Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To determine the presence of adhesion molecules on monocytes/macrophages (Mϕ) from peripheral blood (PB) and synovial fluid (SF) in patients with osteoarthritis (OA) and inflammatory joint diseases (rheumatoid (RA) and reactive arthritis (ReA)) in order to improve our understanding of the possible mechanisms underlying the inflammatory process. METHODS—Whole blood and SF cells were stained with monoclonal antibodies against CD11a (LFA-1), CD15 s (sialyl-Lewis X), CD44, CD54, VLA-4, and HLA-DR counterstained with anti-CD14 antibodies as a Mϕ marker for dual fluorescence analysis by flowcytometry. RESULTS—On PB-Mϕ, CD15s was markedly increased in both RA as well as ReA compared with OA. Furthermore, in the PB LFA-1, CD44, and HLA-DR showed a higher surface density on Mϕ in ReA than in OA. Comparison between SF and PB showed significantly higher CD44 and CD54 expression on SF-Mϕ. These molecules play an important part in lymphocyte-Mϕ interaction. CONCLUSION—In PB from patients with inflammatory joint diseases, Mϕ are activated, allowing recruitment into the synovial compartment. These disorders, in contrast with OA seem to be "systemic" in nature. Within the SF, different adhesion molecules are expressed on CD14+ Mϕ as compared with PB.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (66.8 KB).
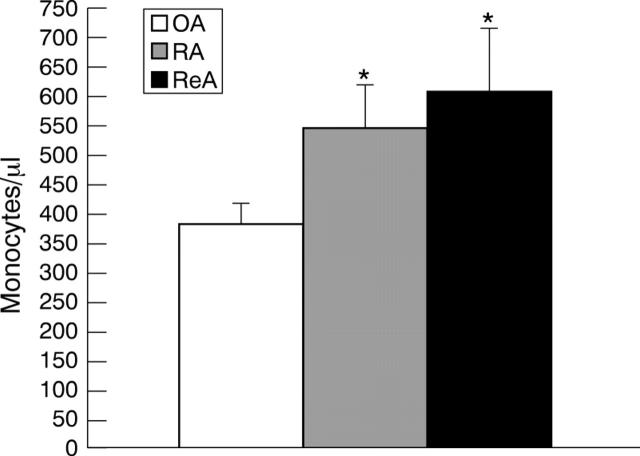
Figure 1 .
Absolute monocyte counts in the peripheral blood of patients with osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid (RA) and reactive arthritis (ReA) are shown. Columns represent mean (SD) values of monocytes/µl.