Abstract
OBJECTIVE—This study investigated the predictive value of rises in IgM class antibodies against double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) for ensuing relapses in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in comparison with rises in IgG class antibodies. In addition, it was analysed whether rises in IgM class anti-dsDNA were associated with specific clinical manifestations of SLE. METHODS—Thirty four of a cohort of 72 SLE patients who were positive for IgM class anti-dsDNA at the start of the study or at the time of a relapse were analysed monthly for class specific anti-dsDNA levels during a median observation period of 19.6 months. Disease activity was scored according to the SLE Disease Activity Index. Anti-dsDNA were measured by IgM and IgG class enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and by Farr assay. RESULTS—During the study 18 of 34 patients experienced 26 relapses. Twenty two (85%) of the relapses were accompanied by a positive test for IgM class anti-dsDNA by ELISA, 23 (89%) were positive for IgG class anti-dsDNA by ELISA, and 25 (96%) were positive by Farr assay. Patients with rises in IgG class anti-dsDNA by ELISA or in anti-dsDNA by Farr assay had a significantly higher cumulative risk for relapses than patients without those increases (p=0.04 and p=0.03, respectively). This was not the case for rises in IgM class anti-dsDNA (p=0.16). Moreover, a rise in IgM class anti-dsDNA before a relapse was not associated, expressed in terms of odds ratios, with specific clinical manifestations of SLE. CONCLUSION—Relapses of SLE are frequently accompanied by IgM class anti-dsDNA. Rises of IgM class anti-dsDNA, in contrast with rises in IgG class anti-dsDNA, are not a sensitive tool for predicting a relapse and are not associated with specific clinical manifestations of SLE.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (111.5 KB).
Figure 1 .
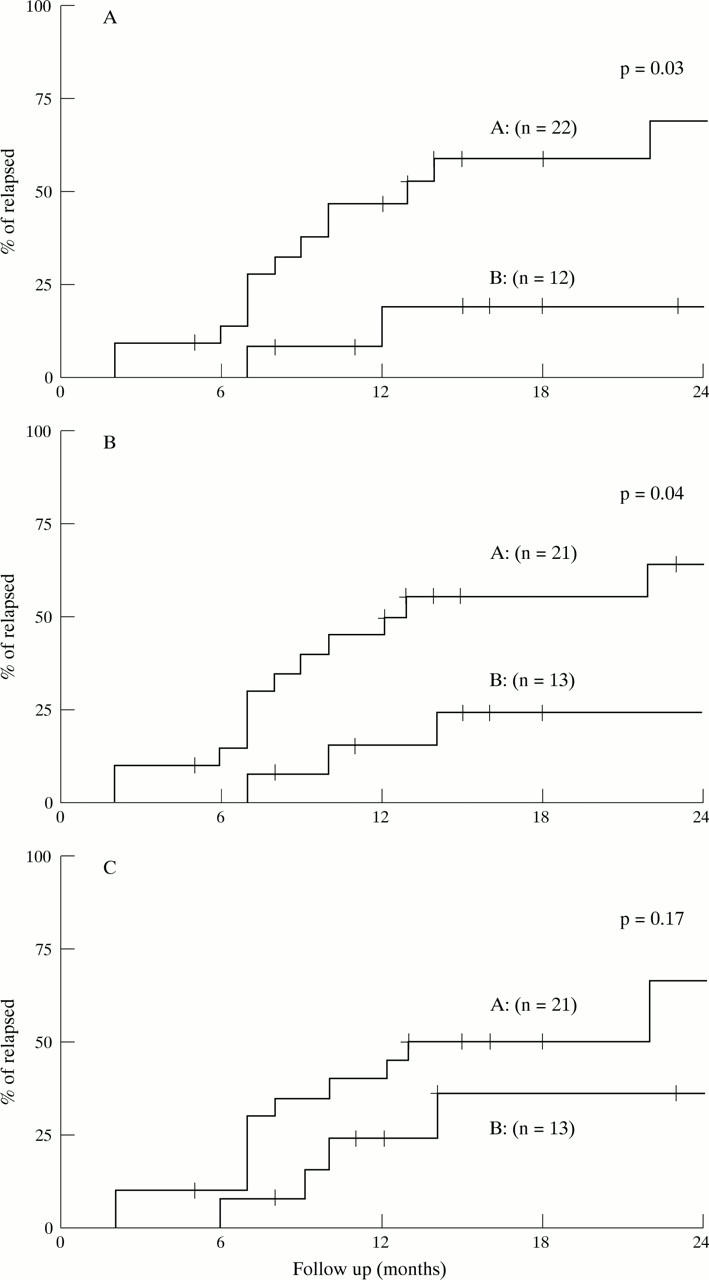
Cumulative risk of relapses in SLE patients with a rise in anti-dsDNA (line A) and without a rise in anti-dsDNA (line B), determined by Farr assay (A), by IgG class ELISA (B), and by IgM class ELISA (C). The p values were calculated by the Gehan-Wilcoxon method.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aotsuka S., Okawa M., Ikebe K., Yokohari R. Measurement of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies in major immunoglobulin classes. J Immunol Methods. 1979;28(1-2):149–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootsma H., Spronk P., Derksen R., de Boer G., Wolters-Dicke H., Hermans J., Limburg P., Gmelig-Meyling F., Kater L., Kallenberg C. Prevention of relapses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1995 Jun 24;345(8965):1595–1599. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clough J. D., Valenzuela R. Relationship of renal histopathology in SLE nephritis to immunoglobulin class of anti-DNA. Am J Med. 1980 Jan;68(1):80–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esdaile J. M., Abrahamowicz M., Joseph L., MacKenzie T., Li Y., Danoff D. Laboratory tests as predictors of disease exacerbations in systemic lupus erythematosus. Why some tests fail. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Mar;39(3):370–378. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltkamp T. E. Standards for ANA and anti-DNA. Clin Rheumatol. 1990 Mar;9(1 Suppl 1):74–78. doi: 10.1007/BF02205554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylkema M. N., Huygen H., Kramers C., vd Wal T. J., de Jong J., van Bruggen M. C., Swaak A. J., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Clinical evaluation of a modified ELISA, using photobiotinylated DNA, for the detection of anti-DNA antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Mar 29;170(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Dudeney C., Williams W., Addison I., Charles S., Clarke J., Todd-Pokropek A. Measurement of anti-DNA antibodies: a reappraisal using five different methods. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jun;46(6):448–456. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.6.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippner H., Merle S., Jörgens K., Pirlet K. Antibodies to dsDNA and ssDNA in the immunoglobulin classes IgG and IgM: prognostic value in the course of SLE. Z Rheumatol. 1984 Sep-Oct;43(5):265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miniter M. F., Stollar B. D., Agnello V. Reassessment of the clinical significance of native DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Sep;22(9):959–968. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namboodiri M. S., Nagpal S., Rao P. V. Induction of anti-DNA IgG and IgE antibodies in BALB/c mice. J Autoimmun. 1992 Oct;5(5):653–663. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90161-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura M., Kanayama Y., Amastu K., Negoro N., Kohda S., Takeda T., Inoue T. Significance of enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies to double stranded and single stranded DNA in patients with lupus nephritis: correlation with severity of renal histology. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jan;52(1):14–20. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennebaker J. B., Gilliam J. N., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin classes of DNA binding activity in serum and skin in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1331–1338. doi: 10.1172/JCI108892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri M., Genovese M., Engle E., Hochberg M. Definition, incidence, and clinical description of flare in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):937–944. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N. F., Stollar B. D. The relation of immunoglobulin class, pattern of anti-nuclear antibody, and complement-fixing antibodies to DNA in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1785–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI105669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer R. D., Gilliam J. N. DNA antibody class, subclass, and complement fixation in systemic lupus erythematosus with and without nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Aug;10(4):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Groenwold J., Bronsveld W. Predictive value of complement profiles and anti-dsDNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 May;45(5):359–366. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.5.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak T., Smeenk R. Detection of anti-dsDNA as a diagnostic tool: a prospective study in 441 non-systemic lupus erythematosus patients with anti-dsDNA antibody (anti-dsDNA). Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Apr;44(4):245–251. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.4.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Disordered immunologic regulation and autoimmunity. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:240–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax W. J., Kramers C., van Bruggen M. C., Berden J. H. Apoptosis, nucleosomes, and nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int. 1995 Sep;48(3):666–673. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werle E., Blazek M., Fiehn W. The clinical significance of measuring different anti-dsDNA antibodies by using the Farr assay, an enzyme immunoassay and a Crithidia luciliae immunofluorescence test. Lupus. 1992 Dec;1(6):369–377. doi: 10.1177/096120339200100606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Hummel E. J., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):634–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


