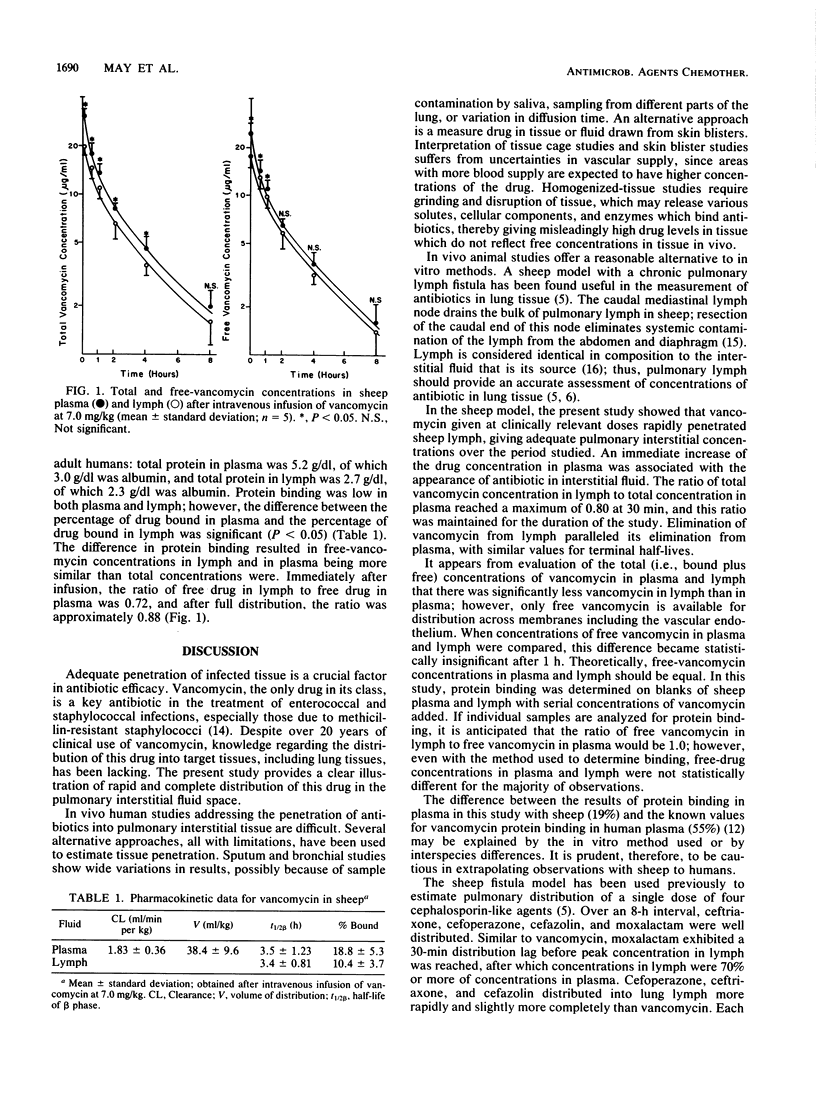
Abstract
The distribution of antibiotics into target tissues is a crucial factor in therapeutic efficacy. To estimate the availability of systemically administered vancomycin to the interstitial fluid in the lung, we have used a sheep model with a chronic pulmonary lymph fistula to collect simultaneously series of plasma and pulmonary lymph specimens during a 6-h period after an intravenous dose of vancomycin (7 mg/kg). After a minor delay in transit from blood to lymph, vancomycin was completely distributed to pulmonary lymph with a ratio of free drug in lymph to free drug in plasma of 0.9. This suggests that vancomycin is an excellent choice for treating pulmonary infections by susceptible organisms.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergogne-Berezin E., Morel C., Benard Y., Berthelot G., Kafe H. Pharmacokinetic study of beta-lactam antibiotics in bronchial secretions. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):267–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergogne-Berezin E. Penetration of antibiotics into the respiratory tree. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):171–174. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk S. L., Verghese A., Holtsclaw S. A., Smith J. K. Enterococcal pneumonia. Occurrence in patients receiving broad-spectrum antibiotic regimens and enteral feeding. Am J Med. 1983 Jan;74(1):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. H., Hoeprich P. D., Demling R., Gunther R., Merry J. M., Franti C. E., Miner D. J. Entry of four cephalosporins into the ovine lung. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):264–270. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Moellering R. C., Jr, Greenblatt D. J. Single-dose kinetics of intravenous vancomycin. J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;20(4 Pt 1):197–201. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1980.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuperman A. S., Fernandez R. B. Subacute staphylococcal pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Jan;101(1):95–100. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert H. P. Clinical significance of tissue penetration of antibiotics in the respiratory tract. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Krogstad D. J., Greenblatt D. J. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in normal subjects and in patients with reduced renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3 Suppl:S230–S235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotschafer J. C., Crossley K., Zaske D. E., Mead K., Sawchuk R. J., Solem L. D. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin: observations in 28 patients and dosage recommendations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):391–394. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenzer K. S., Wang C. H., Anhalt J. P. Automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay for monitoring vancomycin. Ther Drug Monit. 1983;5(3):341–345. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198309000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell T. C., Packham D. R., Shanker S., Foldes M., Munro R. Vancomycin therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):344–350. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub N. C., Bland R. D., Brigham K. L., Demling R., Erdmann A. J., 3rd, Woolverton W. C. Preparation of chronic lung lymph fistulas in sheep. J Surg Res. 1975 Nov;19(5):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(75)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Magyar Z. s., Pósch E. The relationship between tissue fluid and lymph. Lymphology. 1976 Dec;9(4):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. A., Pierce T. H., Goldstein E., Hoeprich P. D. Penetration of antimicrobial agents into bronchial secretions. Am J Med. 1975 Aug;59(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


