Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To evaluate the influence of fasting on the antigen specific immune responsiveness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy volunteers. METHODS—Seven rheumatoid arthritis patients and 17 healthy volunteers were immunised perorally or parenterally with influenza virus vaccine after a three to six day long period of total energy deprivation (water fast). The subsequent antigen specific antibody mediated immune response was recorded in the blood at the single cell level by the ELISPOT method. RESULTS—Short term starvation induced an enhanced antigen specific mucosa derived B lymphocyte response in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy volunteers. In contrast, the systemic B cell responses were not significantly altered by a total energy deprivation. CONCLUSIONS—Short term starvation increases the mucosa derived B cell responsiveness, while systemic responsiveness is largely unaffected. The similar pattern of response in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy volunteers indicates that fasting alters the mucosal immune response independently of medical treatment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (130.4 KB).
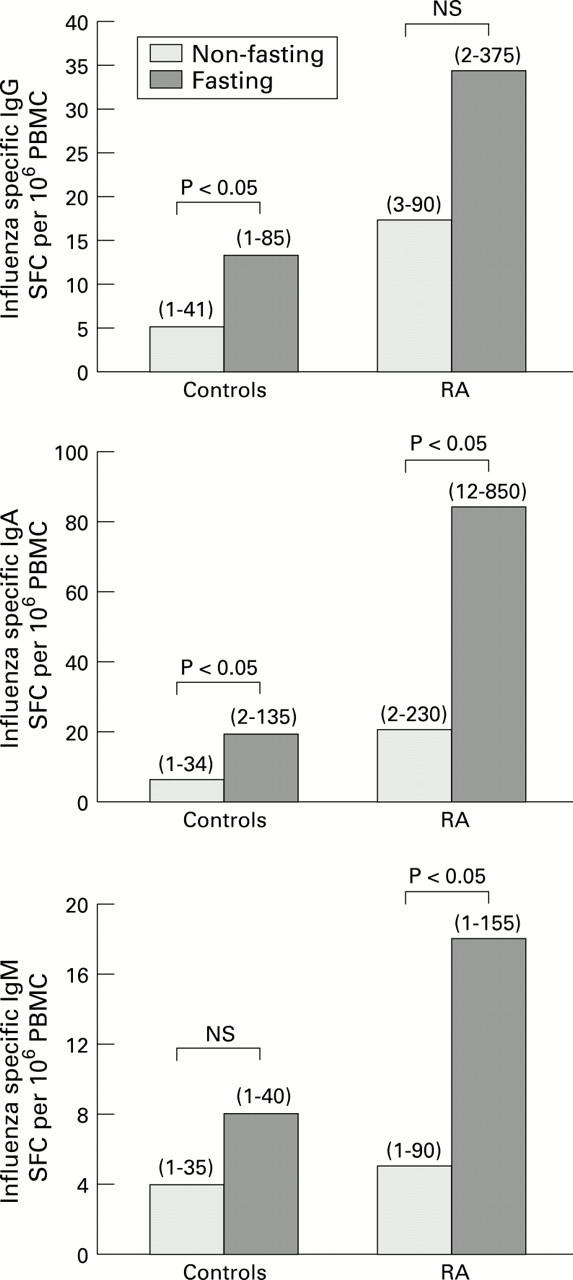
Influenza specific immunoglobulin secreting cells (SFC) of IgG, IgA, and IgM classes in fasting and non-fasting rheumatoid arthritis patients (n = 6) and healthy volunteers (n = 12). The results are presented as geometric means (range).


