Abstract
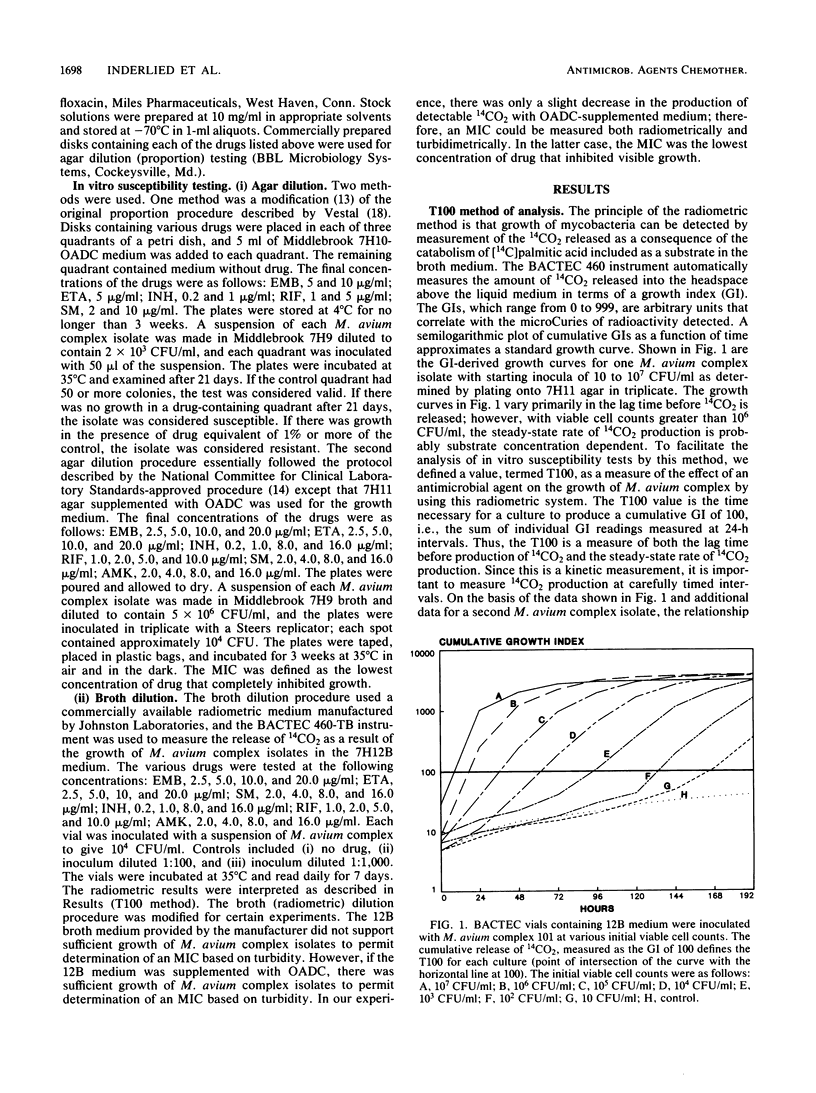
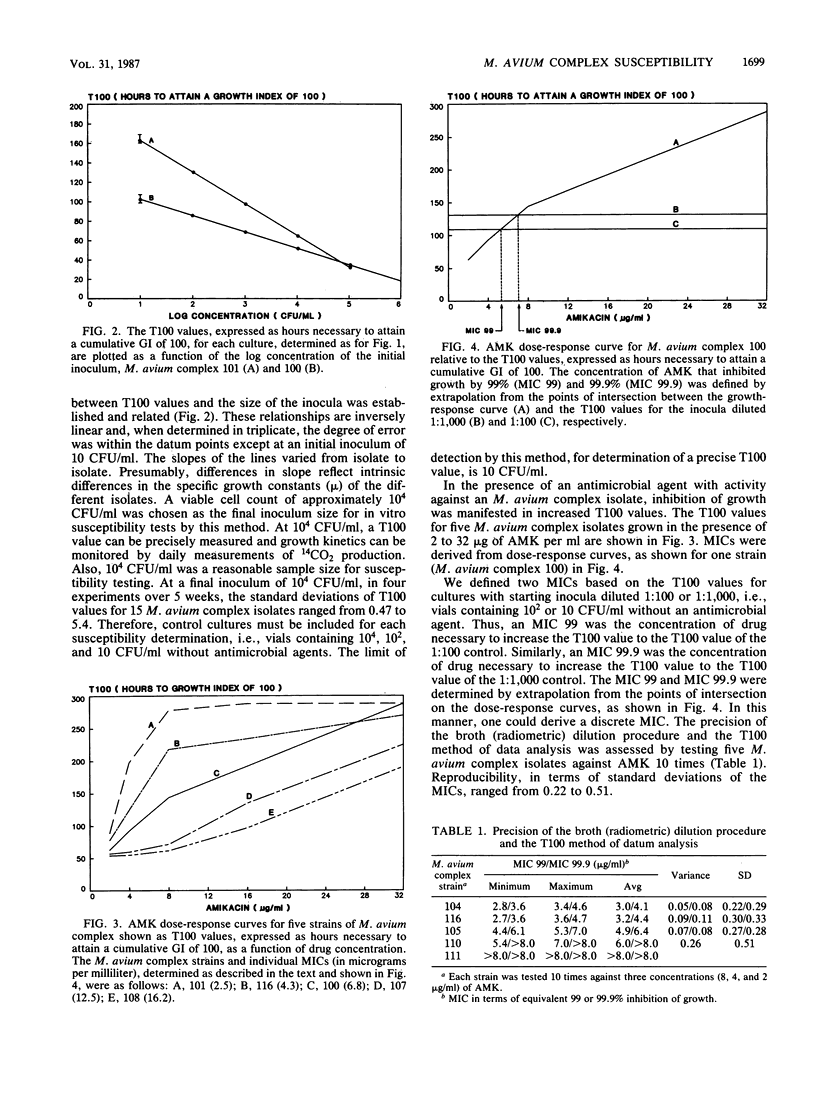
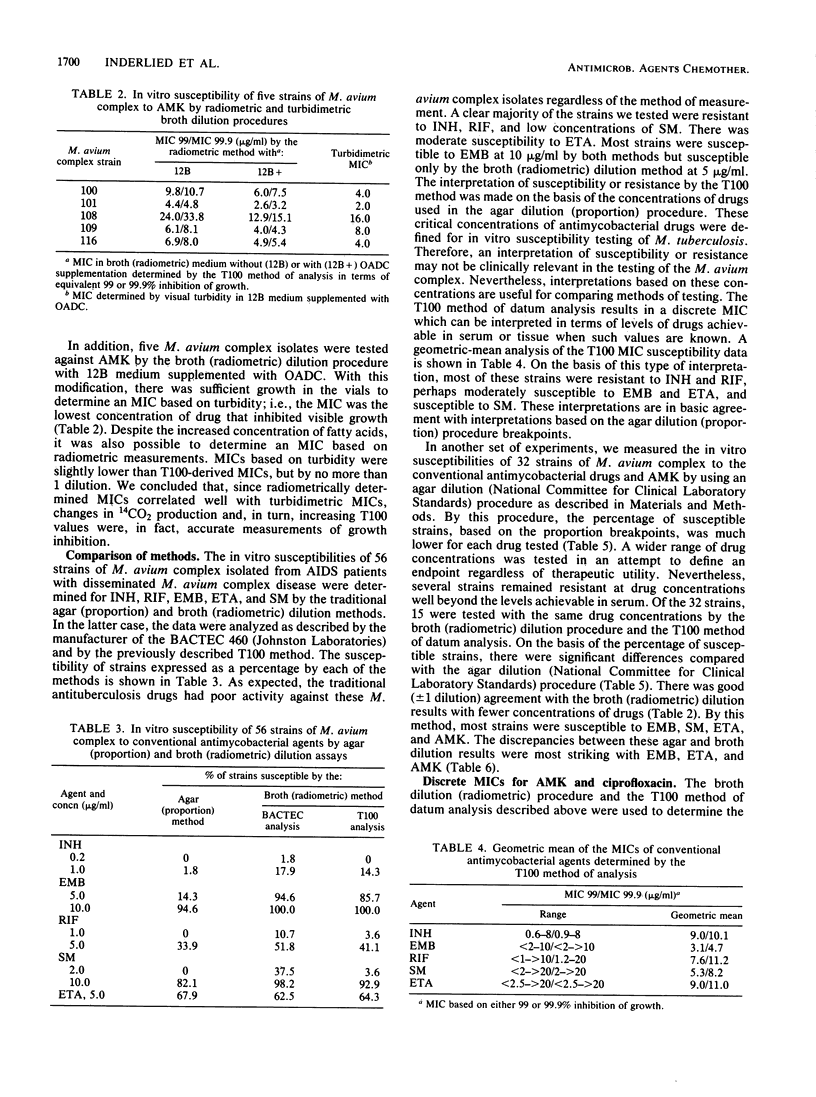
Various methods were used to determine the in vitro susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium complex strains isolated from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Our results confirm the noted resistance of the M. avium complex to conventional antituberculosis agents. The procedures used were both agar dilution and broth dilution, including a commercially available radiometric system (BACTEC; Johnston Laboratories, Towson, Md.). In general, all strains were more resistant by an agar dilution procedure than by a broth dilution procedure. Radiometric data were analyzed by defining a value, termed T100, which provides a discrete MIC. The broth (radiometric) procedure is reproducible and convenient for screening antimicrobial agents for in vitro activity and assessing potential therapeutic efficacy. Nevertheless, there is no standard procedure for determining the in vitro susceptibility of the M. avium complex, and appropriate clinical correlation studies are needed to accurately assess the clinical relevance of any in vitro result.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron E. J., Young L. S. Amikacin, ethambutol, and rifampin for treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;5(3):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(86)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson P. T., Khanijo V., Goble M., Moulding T. S. Treatment of disease due to Mycobacterium intracellulare. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):1052–1059. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.5.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutt A. K., Stead W. W. Long-term results of medical treatment in Mycobacterium intracellulare infection. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):449–453. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90792-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engbaek H. C., Vergmann B., Baess I. Non-photochromogenic mycobacteria serotype Davis. The inhomogeneity within the serological group and the relationship to Mycobacterium avium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(5):619–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenlon C. H., Cynamon M. H. Comparative in vitro activities of ciprofloxacin and other 4-quinolones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):386–388. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay J. D., DeYoung D. R., Roberts G. D. In vitro activities of norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. avium complex, M. chelonei, M. fortuitum, and M. kansasii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):94–96. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good R. C., Snider D. E., Jr Isolation of nontuberculous mycobacteria in the United States, 1980. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):829–833. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Iseman M. D., Lindholm-Levy P. J. Ethambutol MICs and MBCs for Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):927–932. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Iseman M. D., Lindholm-Levy P. J., Kanes W. Determination of ansamycin MICs for Mycobacterium avium complex in liquid medium by radiometric and conventional methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):570–575. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Cohn D. L., Roberts R. B., Masur H., Miller R. A., Tsang A. Y., Iseman M. D. Mycobacterium avium-M. intracellulare isolates from patients with or without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):955–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. M., Roberts G. D. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against the Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 May;7(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kertcher J. A., Chen M. F., Charache P., Hwangbo C. C., Camargo E. E., McIntyre P. A., Wagner H. N., Jr Rapid radiometric susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Apr;117(4):631–637. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi N., Frehel C., Ryter A., Ohayon H., Lesourd M., David H. L. Multiple drug resistance in Mycobacterium avium: is the wall architecture responsible for exclusion of antimicrobial agents? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):666–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders W. E., Jr, Hartwig C., Schneider N., Cacciatore R., Valdez H. Activity of amikacin against Mycobacteria in vitro and in murine tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1982 Sep;63(3):201–208. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(82)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi S. H., Hawkins J. E., Laszlo A. Interlaboratory drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by a radiometric procedure and two conventional methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):919–923. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.919-923.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jan;119(1):107–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yangco B. G., Eikman E. A., Solomon D. A., Deresinski S. C., Madden J. A. Rapid radiometric method for determining drug susceptibility of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):534–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Berlin O. G., Inderlied C. B. Activity of ciprofloxacin and other fluorinated quinolones against mycobacteria. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):23–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Inderlied C. B., Berlin O. G., Gottlieb M. S. Mycobacterial infections in AIDS patients, with an emphasis on the Mycobacterium avium complex. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1024–1033. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


