Abstract
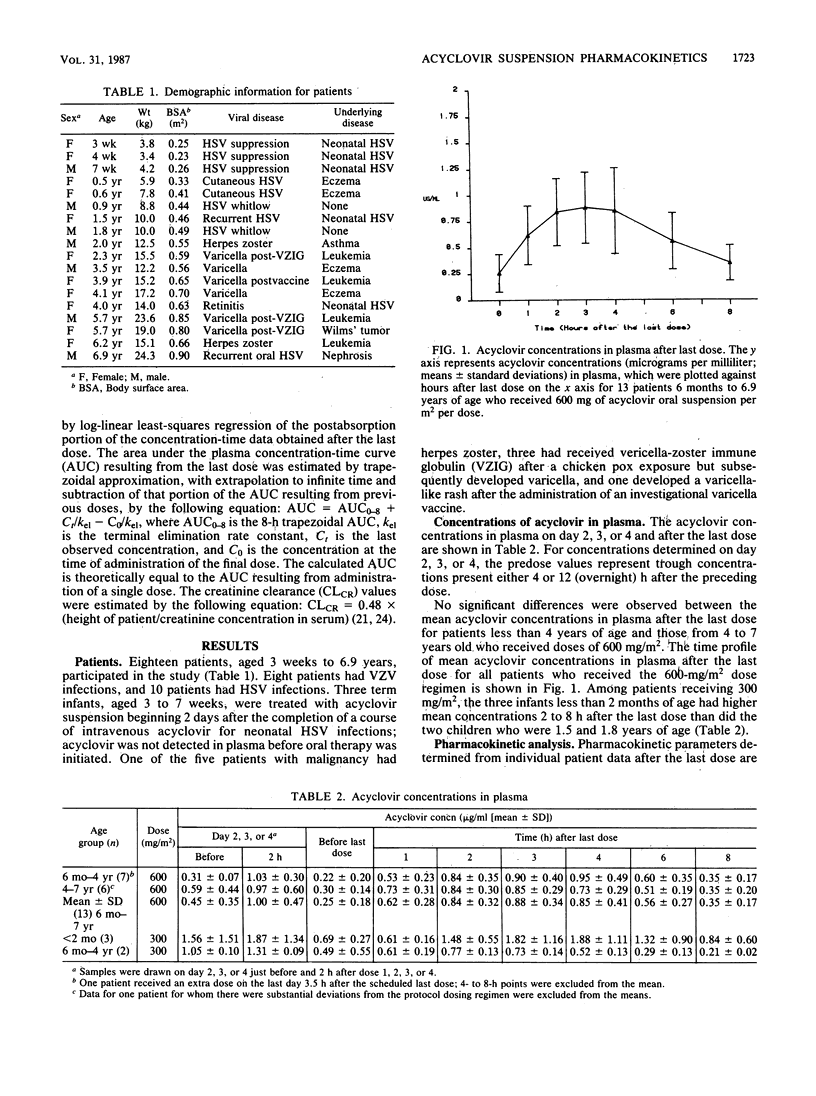
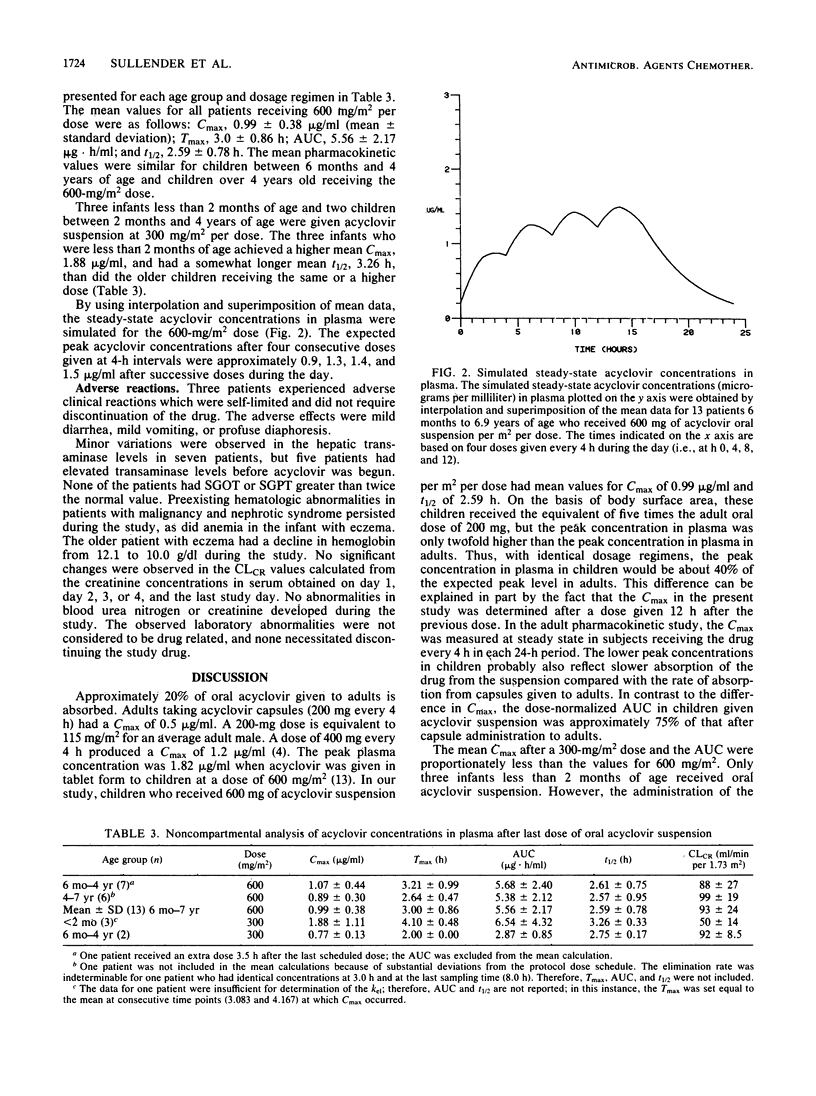
Eighteen children from 3 weeks to 6.9 years of age were given an oral acyclovir suspension for herpes simplex or varicella-zoster virus infections. Thirteen patients who were 6 months to 6.9 years old received 600 mg/m2 per dose, and three infants and two children less than 2 years old were given 300 mg/m2 per dose. The drug was given four times a day, except to one infant who was treated with three doses a day. Among the 13 children who received the 600-mg/m2 dose, the maximum concentration in plasma (Cmax) was 0.99 +/- 0.38 microgram/ml (mean +/- standard deviation), the time to maximum concentration (Tmax) was 3.0 +/- 0.86 h, the area under the curve (AUC) was 5.56 +/- 2.17 micrograms.h/ml, and the elimination half-life (t1/2) was 2.59 +/- 0.78 h. The three infants less than 2 months of age who received the 300-mg/m2 dose had a Cmax of 1.88 +/- 1.11 micrograms/ml, a Tmax of 4.10 +/- 0.48 h, an AUC of 6.54 +/- 4.32 micrograms.h/ml, and a t1/2 of 3.26 +/- 0.33 h. The acyclovir suspension was well tolerated by young children. No adverse effects requiring discontinuation of the drug occurred.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum M. R., Liao S. H., de Miranda P. Overview of acyclovir pharmacokinetic disposition in adults and children. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):186–192. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Dillon M., Lovett M., Acuna G., Taylor S., Cherry J. D., Johnson B. L., Wiesmeier E., Growdon W., Creagh-Kirk T. Treatment of first episodes of genital herpes simplex virus infection with oral acyclovir. A randomized double-blind controlled trial in normal subjects. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 21;308(16):916–921. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304213081602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Adams H. G., Brown Z. A., Holmes K. K. Genital herpes simplex virus infections: clinical manifestations, course, and complications. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):958–972. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. M., Critchlow C., Benedetti J., Mertz G. J., Connor J. D., Hintz M. A., Fahnlander A., Remington M., Winter C., Corey L. A double-blind study of oral acyclovir for suppression of recurrences of genital herpes simplex virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1551–1556. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann I. M., Prentice H. G., Blacklock H. A., Ross M. G., Brigden D., Rosling A. E., Burke C., Crawford D. H., Brumfitt W., Hoffbrand A. V. Acyclovir prophylaxis against herpes virus infections in severely immunocompromised patients: randomised double blind trial. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Aug 6;287(6389):384–388. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6389.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz M., Connor J. D., Spector S. A., Blum M. R., Keeney R. E., Yeager A. S. Neonatal acyclovir pharmacokinetics in patients with herpes virus infections. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):210–214. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz G. J., Critchlow C. W., Benedetti J., Reichman R. C., Dolin R., Connor J., Redfield D. C., Savoia M. C., Richman D. D., Tyrrell D. L. Double-blind placebo-controlled trial of oral acyclovir in first-episode genital herpes simplex virus infection. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1147–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Wade J. C., Mitchell C. D., Saral R., Lietman P. S., Durack D. T., Levin M. J., Segreti A. C., Balfour H. H., Jr Multicenter collaborative trial of intravenous acyclovir for treatment of mucocutaneous herpes simplex virus infection in the immunocompromised host. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli V. M., Marshall W. C., Yeo J., McKendrick G. D. Acyclovir administered perorally in immunocompromised children with varicella-zoster infections. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):478–478. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli V. M., Marshall W. C., Yeo J., McKendrick G. D. High-dose oral acyclovir for children at risk of disseminated herpesvirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):372–372. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson E., Hovi T., Ahonen J., Fiddian A. P., Salmela K., Höckerstedt K., Eklund B., von Willebrand E., Häyry P. Prophylactic oral acyclovir after renal transplantation. Transplantation. 1985 Mar;39(3):279–281. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198503000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Kirk L. E., Keeney R. E. Acyclovir therapy of chickenpox in immunosuppressed children--a collaborative study. J Pediatr. 1982 Oct;101(4):622–625. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80725-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn R. P., de Miranda P., Gerald L., Good S. S. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for the antiviral agent BW248U [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine]. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichman R. C., Badger G. J., Mertz G. J., Corey L., Richman D. D., Connor J. D., Redfield D., Savoia M. C., Oxman M. N., Bryson Y. Treatment of recurrent genital herpes simplex infections with oral acyclovir. A controlled trial. JAMA. 1984 Apr 27;251(16):2103–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards D. M., Carmine A. A., Brogden R. N., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Acyclovir. A review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1983 Nov;26(5):378–438. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198326050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saral R., Ambinder R. F., Burns W. H., Angelopulos C. M., Griffin D. E., Burke P. J., Lietman P. S. Acyclovir prophylaxis against herpes simplex virus infection in patients with leukemia. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):773–776. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saral R., Burns W. H., Laskin O. L., Santos G. W., Lietman P. S. Acyclovir prophylaxis of herpes-simplex-virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 9;305(2):63–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107093050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Feld L. G., Langford D. J. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr. 1984 Jun;104(6):849–854. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus S. E., Takiff H. E., Seidlin M., Bachrach S., Lininger L., DiGiovanna J. J., Western K. A., Smith H. A., Lehrman S. N., Creagh-Kirk T. Suppression of frequently recurring genital herpes. A placebo-controlled double-blind trial of oral acyclovir. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1545–1550. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The infected hip arthroplasty. Lancet. 1984 Sep 8;2(8402):557–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub S. L., Johnson C. E. Comparison of methods of estimating creatinine clearance in children. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1980 Feb;37(2):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley R. J., Alford C. A., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T., Luby J. P., Aoki F. Y., Hanley D., Nahmias A. J., Soong S. J. Vidarabine versus acyclovir therapy in herpes simplex encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 16;314(3):144–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601163140303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Miranda P., Blum M. R. Pharmacokinetics of acyclovir after intravenous and oral administration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Sep;12 (Suppl B):29–37. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.suppl_b.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



