Abstract
Aims: To study the prevalence and severity of liver diseases of transfusion dependent thalassaemia major patients, and correlate the histological and biochemical changes of iron overload in liver with the peripheral blood markers.
Method: Liver biopsy was performed to assess the histological changes and liver iron content (LIC).
Results: One hundred patients were evaluated (median age 11.7 years, range 1.5–27). A total of 81 liver biopsies were performed in 73 patients; 43 samples were analysed for LIC. Grade 3–4 haemosiderosis and hepatic fibrosis was found in 44% and 30% of patients respectively; both were significantly associated with higher serum ferritin, liver enzymes, and LIC. Very high LIC (>15 mg/g dry weight) was present in 16.3% of patients.
Conclusion: Severe haemosiderosis and hepatic fibrosis were common in patients with thalassaemia major despite the use of chelation therapy. Liver biopsy provided information on fibrosis and LIC which could not be accurately predicted from peripheral blood markers.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (112.6 KB).
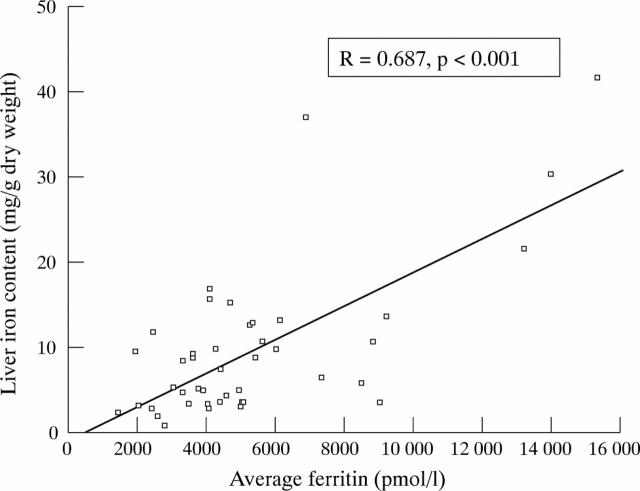
Figure 1 .
Relation between serum ferritin and liver iron content.
Figure 2 .
Relation between grading of haemosidrosis and liver iron content.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldouri M. A., Wonke B., Hoffbrand A. V., Flynn D. M., Laulicht M., Fenton L. A., Scheuer P. J., Kibbler C. C., Allwood C. A., Brown D. Iron state and hepatic disease in patients with thalassaemia major, treated with long term subcutaneous desferrioxamine. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Nov;40(11):1353–1359. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.11.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelucci E., Baronciani D., Lucarelli G., Baldassarri M., Galimberti M., Giardini C., Martinelli F., Polchi P., Polizzi V., Ripalti M. Needle liver biopsy in thalassaemia: analyses of diagnostic accuracy and safety in 1184 consecutive biopsies. Br J Haematol. 1995 Apr;89(4):757–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1995.tb08412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelucci E., Baronciani D., Lucarelli G., Giardini C., Galimberti M., Polchi P., Martinelli F., Baldassarri M., Muretto P. Liver iron overload and liver fibrosis in thalassemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1993;12 (Suppl 1):29–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelucci E., Brittenham G. M., McLaren C. E., Ripalti M., Baronciani D., Giardini C., Galimberti M., Polchi P., Lucarelli G. Hepatic iron concentration and total body iron stores in thalassemia major. N Engl J Med. 2000 Aug 3;343(5):327–331. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200008033430503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgna-Pignatti C., Rugolotto S., De Stefano P., Piga A., Di Gregorio F., Gamberini M. R., Sabato V., Melevendi C., Cappellini M. D., Verlato G. Survival and disease complications in thalassemia major. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Jun 30;850:227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittenham G. M., Griffith P. M., Nienhuis A. W., McLaren C. E., Young N. S., Tucker E. E., Allen C. J., Farrell D. E., Harris J. W. Efficacy of deferoxamine in preventing complications of iron overload in patients with thalassemia major. N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 1;331(9):567–573. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199409013310902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright G. E., Edwards C. Q., Kravitz K., Skolnick M., Amos D. B., Johnson A., Buskjaer L. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Phenotypic expression of the disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 26;301(4):175–179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907263010402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. A., Porter J. B. Long-term outcome of continuous 24-hour deferoxamine infusion via indwelling intravenous catheters in high-risk beta-thalassemia. Blood. 2000 Feb 15;95(4):1229–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Woo J. S., Wan C. W., Machenry C., Wong V., Ma H. K., Chan V., Chan T. K. Evaluation of a prenatal screening procedure for beta-thalassaemia carriers in a Chinese population based on the mean corpuscular volume (MCV). Prenat Diagn. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):59–65. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970050111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean G., Terzoli S., Mauri R., Borghetti L., Di Palma A., Piga A., Magliano M., Melevendi M., Cattaneo M. Cirrhosis associated with multiple transfusions in thalassaemia. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jan;59(1):67–70. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. E., De Virgilis S., Argiolu F., Farci P., Mazzoleni A. P., Lisci V., Rapicetta M., Clemente M. G., Nurchis P., Arnone M. Evaluation of antibodies to hepatitis C virus in a long-term prospective study of posttransfusion hepatitis among thalassemic children: comparison between first- and second-generation assay. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1993 May;16(4):458–464. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199305000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucarelli G., Galimberti M., Polchi P., Angelucci E., Baronciani D., Giardini C., Andreani M., Agostinelli F., Albertini F., Clift R. A. Marrow transplantation in patients with thalassemia responsive to iron chelation therapy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 16;329(12):840–844. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309163291204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer H. S., Lloyd-Still J. D., Ingrisano C., Gonzalez-Crussi F., Honig G. R. A prospective evaluation of iron chelation therapy in children with severe beta-thalassemia. A six-year study. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Mar;142(3):287–292. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150030057020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri N. F., Brittenham G. M. Iron-chelating therapy and the treatment of thalassemia. Blood. 1997 Feb 1;89(3):739–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri N. F., Buncic J. R., Chew E., Gallant T., Harrison R. V., Keenan N., Logan W., Mitchell D., Ricci G., Skarf B. Visual and auditory neurotoxicity in patients receiving subcutaneous deferoxamine infusions. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 3;314(14):869–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604033141402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri N. F., Koren G., Harris J., Khattak S., Freedman M. H., Templeton D. M., Bailey J. D., Reilly B. J. Growth failure and bony changes induced by deferoxamine. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1992 Spring;14(1):48–56. doi: 10.1097/00043426-199221000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri N. F., Nathan D. G., MacMillan J. H., Wayne A. S., Liu P. P., McGee A., Martin M., Koren G., Cohen A. R. Survival in medically treated patients with homozygous beta-thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 1;331(9):574–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199409013310903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. B., Jaswon M. S., Huehns E. R., East C. A., Hazell J. W. Desferrioxamine ototoxicity: evaluation of risk factors in thalassaemic patients and guidelines for safe dosage. Br J Haematol. 1989 Nov;73(3):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telfer P. T., Garson J. A., Whitby K., Grant P. R., Yardumian A., Hoffbrand A. V., Wonke B. Combination therapy with interferon alpha and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection in thalassaemic patients. Br J Haematol. 1997 Sep;98(4):850–855. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.2953112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurlo M. G., De Stefano P., Borgna-Pignatti C., Di Palma A., Piga A., Melevendi C., Di Gregorio F., Burattini M. G., Terzoli S. Survival and causes of death in thalassaemia major. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):27–30. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]