Abstract
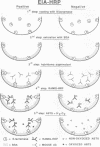
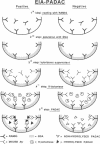
At least 28 plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases have been described in gram-negative bacteria. To assess the relationship among these enzymes, we produced and characterized 28 murine monoclonal antibodies to the TEM-1 plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase. Radial immunodiffusion identified 3 monoclonal antibodies as immunoglobulin M (IgM), 18 as subclass IgG1, 2 as IgG2a, and 5 as IgG2b. Using a newly described enzyme immunoassay, cross-reactivity of 16 of these monoclonal antibodies was tested against 24 plasmid-determined beta-lactamases. The 16 monoclonal antibodies cross-reacted with TEM-2 and TLE-1 and, to a certain extent, SHV-1. Different levels of cross-reactivity were also observed with OXA-3 (11 of 16), OXA-7 (8 of 16), OXA-1 (2 of 16), OXA-6 (2 of 16), and AER-1 (2 of 16). Six monoclonal antibodies demonstrated partial neutralization of beta-lactamase activity. This study suggests that common epitopes are shared by nine biochemically distinct plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases. On the basis of cross-reactivities with these monoclonal antibodies, we identified four epitopes on TEM-1, TEM-2, TLE-1, and SHV-1 beta-lactamases.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON E. S., DATTA N. RESISTANCE TO PENICILLINS AND ITS TRANSFER IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. Lancet. 1965 Feb 20;1(7382):407–409. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P. The structure of beta-lactamases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):321–331. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa Y., Ohta M., Kido N., Fujii Y., Komatsu T., Kato N. Close evolutionary relationship between the chromosomally encoded beta-lactamase gene of Klebsiella pneumoniae and the TEM beta-lactamase gene mediated by R plasmids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobrowski M. M., Matthew M., Barth P. T., Datta N., Grinter N. J., Jacob A. E., Kontomichalou P., Dale J. W., Smith J. T. Plasmid-determined beta-lactamase indistinguishable from the chromosomal beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):149–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.149-157.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:3–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright S. J., Waley S. G. Purification of beta-lactamases by affinity chromatography on phenylboronic acid-agarose. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):505–512. doi: 10.1042/bj2210505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chond D. V., Goldner M. Inhibition and enhancement of cephalosporin beta-lactamase activity by specific antisera. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Aug;16(8):647–650. doi: 10.1139/m70-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey R. C., Clark N. C., Thornsberry C. A gene probe for TEM type beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):154–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson I., Kamme C. Characterization of the plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in Branhamella catarrhalis, with special reference to substrate affinity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Feb;15(2):139–149. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Medeiros A. A., Cohenford M., Jacoby G. A. Genetic and biochemical properties of AER-1, a novel carbenicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase from Aeromonas hydrophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):479–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W. R factors from Providence. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):171–181. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland S., Dale J. W. Immunological comparison between OXA-2 beta-lactamase and those mediated by other R plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):989–991. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack G. W., Richmond M. H. A comparative study of eight distinct beta-lactamases synthesized by gram-negative bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Apr;61(1):43–61. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Sutton L. beta-Lactamases and beta-lactam resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):703–705. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T., Normark S. Sequence elements determining ampC promoter strength in E. coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):875–881. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D., Koprowski H. Molecular recognition and the future of monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):200–202. doi: 10.1038/296200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goffic F., Andrillon-Spiegel J., Letarte R. Immunogical study of anti-beta-lactamase antibodies by acidimetric methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):676–679. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R. C., Medeiros A. A., Jacoby G. A. Molecular cloning and DNA homology of plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R., Roy P. H. Mapping of the plasmid (pLQ3) from Achromobacter and cloning of its cephalosporinase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Jones C. S. Characterization of NPS-1, a novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase, from two Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):99–103. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W., Smith J. T. Types of beta-lactamase determined by plasmids in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.657-662.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases of Gram-negative bacteria: properties and distribution. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):349–358. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A. Beta-lactamases. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jan;40(1):18–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Cohenford M., Jacoby G. A. Five novel plasmid-determined beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):715–719. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Levesque R., Jacoby G. A. An animal source for the ROB-1 beta-lactamase of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Yoshida T. Monoclonal antibodies against species-specific cephalosporinase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):693–697. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent M. E., Hedges R. W. The nature of the genetic determinant for the SHV-1 beta-lactamase. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):239–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00397222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawara H. Antibiotic resistance in pathogenic and producing bacteria, with special reference to beta-lactam antibiotics. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):591–619. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.591-619.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrocheilou V., Sykes R. B., Richmond M. H. Novel R-plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jul;12(1):126–128. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. New plasmid-mediated oxacillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):415–422. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Jacoby G. A. Properties of PSE-2 beta-lactamase and genetic basis for its production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):362–369. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A. M., Paul G. C., Thabaut A. P., Jacoby G. A. Properties of a novel carbenicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase (CARB-4) specified by an IncP-2 plasmid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):519–520. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid A. J., Amyes S. G. Plasmid penicillin resistance in Vibrio cholerae: identification of new beta-lactamase SAR-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):245–247. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H. Immunological techniques for studying beta-lactamases. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:86–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roupas A., Pitton J. S. R factor-mediated and chromosomal resistance to ampicillin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):186–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy C., Foz A., Segura C., Tirado M., Fuster C., Reig R. Plasmid-determined beta-lactamases identified in a group of 204 ampicillin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Nov;12(5):507–510. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.5.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. G., Medeiros A. A., Yolken R. H., Moxon E. R. Ampicillin treatment failure of apparently beta-lactamase-negative Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis due to novel beta-lactamase. Lancet. 1981 Nov 7;2(8254):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Hiruma R., Kawana N., Kaneko M., Taniyasu F., Inami A. Outer membrane permeation of beta-lactam antibiotics in Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):585–592. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S., Yamagishi S. Drug resistance of enteric bacteria. XIV. Comparison of beta-lactamases in gram-negative rod bacteria resistant to alpha-aminobenzylpenicillin. Jpn J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;12(4):423–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1968.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Takahashi K., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Variant of penicillinase mediated by an R factor in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):620–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.620-629.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Penicillinases of Klebsiella pneumoniae and their phylogenetic relationship to penicillinases mediated by R factors. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1045–1054. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1045-1054.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M., Medeiros A. A., Kron M. A., Currie-McCumber C., Papa E., Vartian C. V. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in members of the family Enterobacteriaceae from Ohio. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):220–224. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. N., Harper P. B., O'Callaghan C. H. Principal beta-lactamases responsible for resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):929–936. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Escherichia coli resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics through a decrease in the affinity of a target for lethality. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):713–715. doi: 10.1038/274713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of the ampicillin resistance gene of Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3737–3741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi S., O'Hara K., Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S. The purification and properties of penicillin beta-lactamases mediated by transmissible R factors in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1969 Jul;66(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton D. E., Scharff M. D. Monoclonal antibodies: a powerful new tool in biology and medicine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:657–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]