Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To demonstrate the expression of laminins (Lns) and their integrin (Int) receptors in different synovial samples and synovial membrane-like interface tissues from well fixed and aseptically loosened total hip replacement (THR), and the potential role of Ln-Int interaction in the production of collagenases and cytokines. METHODS—Immunohistochemical staining was done to detect the distribution of EHS Ln, Ln α2, α3, α5, β1, β2 chains and Int α1, α2, α3, α6, β1, β4 subunits in different samples. Double immunofluorescence labelling was used to find colocalisation of Int α6 subunit and collagenase-1/collagenase-3/TNFα/IL6. RESULTS—General Ln immunoreactivity was detected in all specimens. Ln α5, β1 and β2, but not α2 and α3 chains were seen in the synovial lining and the basement membrane of blood vessels with the intensity/extent of labelling in the following rank order: rheumatoid arthritis (RA) loosened prostheses, osteoarthritis, well fixed prostheses, traumatic knees. Among Int subunits, staining for β1 was usually the strongest, followed by staining for Int α6, α1, α3, and α2 subunits, with the same rank order for overall expression of Lns. Int β4 subunit was not detectable in most of the specimens. Double labelling focused on Int α6 subunit disclosed its frequent colocalisation with collagenases 1 and 3 and with tumour necrosis factor α and interleukin 6 in synovial lining. CONCLUSION—Synovial lining contains Ln-10, Ln-11, and Int α6β1 and α1β1 receptors. In aseptic loosening of THR, interface tissue has a similar Ln subtype and Int receptor composition as RA synovium, which confirms its "lining-like" phenotype. Synovial lining does not contain Ln-5 (α3β3γ2) or Int α6β4, which are components of epithelial hemidesmosomes. The expression of Lns and their Int receptors is upregulated in inflammation. The close spatial relation between Ln and its Int receptors in synovial lining cells containing proteinases and cytokines suggests a potential role in joint destruction and prosthetic loosening.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (10.1 MB).
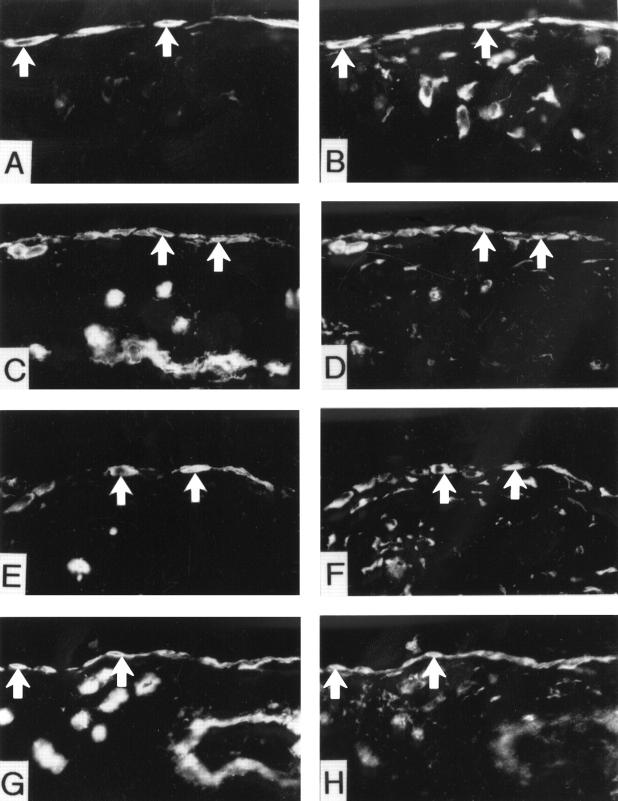
Figure 1 .
EHS Ln immunoreactivity in synovial membrane and interface tissue. The staining was comparatively strong in the lining layers (arrows), sublining area and basement membrane of blood vessels. Weak staining was occasionally found in deep stroma in the pericellular spaces. The staining in RA synovial membrane was usually the strongest (A), followed by interface tissue from aseptic loosening of THR (B), OA synovial membrane (C), the samples from well fixed THR (D) and the synovial samples from traumatic knees (E). For staining control the specific primary rabbit antiserum to human EHS Ln was replaced with rabbit IgG (F).
Figure 2 .
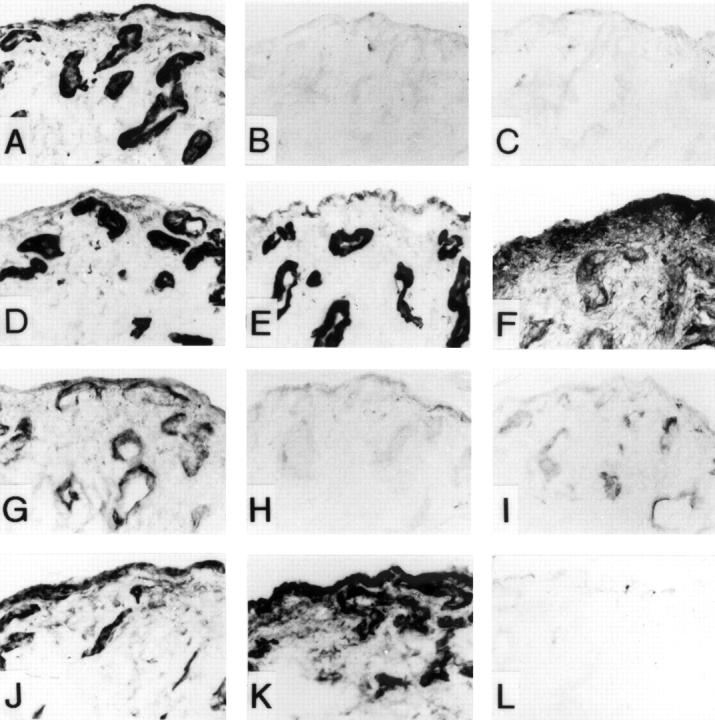
EHS Ln, Ln chains and Int subunits in semi-serial sections of a synovial sample from OA. Panel A: EHS Ln, B: Ln α2 chain, C: Ln α3 chain, D: Ln α5 chain, E: Ln β1 chain, F: Ln β2 chain. Panel G: Int α1 subunit, H: α2 subunit, I: α3 subunit, J: α6 subunit, K: β1 subunit, L: β4 subunit.
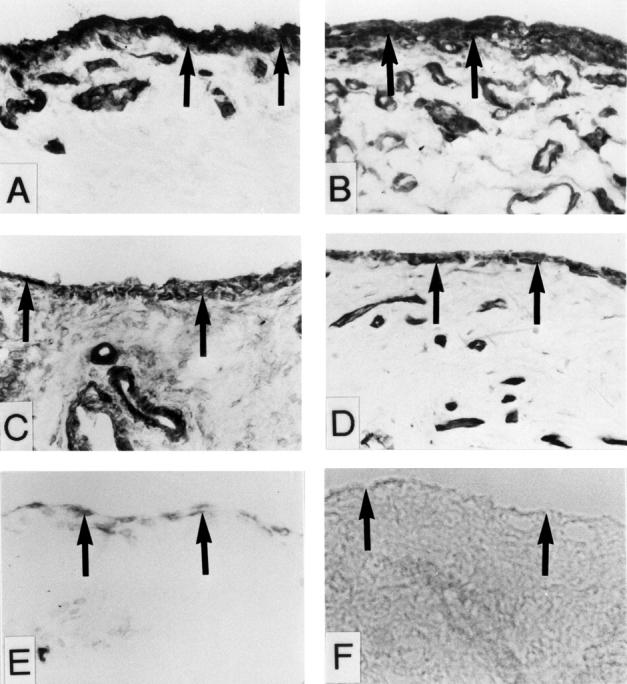
Figure 3 .
Int α6 subunit staining was intense around the cells in the lining layer and in vascular endothelial cells. Occasionally, weak cellular staining was detected in sublining and deep stroma. Staining was the strongest in RA samples (A), followed by interface tissue from aseptic loosening of THR (B), OA synovial membrane (C), interface tissue from well fixed prostheses (D) and synovial membrane from knee injuries (E). For staining control the primary mouse antihuman Int α6 IgG1 was replaced with monoclonal IgG1 with an irrelevant specificity (F).
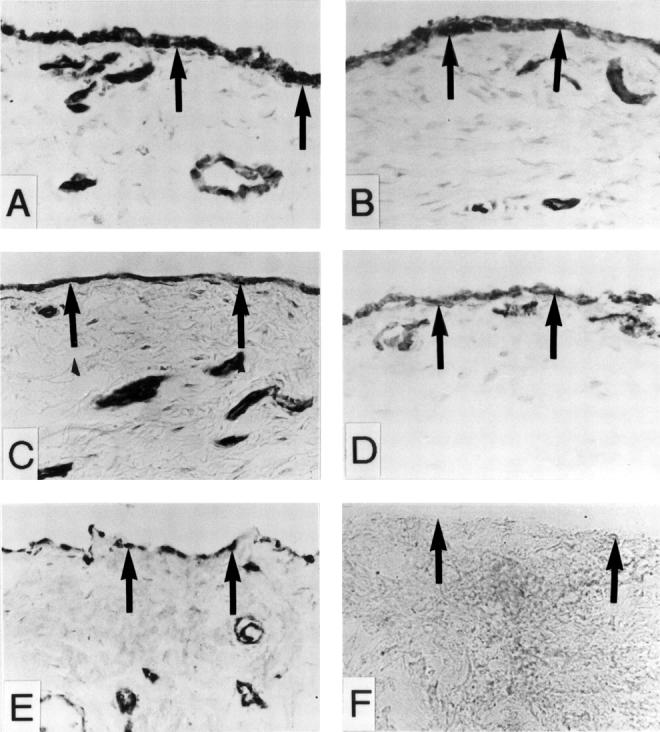
Figure 4 .
Double immunofluorescence labelling for Int α6 subunit and MMP-1, MMP-13, TNF-α or IL6 in OA. Some of the double positive cells have been marked with arrows. Panel A and B: α6 subunit and MMP-1 double labelling, A: α6 positive cells, B: MMP-1 positive cells; Panel C and D: α6 subunit and MMP-13 double labelling, C: α6 positive cells, D: MMP-13 positive cells; Panel E and F: α6 subunit and TNFα double labelling, E: α6 positive cells, F: TNFα positive cells; Panel G and H: α6 subunit and IL6 double labelling, G: α6 positive cells, H: IL6 positive cells.
Figure 5 .
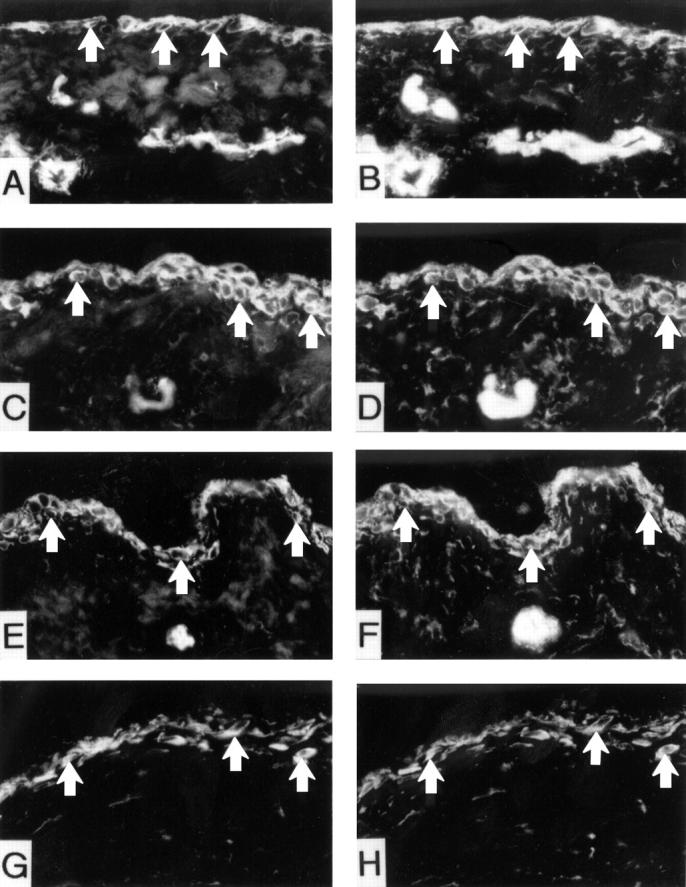
Double immunofluorescence labelling for Int α6 subunit and MMP-1, MMP-13, TNFα or IL6 in synovial membrane-like interface tissues from a patient with aseptic loosening of THR. Panel A and B: α6 subunit and MMP-1 double labelling, A: α6 positive cells, B: MMP-1 positive cells; Panel C and D: α6 subunit and MMP-13 double labelling, C: α6 positive cells, D: MMP-13 positive cells; Panel E and F: α6 subunit and TNFα double labelling, E: α6 positive cells, F: TNFα positive cells; Panel G and H: α6 subunit and IL6 double labelling, G: α6 positive cells, H: IL6 positive cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champliaud M. F., Lunstrum G. P., Rousselle P., Nishiyama T., Keene D. R., Burgeson R. E. Human amnion contains a novel laminin variant, laminin 7, which like laminin 6, covalently associates with laminin 5 to promote stable epithelial-stromal attachment. J Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;132(6):1189–1198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.6.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deleuran B. W., Chu C. Q., Field M., Brennan F. M., Mitchell T., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Localization of tumor necrosis factor receptors in the synovial tissue and cartilage-pannus junction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Implications for local actions of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Oct;35(10):1170–1178. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derevianko A., D'Amico R., Simms H. Polymorphonuclear leucocyte (PMN)-derived inflammatory cytokines--regulation by oxygen tension and extracellular matrix. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Dec;106(3):560–567. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.d01-871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dogic D., Rousselle P., Aumailley M. Cell adhesion to laminin 1 or 5 induces isoform-specific clustering of integrins and other focal adhesion components. J Cell Sci. 1998 Mar;111(Pt 6):793–802. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P. Receptors for laminins during epithelial morphogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;8(5):700–706. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Davis G. E., Dickerson K., Ruoslahti E., Varon S., Manthorpe M. Mapping of domains in human laminin using monoclonal antibodies: localization of the neurite-promoting site. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2457–2465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Wewer U. M. Domains of laminin. J Cell Biochem. 1996 Jun 15;61(4):493–501. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19960616)61:4%3C493::AID-JCB2%3E3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felch M. E., Willis R. A., Penney D. P., Keng P. C., Phipps R. P. Expression of alpha 6 beta 1 integrin, the laminin receptor, on subsets of normal murine lung fibroblasts and its upregulation by the inflammatory cytokines IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha. Reg Immunol. 1992 Nov-Dec;4(6):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fradet Y., Cordon-Cardo C., Thomson T., Daly M. E., Whitmore W. F., Jr, Lloyd K. O., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human bladder cancer defined by mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):224–228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giltay J. C., Brinkman H. J., Modderman P. W., von dem Borne A. E., van Mourik J. A. Human vascular endothelial cells express a membrane protein complex immunochemically indistinguishable from the platelet VLA-2 (glycoprotein Ia-IIa) complex. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Schiller A. L., Roelke M., Rourke C. M., O'Neil D. A., Harris W. H. The synovial-like membrane at the bone-cement interface in loose total hip replacements and its proposed role in bone lysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983 Jun;65(5):575–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Sanchez-Madrid F., Flotte T. J., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Bhan A. K., Springer T. A., Strominger J. L. Glycoproteins of 210,000 and 130,000 m.w. on activated T cells: cell distribution and antigenic relation to components on resting cells and T cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3011–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukkanen M., Corbett S. A., Platts L. A., Konttinen Y. T., Santavirta S., Hughes S. P., Polak J. M. Nitric oxide in the local host reaction to total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998 Jul;(352):53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Murphy M. D., Olsson C. V., Brunken W. J. S-laminin expression in adult and developing retinae: a potential cue for photoreceptor morphogenesis. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):399–413. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90269-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter D. D., Shah V., Merlie J. P., Sanes J. R. A laminin-like adhesive protein concentrated in the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):229–234. doi: 10.1038/338229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai S., Konttinen Y. T., Jumppanen M., Lindy O., Ceponis A., Kemppinen P., Sorsa T., Santavirta S., Xu J. W., Lopéz-Otín C. High levels of expression of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) in pathological conditions associated with a foreign-body reaction. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998 Jul;80(4):701–710. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.80b4.7952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola S., Savunen O., Halme T., Uitto J., Peltonen J. Basement membranes during development of human nerve: Schwann cells and perineurial cells display marked changes in their expression profiles for laminin subunits and beta 1 and beta 4 integrins. J Neurocytol. 1993 Mar;22(3):215–230. doi: 10.1007/BF01246360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan K. M., Falcone D. J. Role of laminin in matrix induction of macrophage urokinase-type plasminogen activator and 92-kDa metalloproteinase expression. J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 28;272(13):8270–8275. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.13.8270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Kurvinen H., Takagi M., Michelsson J. E., Eklund K. K., Nordsletten L., Buø L., Aasen A. O., Santavirta S. Interleukin-1 and collagenases around loosening total hip prostheses. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996 May-Jun;14(3):255–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Waris V., Xu J. W., Jiranek W. A., Sorsa T., Virtanen I., Santavirta S. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 and 2 in the synovial-like interface membrane between implant and bone in loosening of total hip arthroplasty. J Rheumatol. 1997 Apr;24(4):694–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Sigurdson S. L., Sheppard D., Lwebuga-Mukasa J. S. Differential modulation of integrin receptors and extracellular matrix laminin by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in rat alveolar epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1995 Dec;221(2):385–394. doi: 10.1006/excr.1995.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassus J., Salo J., Jiranek W. A., Santavirta S., Nevalainen J., Matucci-Cerinic M., Horák P., Konttinen Y. Macrophage activation results in bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998 Jul;(352):7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivo I., Engvall E. Merosin, a protein specific for basement membranes of Schwann cells, striated muscle, and trophoblast, is expressed late in nerve and muscle development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1544–1548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesi P., Dahl D., Vaheri A. Laminin is produced by early rat astrocytes in primary culture. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):920–924. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindy O., Konttinen Y. T., Sorsa T., Ding Y., Santavirta S., Ceponis A., López-Otín C. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 (collagenase 3) in human rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1391–1399. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M. Laminin receptors: achieving specificity through cooperation. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;5(11):419–423. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Patton B. L., Lentz S. I., Gilbert D. J., Snider W. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Sanes J. R. The laminin alpha chains: expression, developmental transitions, and chromosomal locations of alpha1-5, identification of heterotrimeric laminins 8-11, and cloning of a novel alpha3 isoform. J Cell Biol. 1997 May 5;137(3):685–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.137.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S., Yagita H., Maruyama T., Hashimoto H., Miyasaka N., Okumura K. Beta 1 integrin-mediated interaction with extracellular matrix proteins regulates cytokine gene expression in synovial fluid cells of rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):863–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutabarrik A., Nakanishi I., Zaid D., Namiki M., Kawaguchi N., Onishi S., Ishibashi M., Okuyama A. Interleukin-1-beta activation of cultured glomerular epithelial cells. Exp Nephrol. 1994 May-Jun;2(3):196–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkari L., Aho H., Yli-Jama T., Larjava H., Jalkanen M., Heino J. Expression of integrin family of cell adhesion receptors in rheumatoid synovium. Alpha 6 integrin subunit in normal and hyperplastic synovial lining cell layer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1019–1027. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock L. E., Lalor P., Revell P. A. Type IV collagen and laminin in the synovial intimal layer: an immunohistochemical study. Rheumatol Int. 1990;9(6):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00541324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselle P., Lunstrum G. P., Keene D. R., Burgeson R. E. Kalinin: an epithelium-specific basement membrane adhesion molecule that is a component of anchoring filaments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(3):567–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmivirta K., Sorokin L. M., Ekblom P. Differential expression of laminin alpha chains during murine tooth development. Dev Dyn. 1997 Nov;210(3):206–215. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199711)210:3<206::AID-AJA2>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Engvall E., Butkowski R., Hunter D. D. Molecular heterogeneity of basal laminae: isoforms of laminin and collagen IV at the neuromuscular junction and elsewhere. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1685–1699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santala P., Heino J. Regulation of integrin-type cell adhesion receptors by cytokines. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23505–23509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkissian M., Lafyatis R. Integrin engagement regulates proliferation and collagenase expression of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1999 Feb 1;162(3):1772–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Janssen H., Hogervorst F., Calafat J., Hilgers J. A complex of platelet glycoproteins Ic and IIa identified by a rat monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10376–10383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Linders C. J., Modderman P. W., Damsky C. H., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Integrin recognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1, E3, E8) and evidence that alpha 6 beta 1 but not alpha 6 beta 4 functions as a major receptor for fragment E8. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2145–2155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin L. M., Pausch F., Durbeej M., Ekblom P. Differential expression of five laminin alpha (1-5) chains in developing and adult mouse kidney. Dev Dyn. 1997 Dec;210(4):446–462. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199712)210:4<446::AID-AJA8>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin L. M., Pausch F., Frieser M., Kröger S., Ohage E., Deutzmann R. Developmental regulation of the laminin alpha5 chain suggests a role in epithelial and endothelial cell maturation. Dev Biol. 1997 Sep 15;189(2):285–300. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack S., Gray R. D., Pizzo S. V. Modulation of plasminogen activation and type IV collagenase activity by a synthetic peptide derived from the laminin A chain. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2073–2077. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Santavirta S., Ida H., Ishii M., Akimoto K., Saotome K., Konttinen Y. T. The membrane-type-matrix metalloproteinase/matrix metalloproteinase-2/tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 system in periprosthetic connective-tissue remodeling in loose total-hip prostheses. Lab Invest. 1998 Jun;78(6):735–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiger C. F., Champliaud M. F., Pedrosa-Domellof F., Thornell L. E., Ekblom P., Gullberg D. Presence of laminin alpha5 chain and lack of laminin alpha1 chain during human muscle development and in muscular dystrophies. J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 7;272(45):28590–28595. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.45.28590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Brown J. C. Supramolecular assembly of basement membranes. Bioessays. 1996 Feb;18(2):123–132. doi: 10.1002/bies.950180208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtman H., Futterweit S., Singhal P. Nitric oxide modulates the synthesis of extracellular matrix proteins in cultured rat mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 6;207(1):120–125. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasaturo F., Modesti A., Scarpa S. Interferon gamma modifies fibronectin and laminin synthesis in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 1998 Apr;12(4):895–898. doi: 10.3892/ijo.12.4.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Laitinen A., Tani T., Päkkö P., Laitinen L. A., Burgeson R. E., Lehto V. P. Differential expression of laminins and their integrin receptors in developing and adult human lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1996 Aug;15(2):184–196. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.15.2.8703474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Laitinen L., Korhonen M. Differential expression of laminin polypeptides in developing and adult human kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995 Jun;43(6):621–628. doi: 10.1177/43.6.7769233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Lohi J., Tani T., Korhonen M., Burgeson R. E., Lehto V. P., Leivo I. Distinct changes in the laminin composition of basement membranes in human seminiferous tubules during development and degeneration. Am J Pathol. 1997 Apr;150(4):1421–1431. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Gerecke D. R., Durkin M. E., Kurtz K. S., Mattei M. G., Champliaud M. F., Burgeson R. E., Albrechtsen R. Human beta 2 chain of laminin (formerly S chain): cDNA cloning, chromosomal localization, and expression in carcinomas. Genomics. 1994 Nov 15;24(2):243–252. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wewer U. M., Thornell L. E., Loechel F., Zhang X., Durkin M. E., Amano S., Burgeson R. E., Engvall E., Albrechtsen R., Virtanen I. Extrasynaptic location of laminin beta 2 chain in developing and adult human skeletal muscle. Am J Pathol. 1997 Aug;151(2):621–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J. W., Konttinen Y. T., Lassus J., Natah S., Ceponis A., Solovieva S., Aspenberg P., Santavirta S. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in loosening of total hip replacement (THR). Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996 Nov-Dec;14(6):643–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanni G., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophages and joint erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jan;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ylänne J., Virtanen I. The Mr 140,000 fibronectin receptor complex in normal and virus-transformed human fibroblasts and in fibrosarcoma cells: identical localization and function. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jun 15;43(6):1126–1136. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]