Abstract
Gentamicin is a commonly used antibiotic in the treatment of gram-negative infections including septicemia and pyelonephritis. Bacterial endotoxin is liberated during antibiotic therapy and may lead to endotoxemic shock. Steroids such as hydrocortisone are generally recommended in the treatment of endotoxemic shock. There are very limited data on the influence of endotoxin or corticosteroids on the pharmacology of antibiotics, especially aminoglycosides, which are nephrotoxic. We studied the influence of both Escherichia coli endotoxin and hydrocortisone succinate on the renal uptake of gentamicin in rats. Animals were injected intravenously with endotoxin (0.25 mg/kg) and/or hydrocortisone (25 mg/kg) plus gentamicin (10 mg/kg). Gentamicin levels in the serum and renal parenchyma as well as renal function and histology were evaluated. Both endotoxin and hydrocortisone given alone increased the concentration of gentamicin in the renal cortex (P less than 0.05). Normal values in serum were observed in all groups at most time intervals. When administered together, endotoxin and hydrocortisone did not potentiate each other. The combination of endotoxin and hydrocortisone gave significantly higher levels of gentamicin than endotoxin or hydrocortisone alone when endotoxin was injected 3 h before hydrocortisone (P less than 0.05). Blood pressure and cardiac frequency were normal when gentamicin was given. Endotoxin alone slightly decreased the glomerular filtration rate, and hydrocortisone alone slightly modified renal plasma flow. The combination of both drugs did not significantly affect renal function. No histological lesion was noted on light microscopy in animals receiving endotoxin. Competitive or synergistic activity of endotoxin, gentamicin, and hydrocortisone at the cellular level, especially on membranes or lysosomes, might explain in part our observation on the renal uptake of gentamicin. By increasing the total amount of drug within the kidney, endotoxin and hydrocortisone might increase the risk of nephrotoxicity associated with aminoglycosides.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altura B. M. Role of glucocorticoids in local regulation of blood flow. Am J Physiol. 1966 Dec;211(6):1393–1397. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.6.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert-Tulkens G., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Gentamicin-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis in cultured rat fibroblasts. Quantitative ultrastructural and biochemical study. Lab Invest. 1979 Apr;40(4):481–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Poirier A., Bergeron M. G. Increased nephrotoxicity of gentamicin in pyelonephritic rats. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):106–113. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
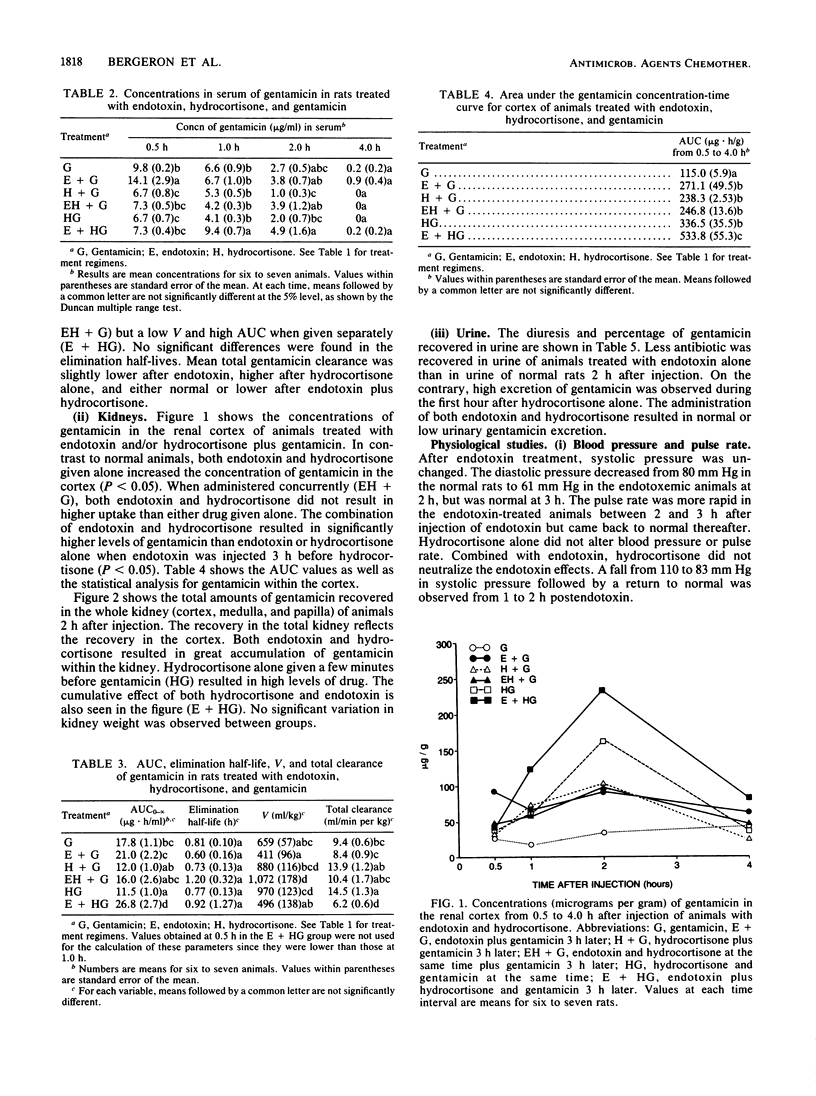
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y. Influence of endotoxin on the intrarenal distribution of gentamicin, netilmicin, tobramycin, amikacin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Bergeron Y., Marois Y. Autoradiography of tobramycin uptake by the proximal and distal tubules of normal and endotoxin-treated rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1005–1009. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Trottier S., Lessard C., Beauchamp D., Gagnon P. M. Disturbed intrarenal distribution of gentamicin in experimental pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1982 Sep;146(3):436–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
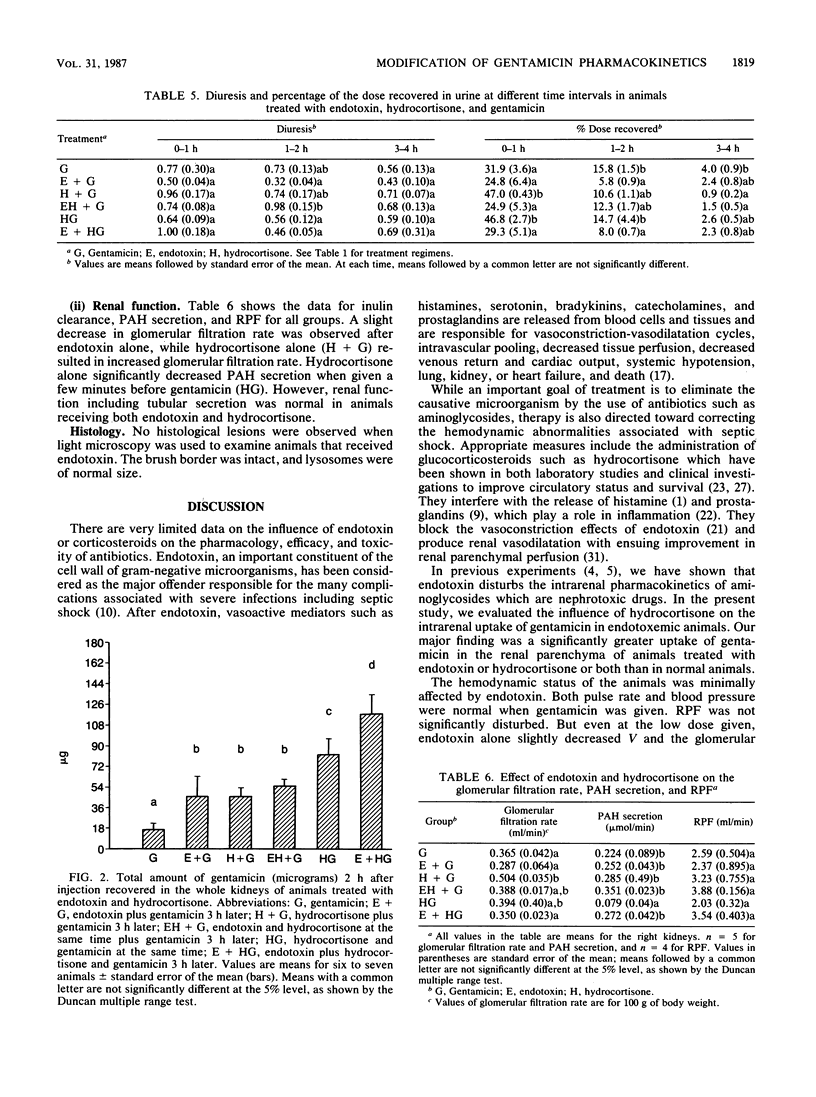
- Bradley S. G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caridis D. T., Reinhold R. B., Woodruff P. W., Fine J. Endotoxaemia in man. Lancet. 1972 Jun 24;1(7765):1381–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBermudez L., Hayslett J. P. Effect of methylprednisolone on renal function and the zonal distribution of blood flow in the rat. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):44–52. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke H., Gutsche H. U., Hartmann F. Excretion of non-protein-bound cortisol in the rat kidney. Clearance and perfusion studies in situ and during isolated perfusion. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1982;181(3):211–219. doi: 10.1007/BF01851192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLER P., MERRILL E. R., JAWETZ E. Effects of cortisone and antibiotics on lethal action of endotoxins in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):716–719. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBERT R. P. Mechanisms of the hemodynamic effects of endotoxin. Physiol Rev. 1960 Apr;40:245–279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin D. V., Tuchek J. M. Plasma acid phosphatase levels in endotoxaemia: modification by drugs and chemically detoxified endotoxins. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy S., Altura B. T., Altura B. M. Pathophysiological basis for the use of steroids in the treatment of shock and trauma. Klin Wochenschr. 1982 Sep 1;60(17):1021–1030. doi: 10.1007/BF01716966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulter H. N., Licht J. H., Bonner E. L., Jr, Glynn R. D., Sebastian A. Effects of glucocorticoid steroids on renal and systemic acid-base metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):F30–F43. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.1.F30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Lysosome membrane stabilization in vivo: effects of steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the integrity of rat liver lysosomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jul;182(1):179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansön P. M., Kühn S. H., Geldenhuys J. J. Lysosomal disruption during the development of endotoxic shock in the baboon. S Afr Med J. 1975 Jun 21;49(26):1041–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth O. E., Wagenknecht L. V., Madsen P. O. The effect of various treatments on renal function during endotoxin shock. An experimental study in dogs. Invest Urol. 1972 Jan;9(4):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl F. A., Jr, Humes J. L., Egan R. W., Ham E. A., Beveridge G. C., Van Arman C. G. Role of prostaglandin endoperoxide PGG2 in inflammatory processes. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):170–173. doi: 10.1038/265170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILLEHEI R. C., LONGERBEAM J. K., BLOCH J. H. PHYSIOLOGY AND THERAPY OF BACTEREMIC SHOCK. EXPERIMENTAL AND CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS. Am J Cardiol. 1963 Nov;12:599–613. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(63)90244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny J., Livni N., Schiller M., Guttman A., Boss J., Rabinovici N. Structural changes in the perfused canine kidney exposed to the direct action of endotoxin. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Mar;16(3):153–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onji T., Liu M. S. Changes in surface charge density on liposomes induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez H. J., Sinha S. K., Starling J., Klahr S. Regulation of renal Na+-K+-ATPase in the rat by adrenal steroids. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):F186–F195. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.2.F186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumer W. Steroids in the treatment of clinical septic shock. Ann Surg. 1976 Sep;184(3):333–341. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197609000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. J., Kokko J. P. Urinary concentrating defect of adrenal insufficiency. Permissive role of adrenal steroids on the hydroosmotic response across the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):234–242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Mogan K. A. Kinetics of endotoxin release during antibiotic therapy for experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;150(3):380–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan T. J., 3rd, Cavanagh D. Corticosteroids in endotoxin shock. Effect on renal vasomotion. Arch Surg. 1966 May;92(5):732–739. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1966.01320230080015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L. The physiological disturbances produced by endotoxins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1954;16:467–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.16.030154.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Hsu C. Y. Augmentation of antibiotic nephrotoxicity by endotoxemia in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Aug;234(2):425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. C., Moore J. N., Eakle N. Gentamicin pharmacokinetics in horses given small doses of Escherichia coli endotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Sep;44(9):1746–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



