Abstract
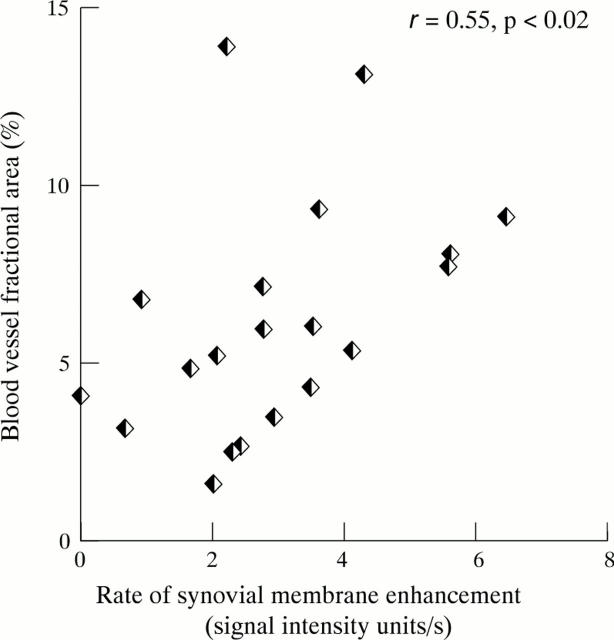
OBJECTIVE—To examine the relation between rate of synovial membrane enhancement, intra-articular pressure (IAP), and histologically determined synovial vascularity in rheumatoid arthritis, using gadolinium-DTPA enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). METHODS—Dynamic gadolinium-DTPA enhanced MRI was performed in 31 patients with knee synovitis (10 patients IAP study, 21 patients vascular morphometry study). Rate of synovial membrane enhancement was quantified by line profile analysis using the image processing package ANALYZE. IAP was measured using an intra-compartmental pressure monitor system. Multiple synovial biopsy specimens were obtained by a blind biopsy technique. Blood vessels were identified immunohistochemically using the endothelial cell marker QBend30 and quantified (blood vessel numerical density and fractional area). RESULTS—Median blood vessel numerical density and fractional area were 77.5/mm2 (IQR; 69.3-110.7) and 5.6% (IQR; 3.4-8.5) respectively. The rate of synovial membrane enhancement (median 2.74 signal intensity units/s, IQR 2.0-3.8) correlated with both blood vessel numerical density (r = 0.46, p < 0.05) and blood vessel fractional area (r = 0.55, p < 0.02). IAP did not influence the rate of enhancement. CONCLUSIONS—Gadolinium-DTPA enhanced MRI may prove to be a valuable technique for evaluating drugs that influence angiogenesis. Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging; rheumatoid arthritis; synovitis; vascularity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (147.9 KB).
Figure 1 .
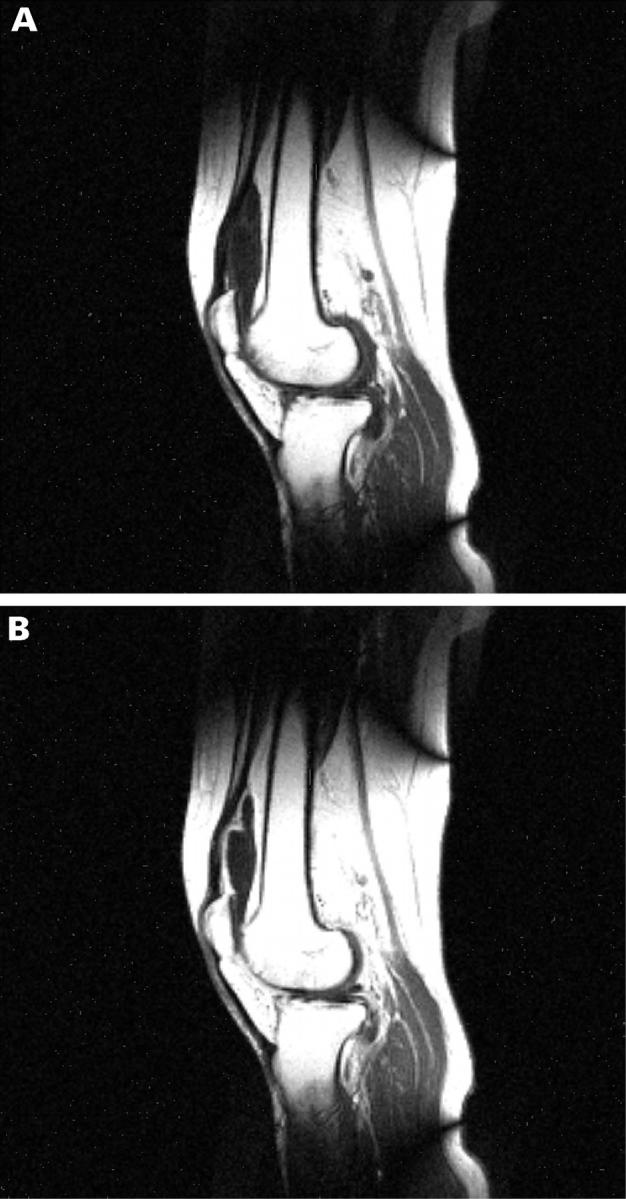
Sagittal section through a rheumatoid knee joint before and after intravenous administration of gadolinium-DTPA.
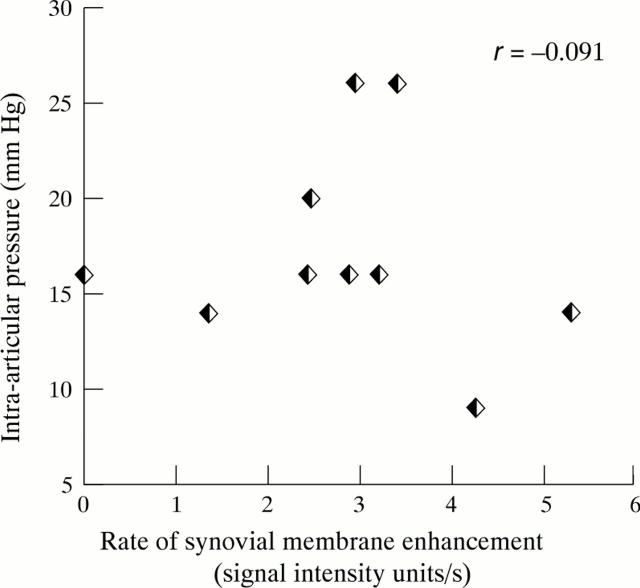
Figure 2 .
Relation between rate of synovial membrane enhancement and resting intra-articular pressure.
Figure 3 .
Relation between rate of synovial membrane enhancement and volume of synovial fluid aspirated.
Figure 4 .
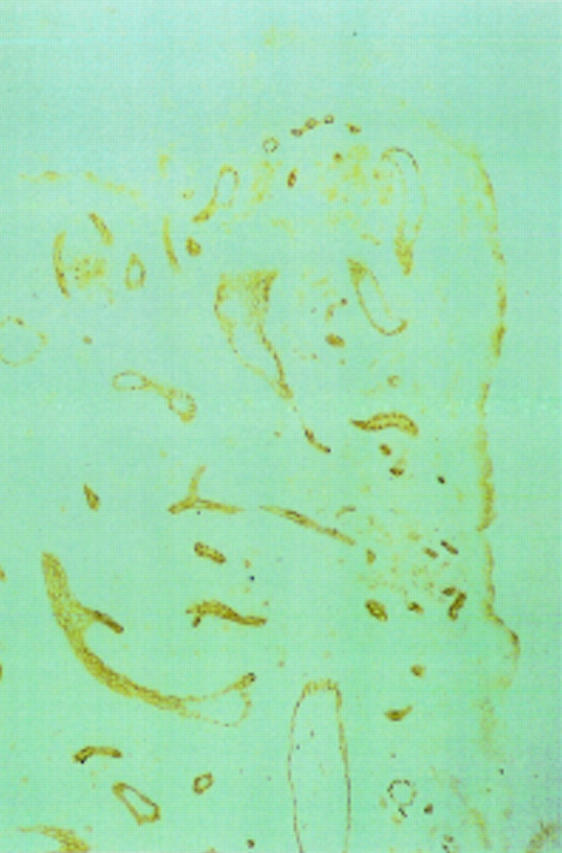
Rheumatoid synovial microvascular endothelium identified immunohistochemically by QBend 30.
Figure 5 .

Relation between rate of synovial membrane enhancement and blood vessel numerical density.
Figure 6 .
Relation between rate of synovial membrane enhancement and blood vessel fractional area.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkengren A. G., Geborek P., Rydholm U., Holtås S., Petterson H. MR imaging of the knee in acute rheumatoid arthritis: synovial uptake of gadolinium-DOTA. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990 Aug;155(2):329–332. doi: 10.2214/ajr.155.2.2115261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake D. R., Merry P., Unsworth J., Kidd B. L., Outhwaite J. M., Ballard R., Morris C. J., Gray L., Lunec J. Hypoxic-reperfusion injury in the inflamed human joint. Lancet. 1989 Feb 11;1(8633):289–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91305-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. J., Cosh J. A. Temperature and biochemical studies of joint inflammation. A preliminary investigation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jul;29(4):386–392. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.4.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colville-Nash P. R., Scott D. L. Angiogenesis and rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jul;51(7):919–925. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.7.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEANDRADE J. R., GRANT C., DIXON A. S. JOINT DISTENSION AND REFLEX MUSCLE INHIBITION IN THE KNEE. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965 Mar;47:313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick C., Whaley K., Saint Onge R. A., Downie W. W., Boyle J. A., Nuki G., Gillespie F. C., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies on inflammation in human knee joints: xenon (133Xe) clearances correlated with clinical assessment in various arthritides and studies on the effect of intra-articularly administered hydrocortisone in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Sci. 1970 Jan;38(1):123–133. doi: 10.1042/cs0380123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick W. C., Onge R. A., Gillepsie F. C., Downie W. W., Nuki G., Gordon I., Whaley K., Boyle J. A., Buchanan W. W. Derivation of knee joint synovial perfusion. Using the Xenon (133Xe) clearance technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Mar;29(2):131–134. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYRING E. J., MURRAY W. R. THE EFFECT OF JOINT POSITION ON THE PRESSURE OF INTRA-ARTICULAR EFFUSION. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964 Sep;46:1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Katsikis P., Brennan F. M., Walker J., Bijl H., Ghrayeb J. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with chimeric monoclonal antibodies to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Dec;36(12):1681–1690. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R. A., Olsen N. J., Spencer-Green G., Yeo K. T., Yeo T. K., Berse B., Jackman R. W., Senger D. R., Dvorak H. F., Brown L. F. Vascular permeability factor/endothelial growth factor (VPF/VEGF): accumulation and expression in human synovial fluids and rheumatoid synovial tissue. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):341–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fina L., Molgaard H. V., Robertson D., Bradley N. J., Monaghan P., Delia D., Sutherland D. R., Baker M. A., Greaves M. F. Expression of the CD34 gene in vascular endothelial cells. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2417–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald O., Soden M., Yanni G., Robinson R., Bresnihan B. Morphometric analysis of blood vessels in synovial membranes obtained from clinically affected and unaffected knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Nov;50(11):792–796. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.11.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Cookson J., Blake D., Coumbe A., Blades S. Quantification of rheumatoid synovitis by magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1610–1617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Williams R. B., Jolliffe V. A., Blake D. R. Intra-articular pressure changes in rheumatoid and normal peripheral joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Aug;54(8):670–673. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.8.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geborek P., Forslind K., Wollheim F. A. Direct assessment of synovial blood flow and its relation to induced hydrostatic pressure changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Apr;48(4):281–286. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Falchuk K. H., Zeiger L. S., Sullivan A. L., Hebert C. L., Adams J. P., Decker J. L. A physiological approach to the assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1167–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI106594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS R., MILLARD J. B., BANERJEE S. K. Radiosodium clearance from the knee joint in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1958 Jun;17(2):189–195. doi: 10.1136/ard.17.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata S., Matsubara T., Saura R., Tateishi H., Hirohata K. Inhibition of in vitro vascular endothelial cell proliferation and in vivo neovascularization by low-dose methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Sep;32(9):1065–1073. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda E., Achen M. G., Breier G., Risau W. Hypoxia-induced transcriptional activation and increased mRNA stability of vascular endothelial growth factor in C6 glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):19761–19766. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.19761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I., Dixon A. S. Intra-articular pressure in rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. 3. Pressure changes during joint use. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jul;29(4):401–408. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayson M. I., St Dixon A. J. Intra-articular pressure in rheumatoid arthritis of the knee. I. Pressure changes during passive joint distension. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 May;29(3):261–265. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevtic V., Rozman B., Watt I., Presetnik M. Use of contrast enhanced MRI in the assessment of therapeutic response to a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. Case study of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis--6- and 24-month follow up. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Oct;34(10):956–959. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.10.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jevtic V., Watt I., Rozman B., Presetnik M., Logar D., Praprotnik S., Tomsic M., Sipek A., Kos-Golja M., Sepe A. Prognostic value of contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA MRI for development of bone erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Dec;35 (Suppl 3):26–30. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_3.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Harlow L. A., Haines G. K., Amento E. P., Unemori E. N., Wong W. L., Pope R. M., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. A cytokine modulating endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 15;152(8):4149–4156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Sieper J., Wolf K. J. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology. 1990 Aug;176(2):473–477. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.2.2367663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick J. R. An investigation into the validity of subatmospheric pressure recordings from synovial fluid and their dependence on joint angle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:55–67. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallya R. K., Mace B. E. The assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis using a multivariate analysis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1981 Feb 1;20(1):14–17. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/20.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara T., Saura R., Hirohata K., Ziff M. Inhibition of human endothelial cell proliferation in vitro and neovascularization in vivo by D-penicillamine. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):158–167. doi: 10.1172/JCI113853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. J., Banquerigo M. L., Brahn E. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis using an angiogenesis inhibitor, AGM-1470, and a microtubule stabilizer, taxol. Cell Immunol. 1994 Aug;157(1):291–299. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. J., Cheng T. P., Banquerigo M. L., Brahn E. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by an angiogenesis inhibitor, AGM-1470, in combination with cyclosporin: reduction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Cell Immunol. 1995 Dec;166(2):196–206. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1995.9978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Stoltenberg M., Henriksen O., Lorenzen I. Quantitative assessment of synovial inflammation by dynamic gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. A study of the effect of intra-articular methylprednisolone on the rate of early synovial enhancement. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jan;35(1):50–59. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.1.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER R. H., PEARSON C. M. A simplified synovial biopsy needle. Arthritis Rheum. 1963 Apr;6:172–176. doi: 10.1002/art.1780060209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleolog E. M. Angiogenesis: a critical process in the pathogenesis of RA--a role for VEGF? Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Oct;35(10):917–919. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock D. J., Banquerigo M. L., Brahn E. Angiogenesis inhibition suppresses collagen arthritis. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1135–1138. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soden M., Rooney M., Cullen A., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Immunohistological features in the synovium obtained from clinically uninvolved knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;28(4):287–292. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Onge R. A., Dick W. C., Bell G., Boyle J. A. Radioactive xenon (133Xe) disappearance rates from the synovial cavity of the human knee joint in normal and arthritic subjects. Ann Rheum Dis. 1968 Mar;27(2):163–166. doi: 10.1136/ard.27.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. R., Blake D. R., Merry P., Revell P. A., Levick J. R. A comparative study by morphometry of the microvasculature in normal and rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Dec;34(12):1508–1513. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamai K., Yamato M., Yamaguchi T., Ohno W. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Aug;37(8):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann H. J., Brasch R. C., Press W. R., Wesbey G. E. Characteristics of gadolinium-DTPA complex: a potential NMR contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Mar;142(3):619–624. doi: 10.2214/ajr.142.3.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]