Abstract
Objectives—To compare peripheral type 1 (T1) and type 2 (T2) T cell activities in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with that found for osteoarthritic (OA) patients and healthy controls and to correlate peripheral T1/T2 cell activity in RA with parameters of the disease. METHODS—Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from patients with RA (n=66), OA (n=19), and healthy controls (n=15). Primary T cell activity in these mononuclear cells was enhanced by means of anti-CD3/anti-CD28, which mimicks stimulation of T cells by activation of the T cell receptor and a major co-stimulatory signal. Interferon gamma (IFNγ) production and interleukin 4 (IL4) production in the three groups were quantified as measures of T1 and T2 cell activity, respectively, and compared. Serum tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C reactive protein (CRP), and joint destruction assessed radiographically of RA patients were determined as parameters of disease activity and correlated with T1/T2 cell activity. RESULTS—Peripheral T cells from RA patients produced significantly less IFNγ and more IL4 than T cells from both age and sex matched OA patients and healthy controls. Moreover, in RA patients both a decrease in IFNγ and an increase in IL4 production correlated with an increase in serum TNFα, ESR, CRP, and joint destruction. Conclusions—These results suggest a role for differential T cell activity in RA. In view of the intra-articular T1 cell predominance the results might be explained by selective T1 cell migration into the joint or peripheral suppression of T1 cell activity.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (155.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
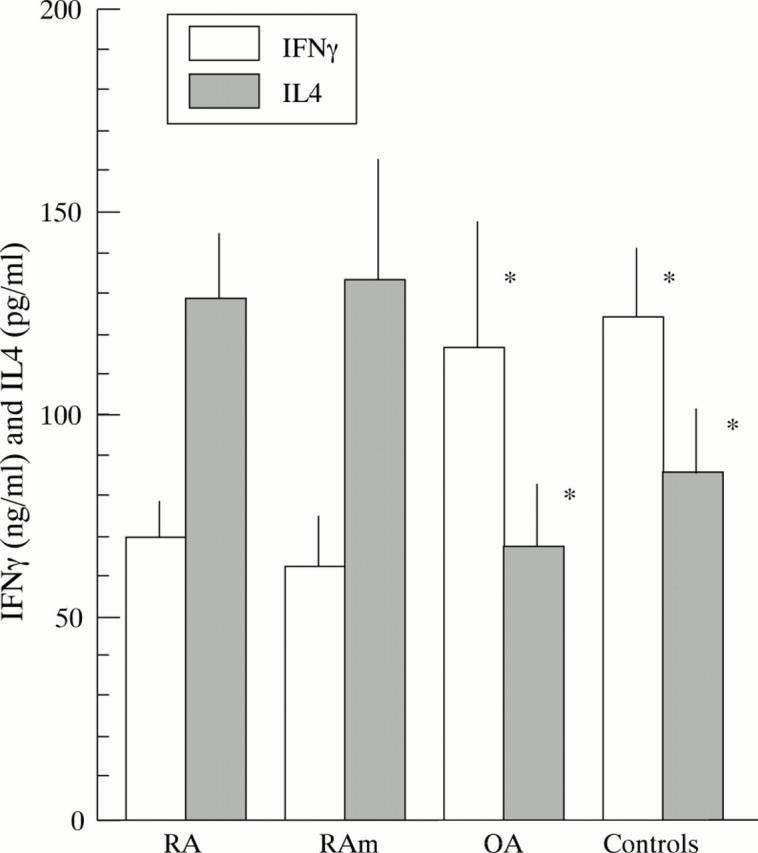
IFNγ and IL4 production by anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated peripheral blood T cells (mononuclear cells) from patients with RA (n=66) and OA (n=19) and healthy controls (C, n=15). Data for a group of patients with RA matched for age and sex with OA patients and healthy controls are also shown (RAm). Means (SEM) are given. * Indicates a statistically significant difference between OA, controls, and RA patients (p⩽0.05).
Figure 2 .
Correlation of IFNγ and IL4 production by anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated peripheral blood T cells (mononuclear cells) from RA patients with serum TNFα.
Figure 3 .
Production of IFNγ and IL4 by anti-CD3/CD28 stimulated peripheral blood T cells (mononuclear cells) from RA patients divided according to the Steinbrocker radiological damage scores on hand radiographs. The numbers of patients per group were: I=14, II=19, III=25, and IV=8. * Indicates a statistically significant difference between group III or IV and group I (p⩽0.05).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrup F., Vestweber D., Borges E., Löhning M., Bräuer R., Herz U., Renz H., Hallmann R., Scheffold A., Radbruch A. P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T-helper-1 but not T-helper-2 cells into inflammed tissues. Nature. 1997 Jan 2;385(6611):81–83. doi: 10.1038/385081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucht A., Larsson P., Weisbrot L., Thorne C., Pisa P., Smedegård G., Keystone E. C., Grönberg A. Expression of interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), IL-10, IL-12 and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) mRNA in synovial fluid cells from patients in the early and late phases of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Mar;103(3):357–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1996.tb08288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Splawski J. B., Thomas R., McFarlin J. E., Schulze-Koops H., Davis L. S., Fujita K., Lipsky P. E. Elevated interleukin-10 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., Mastromauro C., Biagiotti R., Macchia D., Falagiani P., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Purified protein derivative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and excretory-secretory antigen(s) of Toxocara canis expand in vitro human T cells with stable and opposite (type 1 T helper or type 2 T helper) profile of cytokine production. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):346–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI115300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolhain R. J., van der Heiden A. N., ter Haar N. T., Breedveld F. C., Miltenburg A. M. Shift toward T lymphocytes with a T helper 1 cytokine-secretion profile in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Dec;39(12):1961–1969. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchimont P., Reuter A., Vrindts-Gevaert Y., Bastings M., Malaise M., Sondag C., Frere M. C., Gysen P. Production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma and interleukin-2 by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of subjects suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1988;17(3):203–212. doi: 10.3109/03009748809098783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Bluestone J. A., Nadler L. M., Thompson C. B. The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunol Today. 1994 Jul;15(7):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahle P., Saal J. G., Schaudt K., Zacher J., Fritz P., Pawelec G. Determination of cytokines in synovial fluids: correlation with diagnosis and histomorphological characteristics of synovial tissue. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jun;51(6):731–734. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsikis P. D., Chu C. Q., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Immunoregulatory role of interleukin 10 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1517–1527. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. L., Low C. C., Nutman T. B. IgE production in human helminth infection. Reciprocal interrelationship between IL-4 and IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1873–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Kekow J., Carson D. A. Transforming growth factor-beta and cellular immune responses in synovial fluids. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4189–4194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenburg A. M., van Laar J. M., de Kuiper R., Daha M. R., Breedveld F. C. T cells cloned from human rheumatoid synovial membrane functionally represent the Th1 subset. Scand J Immunol. 1992 May;35(5):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Naviliat M., Dupuy d'Angeac A., Sany J., Banchereau J. Low levels of interleukin-4 and high levels of transforming growth factor beta in rheumatoid synovitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1180–1187. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rivier A., Lagier B., Becker W. M., Michel F. B., Bousquet J. Differences in IL-4 release by PBMC are related with heterogeneity of atopy. Immunology. 1994 Jan;81(1):58–64. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle A. J., Chomarat P., Miossec P., Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Førre O., Natvig J. B. Rheumatoid inflammatory T-cell clones express mostly Th1 but also Th2 and mixed (Th0-like) cytokine patterns. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jul;38(1):75–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas D., Mozo L., Zamorano J., Gayo A., Torre-Alonso J. C., Rodríguez A., Gutiérrez C. Upregulated expression of IL-4 receptors and increased levels of IL-4 in rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Autoimmun. 1995 Aug;8(4):587–600. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(95)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romagnani S. Lymphokine production by human T cells in disease states. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:227–257. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruschen S., Stellberg W., Warnatz H. Kinetics of cytokine secretion by mononuclear cells of the blood from rheumatoid arthritis patients are different from those of healthy controls. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):32–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06873.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Koops H., Lipsky P. E., Kavanaugh A. F., Davis L. S. Elevated Th1- or Th0-like cytokine mRNA in peripheral circulation of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Modulation by treatment with anti-ICAM-1 correlates with clinical benefit. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 15;155(10):5029–5037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon A. K., Seipelt E., Sieper J. Divergent T-cell cytokine patterns in inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8562–8566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfgren A. K., Lindblad S., Klareskog L., Andersson J., Andersson U. Detection of cytokine producing cells in the synovial membrane from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Aug;54(8):654–661. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.8.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lier R. A., Brouwer M., Aarden L. A. Signals involved in T cell activation. T cell proliferation induced through the synergistic action of anti-CD28 and anti-CD2 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):167–172. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Pouw-Kraan T., Van Kooten C., Rensink I., Aarden L. Interleukin (IL)-4 production by human T cells: differential regulation of IL-4 vs. IL-2 production. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1237–1241. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westacott C. I., Whicher J. T., Barnes I. C., Thompson D., Swan A. J., Dieppe P. A. Synovial fluid concentration of five different cytokines in rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Sep;49(9):676–681. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.9.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Janadi N., al-Dalaan A., al-Balla S., Raziuddin S. CD4+ T cell inducible immunoregulatory cytokine response in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996 May;23(5):809–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roon J. A., van Roy J. L., Duits A., Lafeber F. P., Bijlsma J. W. Proinflammatory cytokine production and cartilage damage due to rheumatoid synovial T helper-1 activation is inhibited by interleukin-4. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Oct;54(10):836–840. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.10.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Roon J. A., van Roy J. L., Gmelig-Meyling F. H., Lafeber F. P., Bijlsma J. W. Prevention and reversal of cartilage degradation in rheumatoid arthritis by interleukin-10 and interleukin-4. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 May;39(5):829–835. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




