Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To determine the relevance of the functional affinity of IgM rheumatoid factor (RF) to the clinical and serological characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. METHODS—The functional affinity of IgM RF of 57 seropositive rheumatoid arthritis patients was evaluated by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay based on the use of a chaotropic agent. The inhibition index was taken as an estimate of functional affinity. The patient group was divided into high functional affinity subgroup 1 (functional affinity < 0.5, n = 37) and low functional affinity subgroup 2 (functional affinity > 0.5, n = 20). The medical records of all patients were reviewed with a particular note of the disease activity and the articular damage score. RESULTS—The disease duration was shorter (P < 0.01) in subgroup 1 patients [7.9 (SD 6.4) years] than in subgroup 2 patients [13.4 (11.29) years], so that Ritchie's, Lee's, and Steinbrocker's indices were lower in the former than in the latter (P < 0.01, 0.001, and 0.01, respectively). In contrast, erythrocyte sedimentation rates, C reactive protein concentrations, antinuclear antibody, and HLA DR4 prevalences were similar in the two subgroups. CONCLUSIONS—Different forms of RF are present during progression of the disease.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (110.3 KB).
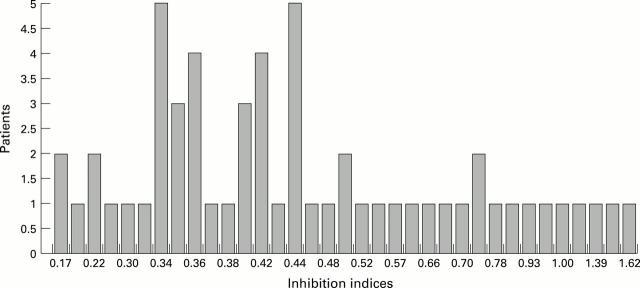
Figure 1 .
Inhibition indices of RF.
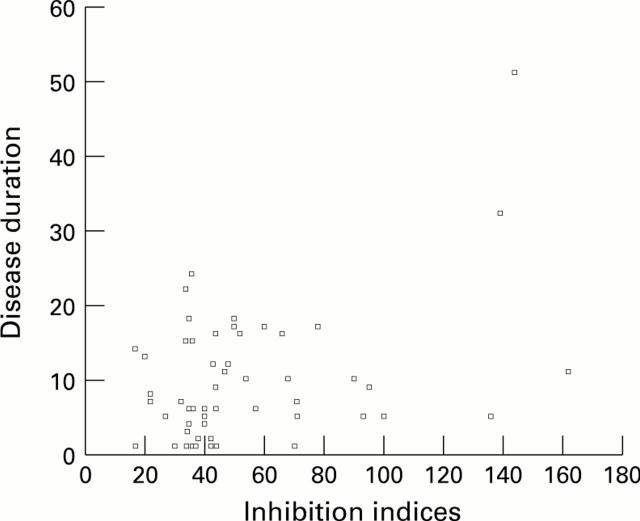
Figure 2 .
Linear correlation of inhibition indices of IgMRF and disease duration.
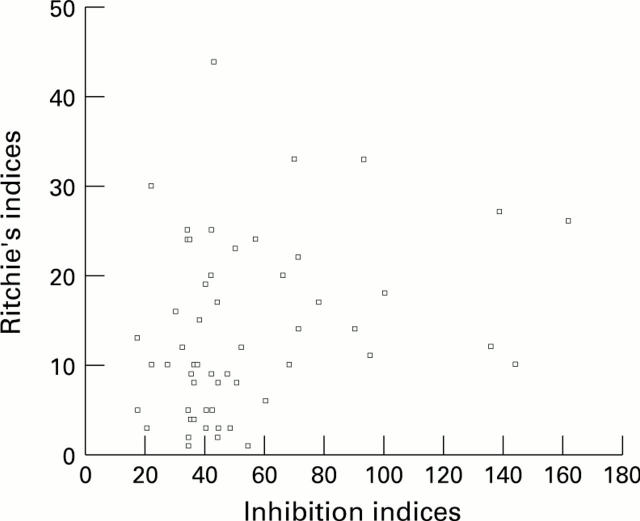
Figure 3 .
Linear correlation of inhibition indices of IgMRF and Ritchie's indices.
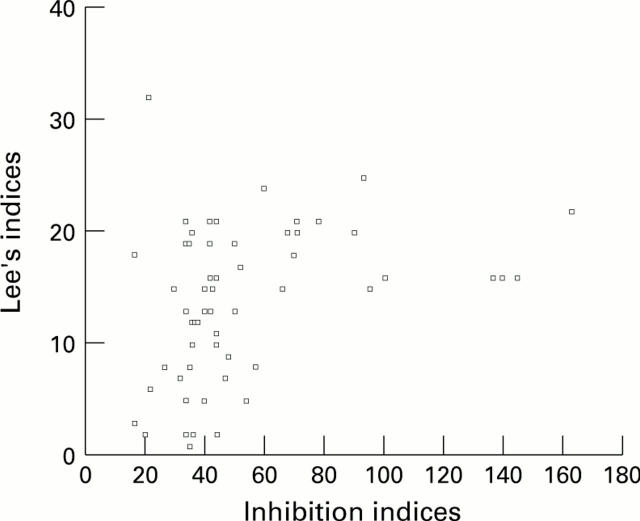
Figure 4 .
Linear correlation of inhibition indices of IgMRF and Lee's indices.
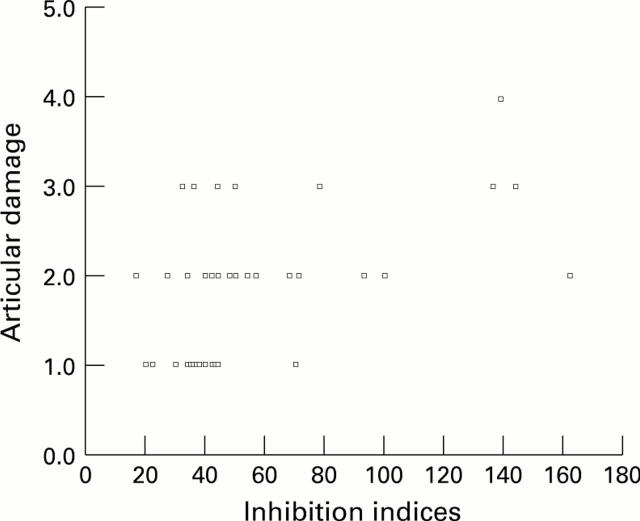
Figure 5 .
Linear correlation of inhibition indices of IgMRF and interphalangeal articular damage (Steinbrocker's indices).