Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate if serum apolipoprotein A-I and A-II (apoAI and apoAII) concentrations change in subjects with systemic amyloidosis secondary to underlying disorders. METHODS—Serum concentrations of apoAI and apoAII were measured in 21 multiple myeloma patients, including eight with amyloidosis; 95 rheumatoid arthritis patients, including 45 with amyloidosis; and 73 haemodialysis patients, including 32 with amyloidosis. RESULTS—ApoAII values tended to be reduced in subjects with amyloidosis in each group, but could not effectively distinguish amyloidosis. However, apoAII/AI ratios were significantly lower in subjects with amyloidosis in all groups. The ratio of 0.2 had diagnostic sensitivity and specificity for amyloidosis; 50% and 100%, respectively, in multiple myeloma; 80% and 78%, respectively, in rheumatoid arthritis; and 46% and 90%, respectively, in patients requiring long term haemodialysis. CONCLUSION—The apoAII/AI ratio can be a useful biochemical marker of suspect amyloidosis in patients with underlying diseases, especially those with rheumatoid arthritis. Keywords: amyloidosis; apolipoprotein; rheumatoid arthritis; haemodialysis
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (104.4 KB).
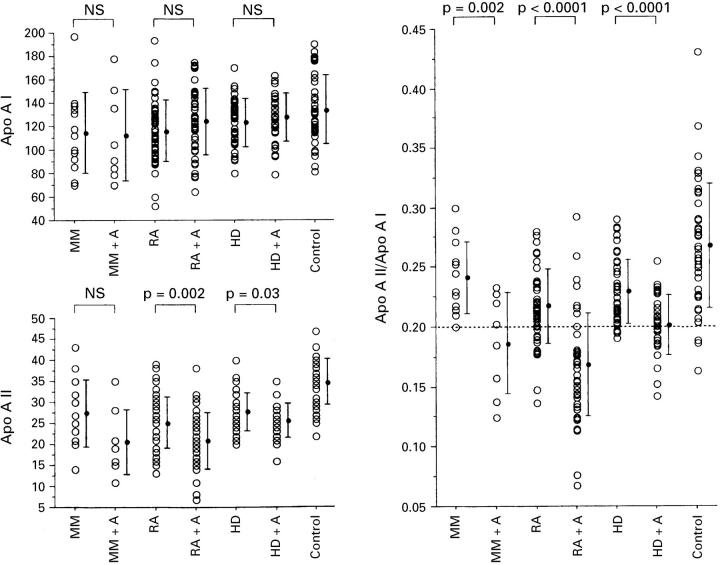
Figure 1 .
Apolipoprotein AI concentrations (ApoAI) (mg/dl), apolipoprotein AII concentrations (ApoAII) (mg/dl), and the apolipoprotein AII/AI ratio (ApoAII/ApoAI) in patients with multiple myeloma (MM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), maintainance haemodialysis (HD), including subjects with amyloidosis (indicated by +A). Bar indicates mean (SD). p Values are also shown also in table 1. NS; not significant.
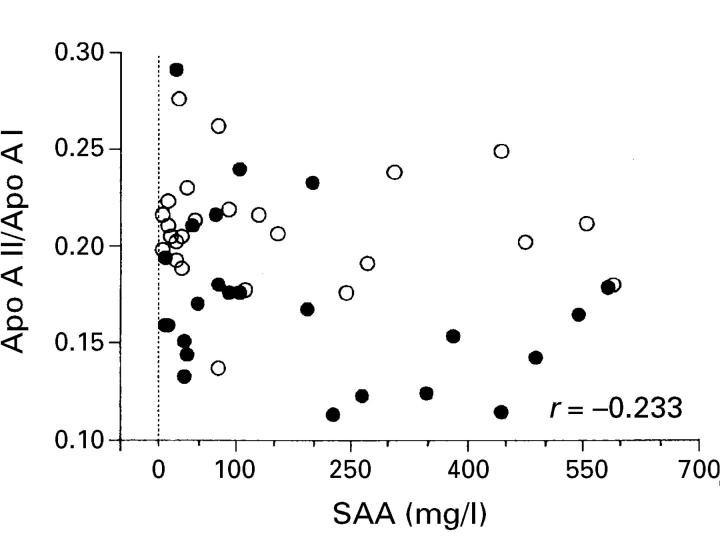
Figure 2 .
Relation between serum amyloid A concentrations (SAA) and the apolipoprotein AII/AI ratio (ApoAII/ApoAI) in 50 rheumatoid arthritis patients with (closed circle, n=25) and without (open circle, n=25) amyloidosis.