Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (74.1 KB).
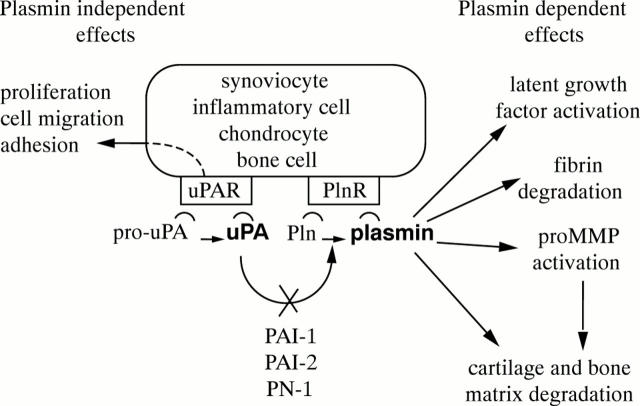
Figure 1 .
Schematic representation of the uPA mediated plasminogen activation within the RA joint. Secreted pro-uPA, as well as active uPA, bind, through the aminoterminal non-catalytic portion, in an autocrine or paracrine way, to uPAR bearing cells. Upon uPAR occupancy, signal transduction may occur, leading to different plasmin independent effects. Alternatively, uPA converts plasminogen into plasmin, which has various different substrates. Plasminogen and plasmin bind to cell surface receptors, through lysine binding sites located in their non-catalytic domain. Active enzymes are indicated by bold style. R= receptor, Pln= plasminogen, MMP= matrix metalloprotease, PN-1= protease nexin 1, PAI= plasminogen activator inhibitor.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan E. H., Martin T. J. The plasminogen activator inhibitor system in bone cell function. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995 Apr;(313):54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altieri D. C. Coagulation assembly on leukocytes in transmembrane signaling and cell adhesion. Blood. 1993 Feb 1;81(3):569–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belch J. J., Madhok R., McArdle B., McLaughlin K., Kluft C., Forbes C. D., Sturrock R. D. The effect of increasing fibrinolysis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a double blind study of stanozolol. Q J Med. 1986 Jan;58(225):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher C., Fawthrop F., Bunning R., Doherty M. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in synovial fluids from normal, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis knees. Ann Rheum Dis. 1996 Apr;55(4):230–236. doi: 10.1136/ard.55.4.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brommer E. J., Dooijewaard G., Dijkmans B. A., Breedveld F. C. Depression of tissue-type plasminogen activator and enhancement of urokinase-type plasminogen activator as an expression of local inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Aug 3;68(2):180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brommer E. J., Dooijewaard G., Dijkmans B. A., Breedveld F. C. Plasminogen activators in synovial fluid and plasma from patients with arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Aug;51(8):965–968. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.8.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Péclat V., So A., Sappino A. P. Plasminogen activation in synovial tissues: differences between normal, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Sep;56(9):550–557. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.9.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. K., Piccoli D. S., Roberts M. J., Muirden K. D., Hamilton J. A. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and beta on resorption of human articular cartilage and production of plasminogen activator by human articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Apr;33(4):542–552. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet P., Schoonjans L., Kieckens L., Ream B., Degen J., Bronson R., De Vos R., van den Oord J. J., Collen D., Mulligan R. C. Physiological consequences of loss of plasminogen activator gene function in mice. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):419–424. doi: 10.1038/368419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Lijnen H. R. Fibrin-specific fibrinolysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Dec 4;667:259–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb51623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier S., Ghosh P. The role of plasminogen in interleukin-1 mediated cartilage degradation. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jul;15(7):1129–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R., Dvorak A. M., Harvey V. S., McDonagh J. Regulation of extravascular coagulation by microvascular permeability. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.3975602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M., Bullough P. G. Synovial and osseous inflammation in failed silicone-rubber prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982 Apr;64(4):574–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Campbell I. K., Wojta J., Cheung D. Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in arthritic disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Dec 4;667:87–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb51602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi H., Tanaka S., Matsuo O. Plasminogen activator in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1987 Jun;14(3):439–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kummer J. A., Abbink J. J., de Boer J. P., Roem D., Nieuwenhuys E. J., Kamp A. M., Swaak T. J., Hack C. E. Analysis of intraarticular fibrinolytic pathways in patients with inflammatory and noninflammatory joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Aug;35(8):884–893. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olman M. A., Mackman N., Gladson C. L., Moser K. M., Loskutoff D. J. Changes in procoagulant and fibrinolytic gene expression during bleomycin-induced lung injury in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1621–1630. doi: 10.1172/JCI118201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani S. A., Mazar A. P., Bernier S. M., Haq M., Bolivar I., Henkin J., Goltzman D. Structural requirements for the growth factor activity of the amino-terminal domain of urokinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14151–14156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronday H. K., Smits H. H., Quax P. H., van der Pluijm G., Löwik C. W., Breedveld F. C., Verheijen J. H. Bone matrix degradation by the plasminogen activation system. Possible mechanism of bone destruction in arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Jan;36(1):9–15. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronday H. K., Smits H. H., Van Muijen G. N., Pruszczynski M. S., Dolhain R. J., Van Langelaan E. J., Breedveld F. C., Verheijen J. H. Difference in expression of the plasminogen activation system in synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 May;35(5):416–423. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.5.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Lecander I., Geborek P. Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in synovial fluid. Difference between inflammatory joint disorders and osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1993 Jan;20(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Skogen W. F., Griffin G. L., Wilner G. D. Effects of fibrinogen derivatives upon the inflammatory response. Studies with human fibrinopeptide B. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1014–1019. doi: 10.1172/JCI112353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang L., Eaton J. W. Fibrin(ogen) mediates acute inflammatory responses to biomaterials. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2147–2156. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltz D. A., Chapman H. A. Reversible cellular adhesion to vitronectin linked to urokinase receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14746–14750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Pippen A. M., Greenberg C. S. Extravascular fibrin formation and dissolution in synovial tissue of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):996–1005. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Loskutoff D. J. Fibrin deposition in tissues from endotoxin-treated mice correlates with decreases in the expression of urokinase-type but not tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 1;97(11):2440–2451. doi: 10.1172/JCI118691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharski L. R., Brown F. E., Memoli V. A., Kisiel W., Kudryk B. J., Rousseau S. M., Hunt J. A., Dunwiddie C., Nutt E. M. Pathways of coagulation activation in situ in rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 May;63(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(92)90008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]