Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To develop and assess a simple, inexpensive method for ascertaining the placement of intra-articular injections for knee osteoarthritis METHODS—During a one year period patients with "dry" osteoarthritis of the knee who received intra-articular therapy were tested by air-arthrography. Along with triamcinolone and lignocaine (lidocaine), 5 ml of air was injected into the joint. On subsequent lateral and anterior-posterior radiographs a correct placement was verified by a sharply defined shadow of air in the suprapatellar pouch, while extra-articular air was diffusely spread in the surrounding tissue. RESULTS—In 51 of 56 cases the injection was correctly placed. In the remaining five cases the injection was immediately repeated and positioned within the joint. No adverse events were seen that could be ascribed to the use of air during the study, although bleeding in the quadriceps was seen one week after an extra-articular injection. CONCLUSION—With mini-air arthrography, it is possible to test the placement of intra-articular injections in knee joints. The method is proposed as a learning tool as well as providing a means of quality assurance in studies involving intra-articular injections.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (1.5 MB).
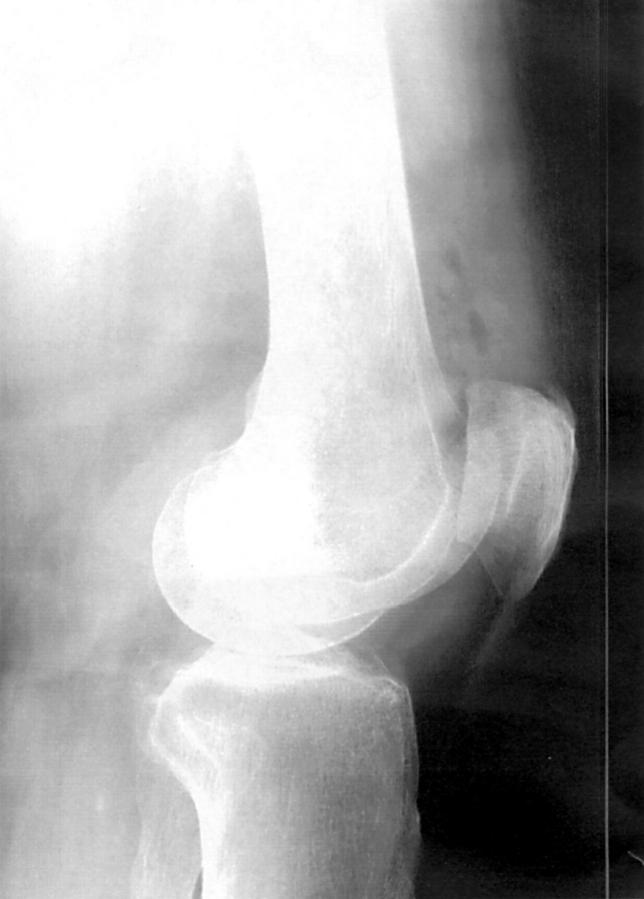
Figure 1 .
Lateral radiograph of an osteoarthritic knee after injection of 5 ml air. Correct placement of the injected substance in the suprapatellar pouch.
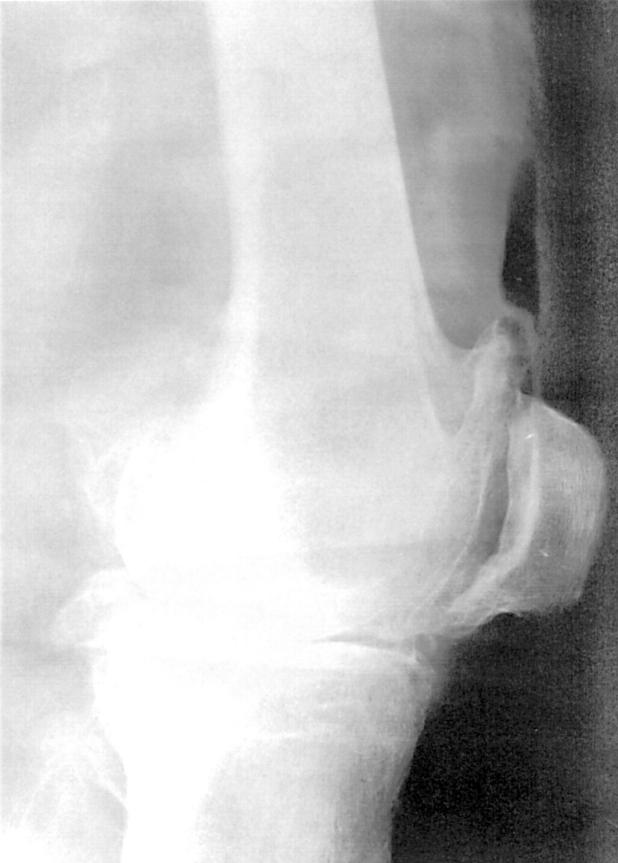
Figure 2 .
Lateral radiograph of an osteoarthritic knee after injection of 5 ml air. The air is distributed in the soft tissues outside the joint.