Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To test the hypothesis that the timing of prednisolone administration might be critical in determining its effect on the diurnal rheumatoid inflammatory process. METHODS—26 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were randomly divided into two equal groups and allocated to low doses of prednisolone at either 2.00 am or 7.30 am. Because of the diurnal variation in disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis, assessments of the two study groups were performed at 7.30 am both at the start of the study (day 1) and after four doses of prednisolone (day 5). The study protocol differences in the time period from the last dose of prednisolone to assessment were 5.5 hours in the 2.00 am group and 24 hours in the 7.30 am group. RESULTS—Administration of low doses of prednisolone (5 or 7.5 mg daily) at 2.00 am had favourable effects on the duration of morning stiffness (P << 0.001), joint pain (P < 0.001), Lansbury index (P << 0.001), Ritchie index (P << 0.001), and morning serum concentrations of IL-6 (P < 0.01). The other study group showed minor but significant effects on morning stiffness (P < 0.05) and circulating concentrations of IL-6 (P < 0.05). Modest and similar improvements of C reactive protein, serum amyloid protein A, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were seen in both study groups. CONCLUSIONS—Administration of low doses of glucocorticoids with a rather short biological half life seems to improve acute rheumatoid arthritis symptoms if it precedes the period of circadian flare in inflammatory activity, as defined by enhanced IL-6 synthesis. Further studies are needed to test the relative merits of different timing protocols of glucocorticoid administration in rheumatoid arthritis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (133.1 KB).
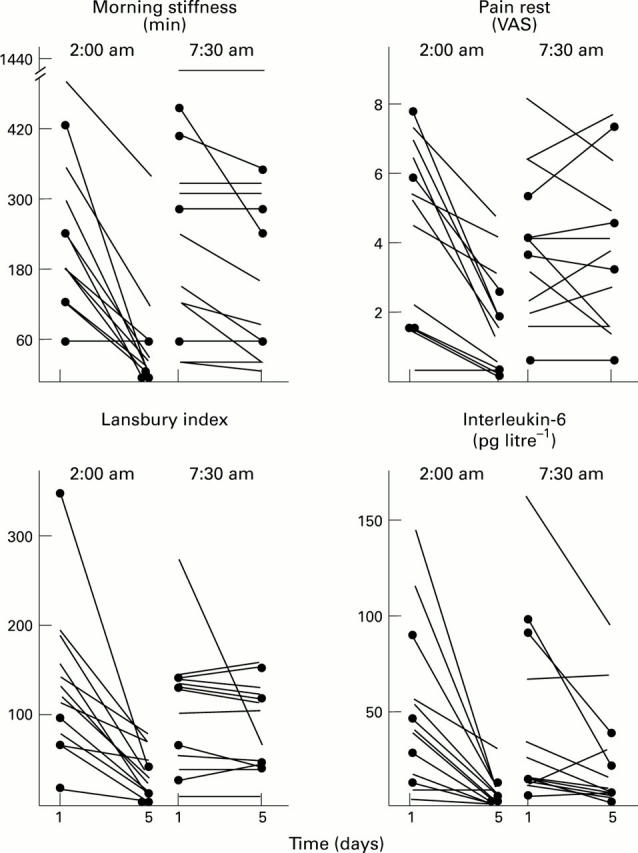
The individual values for morning stiffness, pain at rest, Lansbury index, and serum IL-6 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis before (day 1) and after (day 5) treatment with prednisolone at daily doses of 5 mg or 7.5 mg (circles). The patients who received prednisolone at 2.00 am or at 7.30 am are indicated.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andus T., Geiger T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Tran-Thi T. A., Decker K., Heinrich P. C. Regulation of synthesis and secretion of major rat acute-phase proteins by recombinant human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IL-6) in hepatocyte primary cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 15;173(2):287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidson N. G., Gudbjörnsson B., Elfman L., Rydén A. C., Tötterman T. H., Hällgren R. Circadian rhythm of serum interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Aug;53(8):521–524. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.8.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera P., Boerbooms A. M., Janssen E. M., Sauerwein R. W., Gallati H., Mulder J., de Boo T., Demacker P. N., van de Putte L. B., van der Meer J. W. Circulating soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors, interleukin-2 receptors, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Longitudinal evaluation during methotrexate and azathioprine therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1070–1079. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresford J. N., Gallagher J. A., Poser J. W., Russell R. G. Production of osteocalcin by human bone cells in vitro. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3, 24,25(OH)2D3, parathyroid hormone, and glucocorticoids. Metab Bone Dis Relat Res. 1984;5(5):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0221-8747(84)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock C. G. Corticosteroid-induced lymphopenia, immunosuppression, and body defense. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Apr;88(4):564–566. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-4-564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Hällgren R. Circulating hyaluronic acid levels vary with physical activity in healthy subjects and in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Relationship to synovitis mass and morning stiffness. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Dec;30(12):1333–1338. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathi M. K., Rzewnicki D., Samols D., Jiang S. L., Kushner I. Effect of combinations of cytokines and hormones on synthesis of serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein in Hep 3B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1261–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness J. A., Richter M. B., Panayi G. S., Van de Pette K., Unger A., Pownall R., Geddawi M. Circadian variation in disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Feb 20;284(6315):551–554. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6315.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich P. C., Castell J. V., Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):621–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2650621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hench P. S., Kendall E. C., Slocumb C. H., Polley H. F. The effect of a hormone of the adrenal cortex (17-hydroxy-11-dehydrocorticosterone: compound E) and of pituitary adrenocortical hormone in arthritis: preliminary report. Ann Rheum Dis. 1949 Jun;8(2):97–104. doi: 10.1136/ard.8.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I., Cooper R. G., Denton J., Meager A., Hopkins S. J. Cytokine inter-relationships and their association with disease activity in arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;31(11):725–733. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.11.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Miyaura C., Jin C. H., Akatsu T., Abe E., Nakamura Y., Yamaguchi A., Yoshiki S., Matsuda T., Hirano T. IL-6 is produced by osteoblasts and induces bone resorption. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3297–3303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan J. R. The effect of glucocorticoids on joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. The Arthritis and Rheumatism Council Low-Dose Glucocorticoid Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jul 20;333(3):142–146. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199507203330302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowanko I. C., Pownall R., Knapp M. S., Swannell A. J., Mahoney P. G. Circadian variations in the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and in the therapeutic effectiveness of flurbiprofen at different times of day. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 May;11(5):477–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRochelle G. E., Jr, LaRochelle A. G., Ratner R. E., Borenstein D. G. Recovery of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in patients with rheumatic diseases receiving low-dose prednisone. Am J Med. 1993 Sep;95(3):258–264. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(93)90277-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. C., Ascensao J., McCullough J., Zanjani E. D. Steroid modulation of naturally occurring diurnal variation in circulating pluripotential haematopoietic cells (CFU-GEMM). Br J Haematol. 1983 Dec;55(4):615–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. P., Liu T. Y., Goldman N. D. cis-acting elements responsible for interleukin-6 inducible C-reactive protein gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4136–4142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhok R., Crilly A., Watson J., Capell H. A. Serum interleukin 6 levels in rheumatoid arthritis: correlations with clinical and laboratory indices of disease activity. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Mar;52(3):232–234. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.3.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikle A. W., Tyler F. H. Potency and duration of action of glucocorticoids. Effects of hydrocortisone, prednisone and dexamethasone on human pituitary-adrenal function. Am J Med. 1977 Aug;63(2):200–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara M., Moriya Y., Kishimoto T., Ohsugi Y. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces the proliferation of synovial fibroblastic cells in the presence of soluble IL-6 receptor. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Apr;34(4):321–325. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.4.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsaki Y., Takahashi S., Scarcez T., Demulder A., Nishihara T., Williams R., Roodman G. D. Evidence for an autocrine/paracrine role for interleukin-6 in bone resorption by giant cells from giant cell tumors of bone. Endocrinology. 1992 Nov;131(5):2229–2234. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.5.1425421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickup M. E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of prednisone and prednisolone. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1979 Mar-Apr;4(2):111–128. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197904020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinals R. S., Masi A. T., Larsen R. A. Preliminary criteria for clinical remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1308–1315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780241012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Chapman G. E., Fraser T. R., Davies A. D., Surus A. S., Meyer J., Huq N. L., Ibbertson H. K. Low serum osteocalcin levels in glucocorticoid-treated asthmatics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Feb;62(2):379–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-2-379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag K. G., Koehnke R., Caldwell J. R., Brasington R., Burmeister L. F., Zimmerman B., Kohler J. A., Furst D. E. Low dose long-term corticosteroid therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: an analysis of serious adverse events. Am J Med. 1994 Feb;96(2):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaghecke R., Beuscher D., Kornely E., Specker C. Effects of glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis. Diminished glucocorticoid receptors do not result in glucocorticoid resistance. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Aug;37(8):1127–1131. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Statland B. E., Winkel P., Harris S. C., Burdsall M. J., Saunders A. M. Evaluation of biologic sources of variation of leukocyte counts and other hematologic quantities using very precise automated analyzers. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;69(1):48–54. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/69.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. W., Silman A. J., Kirwan J. R., Currey H. L. Articular indices of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with the acute-phase response. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jun;30(6):618–623. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright V., Plunkett T. G. Scientific assessment of the results of physical treatment--measurement of stiffness. Ann Phys Med. 1966 Nov;8(8):280–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanni G., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophages and joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanker B., Walz G., Wieder K. J., Strom T. B. Evidence that glucocorticosteroids block expression of the human interleukin-6 gene by accessory cells. Transplantation. 1990 Jan;49(1):183–185. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199001000-00040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Benedetti F., Massa M., Robbioni P., Ravelli A., Burgio G. R., Martini A. Correlation of serum interleukin-6 levels with joint involvement and thrombocytosis in systemic juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1158–1163. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen M. A., Westra J., Limburg P. C., van Riel P. L., van Rijswijk M. H. Interleukin-6 in relation to other proinflammatory cytokines, chemotactic activity and neutrophil activation in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Jan;54(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


