Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To compare in vitro expression of β1, β3, and β4 integrins in normal fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FBS) and in FBS from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium and to investigate the adhesion of normal FBS and RA-FBS to the integrin binding extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins: collagen type IV, fibronectin, laminin, and tenascin. METHODS—Expression of integrin receptors of cultured FBS was detected by flow cytometry. Attachment of FBS to ECM proteins was quantified by adhesion assays. Inhibition studies were performed using monoclonal antibodies to the integrin subunits. RESULTS—Compared with normal FBS, RA-FBS showed increased expression of α1 to α6, β1, and β4 integrin subunits and enhanced binding of ECM proteins. Binding to ECM proteins was partly or completely blocked by an anti-β1 integrin antibody and antibodies to α3, α5, and α6 integrin subunits. The blocking efficiency was significantly (P < 0.05) higher in RA-FBS than in normal FBS. CONCLUSIONS—The enhanced expression of the β1 integrin receptors on cultured RA-FBS correlated with increased attachment to ECM proteins. Adhesion of normal and RA-FBS to ECM proteins is mediated through β1 integrin receptors. Therefore, the tight binding of rheumatoid FBS to the matrix via β1 integrins might play a role in ECM remodelling in the rheumatoid process in vivo.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (160.8 KB).
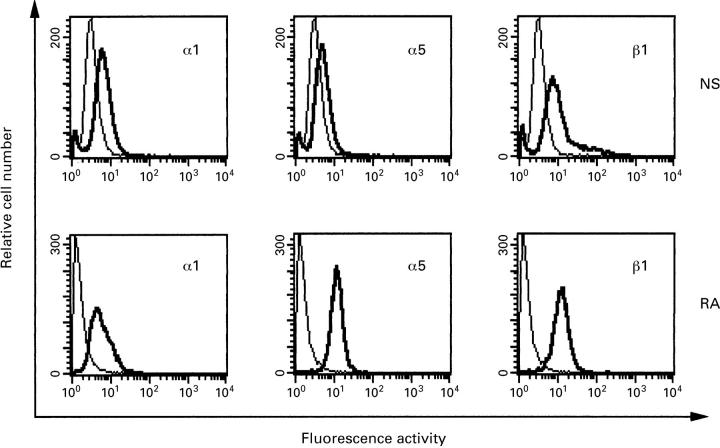
Figure 1 .
Histograms of flow cytometric analysis for the α1, α5, and β1 integrin subunits on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FBS) from normal synovium (NS, upper panels) and from rheumatoid arthritis (RA, lower panels). The fluorescence obtained with isotypic negative control antibodies is plotted as a plain line, the results with anti-integrin antibodies as a bold line.
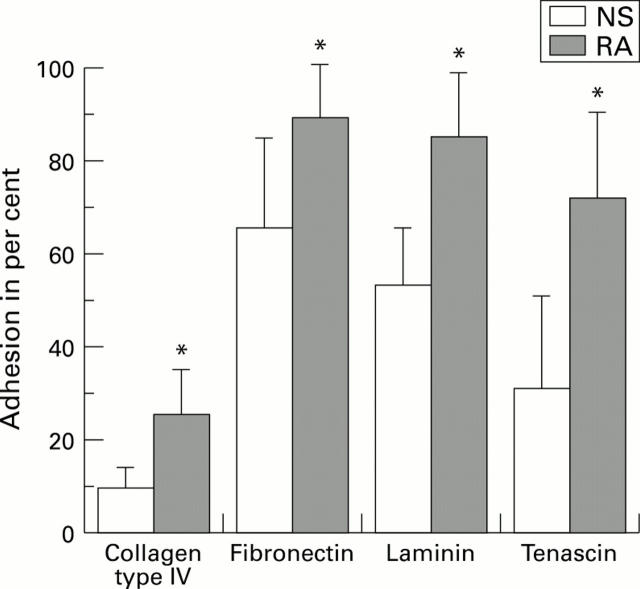
Figure 2 .
Adhesion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FBS) from normal synovium (NS) and from synovium derived from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The assays were performed as described in Methods. The diagram shows percent adhesion of the total number of cells plated. Data are reported as the mean of assays of seven normal FBS cultures and seven rheumatoid arthritis FBS cultures. Bars = SD. *P < 0.05 v normal FBS.
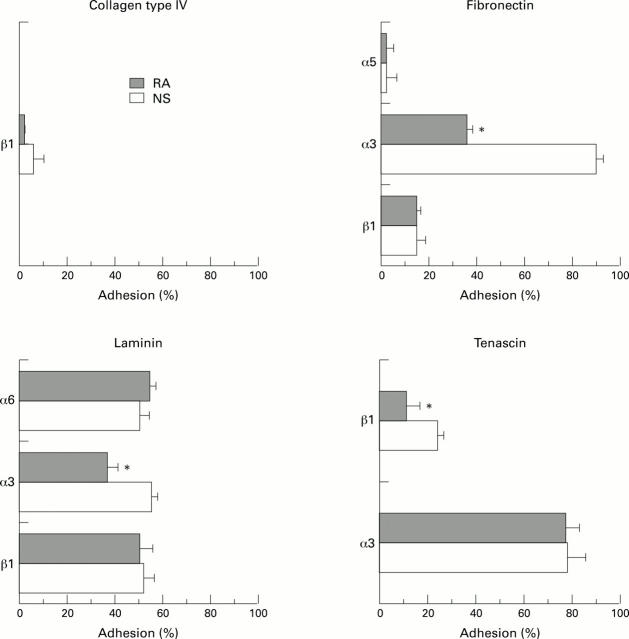
Figure 3 .
Inhibition of adhesion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FBS) from normal synovium (NS) and from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) to the ECM proteins. Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) against α2, α3, α4, α5, α6, β1, and β3 were used; however, only mAb which blocked FBS binding are shown in the figure. Inhibition through the mAb is given as relative percent adhesion compared to adhesion without antibodies (100%). Data represent the means of assays of three normal FBS cultures and of three rheumatoid arthritis FBS cultures. Bars = SD. *P < 0.05 v normal FBS.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M. Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab Invest. 1993 Jan;68(1):4–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. G., Wayner E. A., Bouchard T. S., Kaur P. The role of integrins alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 1 in cell-cell and cell-substrate adhesion of human epidermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1387–1404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castor C. W., Ragsdale C. G., Cabral A. R., Smith E. M., Aaron B. P. Anabolic and catabolic responses of human articular cells to growth factors. J Rheumatol. 1987 May;14(Spec No):67–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutolo M., Picasso M., Ponassi M., Sun M. Z., Balza E. Tenascin and fibronectin distribution in human normal and pathological synovium. J Rheumatol. 1992 Sep;19(9):1439–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eerola E., Pulkki K., Pelliniemi L. J., Granfors K., Vuorio E., Toivanen A. Arthritis-associated changes in flow cytometric characteristics of cultured synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):339–347. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailit J., Ruoslahti E. Regulation of the fibronectin receptor affinity by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12927–12932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard D. H., Grossman S. L., Williams W. V., Weiner D. B., Gross J. L., Eidsvoog K., Dasch J. R. Regulation of synovial cell growth. Coexpression of transforming growth factor beta and basic fibroblast growth factor by cultured synovial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1296–1303. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Okamoto M., Sasano M., Yanagisawa S., Miyamoto T., Nishioka K., Nakamura K., Aotuka S., Kawakami N., Yokohari R. Adherent synovial cells from nonrheumatoid arthritis do not release interleukin 1 beta and prostaglandin E2 spontaneously in longterm culture. J Rheumatol. 1990 Oct;17(10):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauzenberger D., Klominek J., Sundqvist K. G. Functional specialization of fibronectin-binding beta 1-integrins in T lymphocyte migration. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 1;153(3):960–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernvann A., Cynober L., Aussel C., Ekindjian O. G. Rheumatoid arthritis modifies basal and insulin-mediated glucose uptake by human synoviocytes. Cell Mol Biol. 1991;37(5):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U. Measurement of cell numbers by means of the endogenous enzyme hexosaminidase. Applications to detection of lymphokines and cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévesque J. P., Hatzfeld A., Hatzfeld J. Mitogenic properties of major extracellular proteins. Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90122-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. J., Entwistle G., Humphries M. J., Ager A. VCAM-1 is a CS1 peptide-inhibitable adhesion molecule expressed by lymph node high endothelium. J Cell Sci. 1993 Sep;106(Pt 1):109–119. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCroskery P. A., Arai S., Amento E. P., Krane S. M. Stimulation of procollagenase synthesis in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts by mononuclear cell factor/interleukin 1. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 21;191(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80983-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkari L., Aho H., Yli-Jama T., Larjava H., Jalkanen M., Heino J. Expression of integrin family of cell adhesion receptors in rheumatoid synovium. Alpha 6 integrin subunit in normal and hyperplastic synovial lining cell layer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1019–1027. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi N., Barth T., Henne C., Mechterscheimer G., Möller P. Synoviocytes in chronic synovitis in situ and cytokine stimulated synovial cells in vitro neo-express alpha 1, alpha 3 and alpha 5 chains of beta 1 integrins. Virchows Arch. 1994;425(2):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00230354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruan C. G., Xi X. D., Du X. P., Wan H. Y., Wu X., Li P. X., Gu J. M. Studies on monoclonal antibodies against human platelets--a monoclonal antibody to human platelet glycoprotein I--SZ-2. Sci Sin B. 1987 Apr;30(4):404–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlossman S. F., Boumsell L., Gilks W., Harlan J. M., Kishimoto T., Morimoto C., Ritz J., Shaw S., Silverstein R. L., Springer T. A. CD antigens 1993. Blood. 1994 Feb 15;83(4):879–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Messier J. M., Mercurio A. M. The activation dependent adhesion of macrophages to laminin involves cytoskeletal anchoring and phosphorylation of the alpha 6 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2167–2174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriramarao P., Mendler M., Bourdon M. A. Endothelial cell attachment and spreading on human tenascin is mediated by alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha v beta 3 integrins. J Cell Sci. 1993 Aug;105(Pt 4):1001–1012. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.4.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus A. H., Carter W. G., Wayner E. A., Hakomori S. Mechanism of fibronectin-mediated cell migration: dependence or independence of cell migration susceptibility on RGDS-directed receptor (integrin). Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jul;183(1):126–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90423-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H. [Fibronectin in the synovium and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis and in osteoarthritis]. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1994 Apr;68(4):172–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremble P., Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Werb Z. The extracellular matrix ligands fibronectin and tenascin collaborate in regulating collagenase gene expression in fibroblasts. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Apr;5(4):439–453. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.4.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. Identification of multiple cell adhesion receptors for collagen and fibronectin in human fibrosarcoma cells possessing unique alpha and common beta subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1873–1884. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Piotrowicz R. S., Kunicki T. J. The function of multiple extracellular matrix receptors in mediating cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: preparation of monoclonal antibodies to the fibronectin receptor that specifically inhibit cell adhesion to fibronectin and react with platelet glycoproteins Ic-IIa. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1881–1891. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinel R. J., Rosendahl A., Neumann K., Chaloupka B., Erb D., Rothmund M., Santoso S. Expression and function of VLA-alpha 2, -alpha 3, -alpha 5 and -alpha 6-integrin receptors in pancreatic carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1992 Nov 11;52(5):827–833. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Tremble P. M., Behrendtsen O., Crowley E., Damsky C. H. Signal transduction through the fibronectin receptor induces collagenase and stromelysin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):877–889. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Roberts C. R., Castor C. W. Ultrastructural comparison of rheumatoid and nonrheumatoid synovial fibroblasts grown in tissue culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):65–83. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosaki Y., Palmer E. L., Prieto A. L., Crossin K. L., Bourdon M. A., Pytela R., Sheppard D. The integrin alpha 9 beta 1 mediates cell attachment to a non-RGD site in the third fibronectin type III repeat of tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26691–26696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosaki Y., Palmer E. L., Prieto A. L., Crossin K. L., Bourdon M. A., Pytela R., Sheppard D. The integrin alpha 9 beta 1 mediates cell attachment to a non-RGD site in the third fibronectin type III repeat of tenascin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 28;269(43):26691–26696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Gabalawy H., Wilkins J. Beta 1 (CD29) integrin expression in rheumatoid synovial membranes: an immunohistologic study of distribution patterns. J Rheumatol. 1993 Feb;20(2):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]