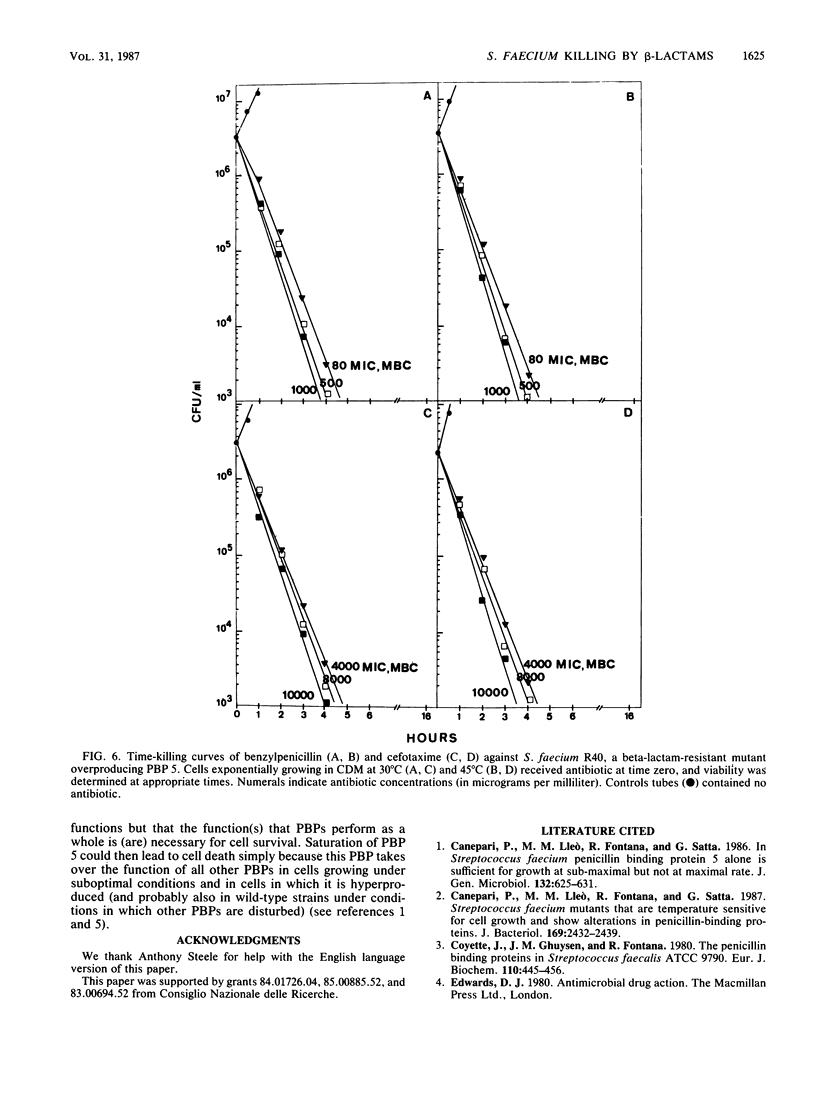
The MICs and MBCs of benzylpenicillin, ampicillin, cefotaxime, and methicillin were evaluated against a Streptococcus (Enterococcus) faecium wild-type strain and against three mutants hyperproducing PBP 5 in cells incubated at both optimal and suboptimal temperatures. In the wild-type strain grown at optimal temperature, the MBCs of all beta-lactams were significantly greater than the MICs (bacteriostatic effect). As opposed to this, in the same cells grown at suboptimal temperature and in the mutants hyperproducing PBP 5 at all temperatures, the MICs of all antibiotics coincided with the MBCs (bactericidal effect). Under all conditions in which the MIC and MBC were the same, with all antibiotics, growth inhibition occurred only at the minimal concentration saturating all penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) (or at higher concentrations). On the contrary, under conditions in which the MIC was lower than the MBC, only some of the PBPs were saturated (or bound) at both the MIC and the MBC, PBP 5 in no case being either saturated or bound. Under all conditions in which saturation of all PBPs was needed for growth inhibition, cells died at all antibiotic MBCs with kinetics which were much faster than those with which they died at the MBCs under conditions in which not all PBPs were saturated (or bound). In addition, under the former conditions, antibiotic concentrations above the MBCs did not significantly accelerate cell death kinetics, while under the latter conditions there was an acceleration in kinetics with increasing antibiotic concentrations up to full saturation of PBPs. It is suggested that the killing that occurs when all PBPs are saturated is a direct consequence of inactivation of PBP functions, while killing occurring when only some of them are saturated or bound is also (or mainly) an indirect consequence of inability of cells to grow and that, in S. faecium, the targets for growth inhibition and cell killing reside in different PBPs: for the latter effect, inactivation of one (or more) of the high-molecular-weight PBPs is sufficient, whereas in the former case inactivation of PBP 5 is necessary (after saturation of all other PBPs).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canepari P., Lleò M. M., Cornaglia G., Fontana R., Satta G. In Streptococcus faecium penicillin-binding protein 5 alone is sufficient for growth at sub-maximal but not at maximal rate. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Mar;132(3):625–631. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-3-625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canepari P., Lleò M. M., Fontana R., Satta G. Streptococcus faecium mutants that are temperature sensitive for cell growth and show alterations in penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2432–2439. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2432-2439.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Ghuysen J. M., Fontana R. The penicillin-binding proteins in Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 9790. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(2):445–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Canepari P., Satta G., Coyette J. Identification of the lethal target of benzylpenicillin in Streptococcus faecalis by in vivo penicillin binding studies. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):70–72. doi: 10.1038/287070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Canepari P., Satta G., Coyette J. Streptococcus faecium ATCC 9790 penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin sensitivity are heavily influenced by growth conditions: proposal for an indirect mechanism of growth inhibition by beta-lactams. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):916–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.916-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Grossato A., Rossi L., Cheng Y. R., Satta G. Transition from resistance to hypersusceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics associated with loss of a low-affinity penicillin-binding protein in a Streptococcus faecium mutant highly resistant to penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):678–683. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. Enterococci. Biologic and epidemiologic characteristics and in vitro susceptibility. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct 25;142(11):2006–2009. doi: 10.1001/archinte.142.11.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Watson B. K., Kunz L. J. Endocarditis due to group D streptococci. Comparison of disease caused by streptococcus bovis with that produced by the enterococci. Am J Med. 1974 Aug;57(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90448-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci. I. Bacteriologic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Shepherd S. T., Chase H. A. Identification of the binding protein which may be the target of penicillin action in Bacillus megaterium. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):568–570. doi: 10.1038/271568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Krogstad D. J. Antibiotic-induced lysis of enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):639–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI110298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Facklam R. R. Antibiotic susceptibility of Streptococcus bovis and other group D streptococci causing endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):228–233. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):502–504. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]