Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To determine whether antisense oligonucleotides targeting c-fos mRNA have the ability to inhibit the growth of interleukin 1 (IL1) stimulated fibroblast-like cells from the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). METHODS—Fibroblast-like cells established from RA synovium were stimulated by IL1 with antisense or sense oligonucleotides complementary to c-fos mRNA, and the proliferation of these cells was determined by 3H-thymidine incorporation. Effect of antisense oligonucleotides on expression of activator protein 1 (AP1) activity was evaluated using electrophoretic mobility shift assay. RESULTS—C-fos antisense oligonucleotides inhibited IL1 stimulated synovial fibroblast proliferation. The expression of AP1 activity induced by IL1 was suppressed by treatment with antisense oligonucleotides. CONCLUSION—These results suggest the feasibility of antisense strategies designed to suppress c-fos expression as therapeutic agents for RA. Keywords: antisense oligonucleotides; c-fos; activator protein 1; synovial fibroblasts
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (116.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) targeting c-fos mRNA inhibit the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts stimulated by interleukin 1β (IL1β). Synovial fibroblasts were cultured for 72 hours containing serially diluted sense or antisense ODNs with IL1β (1 ng/ml). 3H-thymidine incorporation during the last 12 hour pulse of cultures was determined. Data are expressed as the mean (SEM) cpm in triplicate cultures.
Figure 2 .
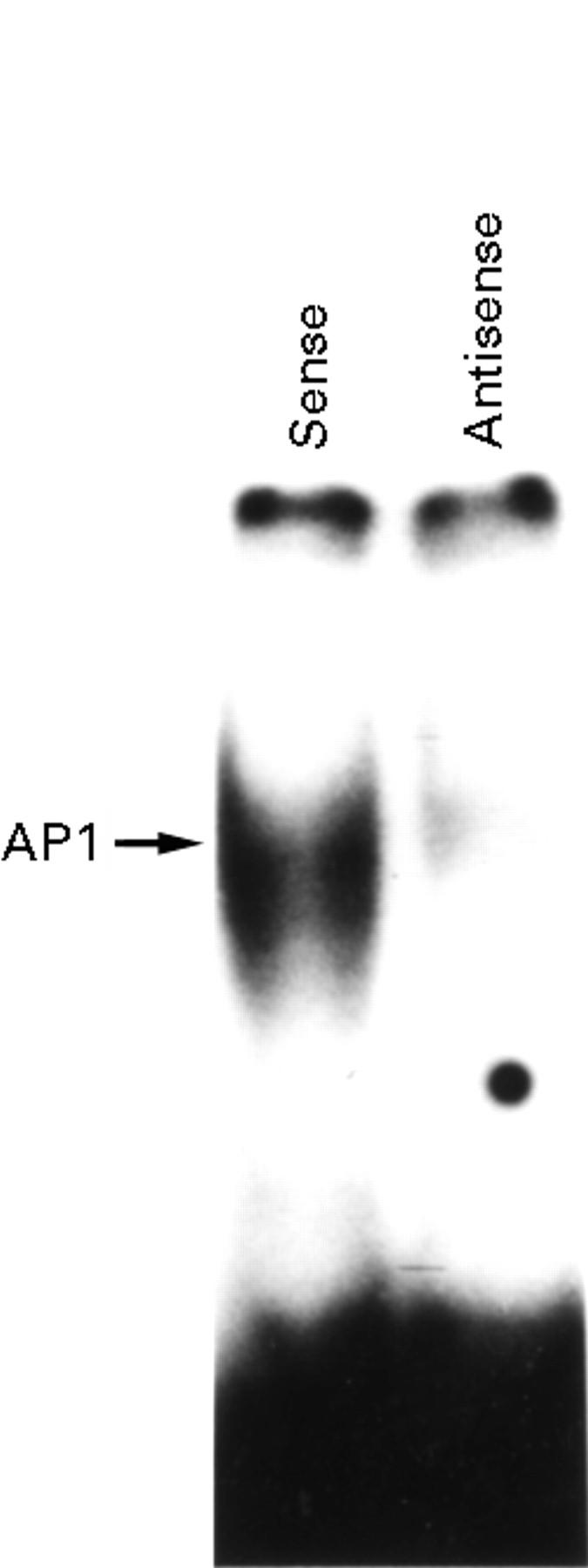
Antisense ODNs targeted to c-fos suppress binding ability of activator protein 1 (AP1). Synovial fibroblasts were cultured for 24 hours treated with IL1β (1 ng/ml) and sense or antisense ODNs (5 µmol/l). AP1 binding ability was examined by electrophoretic mobility shift assay.



