Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (77.5 KB).
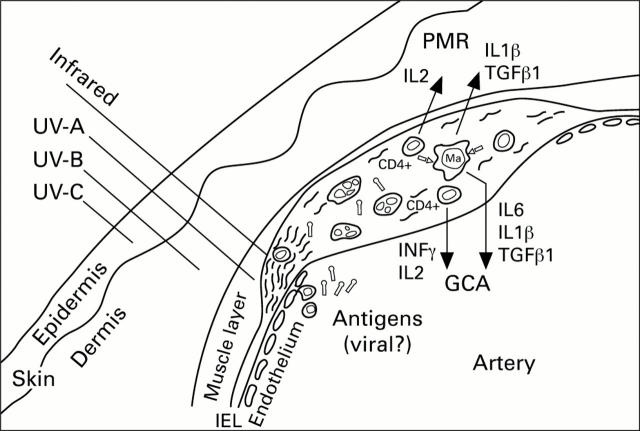
Figure 1 .
Sun radiation of both the infrared and ultraviolet A types damages the internal elastic lamina (IEL) of superficial arteries facilitating the localisation of an unknown aetiological agent (viral proteins or degenerated vascular components?). This antigen is presented by macrophages (Ma ) and is recognised by CD4+ lymphocytes in the context of class II MHC molecules. Macrophages and lymphocytes are stimulated to produce increased amounts of cytokines, which can lead to PMR or to GCA, depending on their pattern. This mechanism is facilitated by predisposing factors, such as old age, female sex, and specific HLA-DRB1 alleles.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBER H. S. Myalgic syndrome with constitutional effects; polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Jun;16(2):230–237. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon P. A., Doherty S. M., Zuckerman A. J. Hepatitis-B antibody in polymyalgia Rheumatica. Lancet. 1975 Sep 13;2(7933):476–478. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boiardi L., Salvarani C., Macchioni P., Casadei Maldini M., Mancini R., Beltrandi E., Portioli I. CD8 lymphocyte subsets in active polymyalgia rheumatica: comparison with elderly-onset and adult rheumatoid arthritis and influence of prednisone therapy. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;35(7):642–648. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.7.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brito J., Biamonti G., Caporali R., Montecucco C. Autoantibodies to human nuclear lamin B2 protein. Epitope specificity in different autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 1;153(5):2268–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg M. B., Donofrio P. D., Segal B. M. Steroid-responsive electromyographic abnormalities in polymyalgia rheumatica. Muscle Nerve. 1990 Feb;13(2):138–141. doi: 10.1002/mus.880130209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. E., Anderson S. M., Young N. S. Erythrocyte P antigen: cellular receptor for B19 parvovirus. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):114–117. doi: 10.1126/science.8211117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino M. A., Accardo S., Montecucco C., Caporali R., Cappelli A., Broggini M. Sun exposure and the polymyalgia rheumatica-giant cell arteritis complex. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Mar-Apr;12(2):229–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino M. A., Caporali R., Montecucco C. M., Rovida S., Baratelli E., Broggini M. A seasonal pattern in the onset of polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jul;49(7):521–523. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.7.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimmino M. A., Grazi G., Balistreri M., Accardo S. Increased prevalence of antibodies to adenovirus and respiratory syncytial virus in polymyalgia rheumatica. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993 May-Jun;11(3):309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elling P., Olsson A. T., Elling H. Synchronous variations of the incidence of temporal arteritis and polymyalgia rheumatica in different regions of Denmark; association with epidemics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Rheumatol. 1996 Jan;23(1):112–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faerk K. K. Simultaneous occurrence of polymyalgia rheumatica in a married couple. J Intern Med. 1992 Jun;231(6):621–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1992.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T. H., Török T. J., Ferguson P. J., Durigon E. L., Zaki S. R., Leung D. Y., Harbeck R. J., Gelfand E. W., Saulsbury F. T., Hollister J. R. Chronic parvovirus B19 infection and systemic necrotising vasculitis: opportunistic infection or aetiological agent? Lancet. 1994 May 21;343(8908):1255–1258. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harle J. R., Pellissier J. F., Desnuelle C., Disdier P., Figarella-Branger D., Weiller P. J. Polymyalgia rheumatica and mitochondrial myopathy: clinicopathologic and biochemical studies in five cases. Am J Med. 1992 Feb;92(2):167–172. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90108-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth S., Ridgeway J., Stewart I., Dyer P. A., Pepper L., Ollier W. Polymyalgia rheumatica is associated with both HLA-DRB1*0401 and DRB1*0404. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;35(7):632–635. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.7.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healey L. A. Long-term follow-up of polymyalgia rheumatica: evidence for synovitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1984 May;13(4):322–328. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(84)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen M., Elling P., Elling H., Olsson A. A genetic approach to the aetiology of giant cell arteritis: depletion of the CD8+ T-lymphocyte subset in relatives of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and arteritis temporalis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1995 Nov-Dec;13(6):745–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M. Ultrasonographic evidence of synovitis in axial joints in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Br J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;31(3):201–203. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/31.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchioni P., Boiardi L., Meliconi R., Salvarani C., Grazia Uguccioni M., Rossi F., Pulsatelli L., Facchini A. Elevated soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in the serum of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica: influence of steroid treatment. J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;21(10):1860–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meliconi R., Pulsatelli L., Uguccioni M., Salvarani C., Macchioni P., Melchiorri C., Focherini M. C., Frizziero L., Facchini A. Leukocyte infiltration in synovial tissue from the shoulder of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. Quantitative analysis and influence of corticosteroid treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1199–1207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro G., Zerbini M., Krzysztofiak A., Gentilomi G., Porcaro M. A., Mango T., Musiani M. Active or recent parvovirus B19 infection in children with Kawasaki disease. Lancet. 1994 May 21;343(8908):1260–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. P. A controlled hematoxylin-eosin for actinic elastosis-lysis. Its versatility and use for vascular damage (actinic arteriopathy) in the skin and orbit. Am J Dermatopathol. 1994 Feb;16(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. P., Regan W. Are we losing focus on the internal elastic lamina in giant cell arteritis? Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):794–798. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperakis S. M., McLennan A. G. Hyperthermia enhances the reactivation of irradiated adenovirus in HeLa cells. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):199–205. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo M. G., Waxman J., Abdoh A. A., Serebro L. H. Correlation between infection and the onset of the giant cell (temporal) arteritis syndrome. A trigger mechanism? Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Mar;38(3):374–380. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani C., Boiardi L., Macchioni P., Casadei Maldini M., Mancini R., Beltrandi E., Rossi F., Portioli I. Serum soluble CD4 and CD8 levels in polymyalgia rheumatica. J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;21(10):1865–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani C., Gabriel S. E., O'Fallon W. M., Hunder G. G. Epidemiology of polymyalgia rheumatica in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1970-1991. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Mar;38(3):369–373. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani C., Gabriel S. E., O'Fallon W. M., Hunder G. G. The incidence of giant cell arteritis in Olmsted County, Minnesota: apparent fluctuations in a cyclic pattern. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Aug 1;123(3):192–194. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-123-3-199508010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani C., Macchioni P., Boiardi L., Rossi F., Casadei Maldini M., Mancini R., Beltrandi E., Spacca C., Lodi L., Portioli I. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors in polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis. Clinical and laboratory correlations. J Rheumatol. 1992 Jul;19(7):1100–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenblick M., Nesher G., Friedlander Y., Rubinow A. Giant cell arteritis in Jerusalem: a 12-year epidemiological study. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Oct;33(10):938–941. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.10.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. J., Hughes R. A. The aetiopathogenesis of giant cell arteritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Oct;34(10):960–965. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.10.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wernick R., Davey M., Bonafede P. Familial giant cell arteritis: report of an HLA-typed sibling pair and a review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994 Jan-Feb;12(1):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hicok K. C., Hunder G. G., Goronzy J. J. Tissue cytokine patterns in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Oct 1;121(7):484–491. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-7-199410010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Hunder N. N., Hicok K. C., Hunder G. G., Goronzy J. J. HLA-DRB1 alleles in polymyalgia rheumatica, giant cell arteritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Apr;37(4):514–520. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]