Abstract
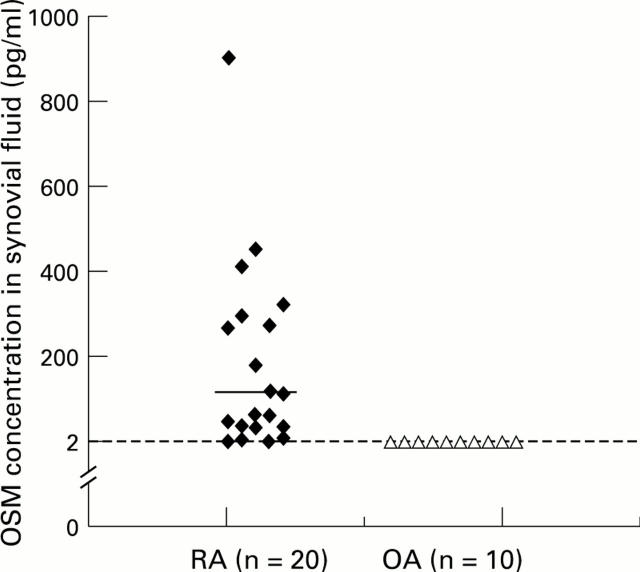
OBJECTIVE—To measure oncostatin M (OSM) in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis (OA). METHODS—20 samples of synovial fluid from patients with RA and 10 samples from patients with OA were examined using an OSM specific sandwich ELISA. RESULTS—OSM was detected at concentrations ranging from 2.36 to 901.82 pg/ml in 18 (90%) of 20 samples of synovial fluid from RA patients. There was no detectable OSM in synovial fluid from OA patients. In the RA patients, the OSM concentration in synovial fluid correlated significantly with the synovial fluid white blood cell count (r=0.67, p<0.01), but not with other laboratory parameters of disease activity. CONCLUSION—These findings suggest that OSM may contribute to joint inflammation in RA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (90.0 KB).
Figure 1 .
Concentration of OSM in RA and OA synovial fluid. OSM concentrations were determined by ELISA as described in Methods. Each point represents a mean result obtained from two independent assay runs. The horizontal bar depicts the median value (p<0.001).
Figure 2 .
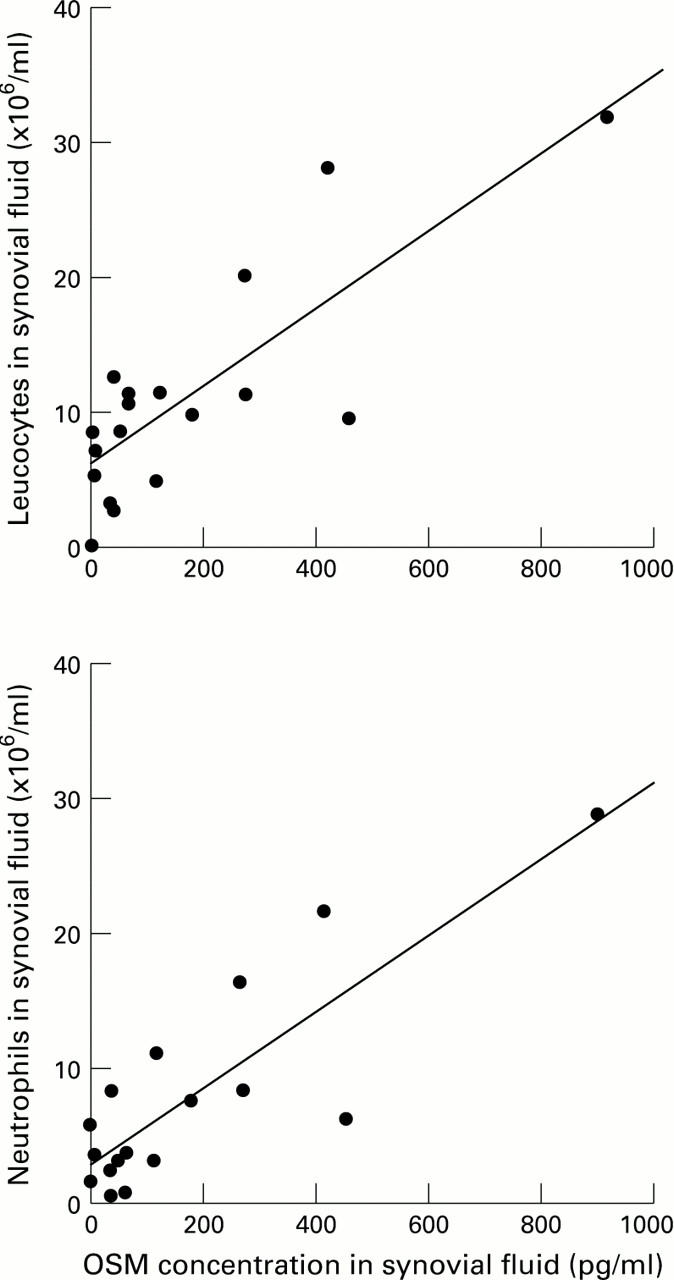
Correlation of OSM concentration with the total white cell count in RA synovial fluid. Synovial fluid OSM concentration and total white cell numbers were determined by ELISA and haemocytometer count respectively as described in Methods.