Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate whether autoreactive mechanisms occur in Lyme disease (LD) by determining IgA, IgG and IgM rheumatoid factor (RF) concentrations and RF associated cross reactive idiotype (CRI) expression in the serum of LD patients, with comparison to patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). METHODS—The RF isotype profiles were determined in 59 patients with LD; erythema migrans (EM) (n=19), neuroborreliosis (NB) (n=20) and Lyme arthritis (LA) (n=20). Mouse monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) G6 and G8 (VH1 gene associated), D12 (VH3 gene associated) and C7 (VκIII gene associated) were then used to determine the RF associated CRI expression on IgM antibodies in 16 of these LD patients (eight seropositive for RF); (EM (n=3), NB (n=6), LA (n=7)). RESULTS—Seven (18%) patients with either NB or LA had increased concentrations of IgA RF compared with none with EM. Significant differences in the number of patients with raised concentrations of IgG RF or IgM RF were not found between the LD patient groups. Five (3NB, 1LA and 1 EM) (31%) and three (2NB and 1LA) (19%) of LD patients had raised concentrations of the CRIs recognised by mAbs G6 and G8, respectively. These CRIs were detected in LD sera both with and without raised concentrations of RF and were not demonstrated on anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies using ELISA. No LD sera tested had raised concentrations of the determinants recognised by mAbs C7 or D12. CONCLUSION—Significantly raised concentrations of IgA RF and increased use of VH1 germline gene associated CRIs are found on IgM antibodies in the serum of LD patients. These data indicate the recruitment of autoreactive B lymphocytes in some patients with the later stages of LD.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.4 KB).
Figure 3 .
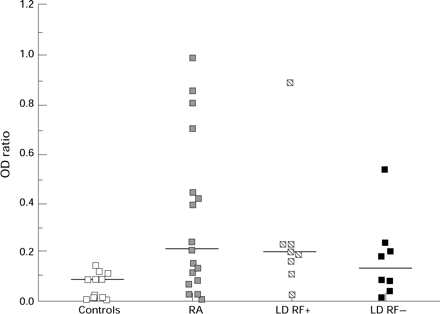
G6 CRI concentrations in controls, patients with RA and patients with LD seropositive (LDRF+) and seronegative (LDRF−) for RF. Bar represents median value.
Figure 4 .
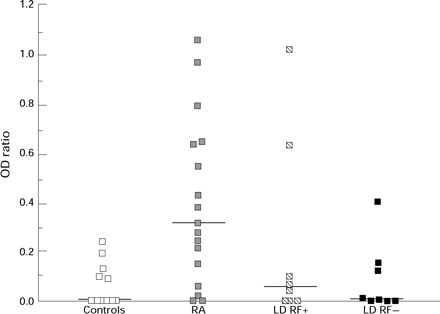
G8 CRI concentrations in controls, patients with RA and patients with LD seropositive (LDRF+) and seronegative (LDRF−) for RF. Bar represents median value.
Figure 1 .
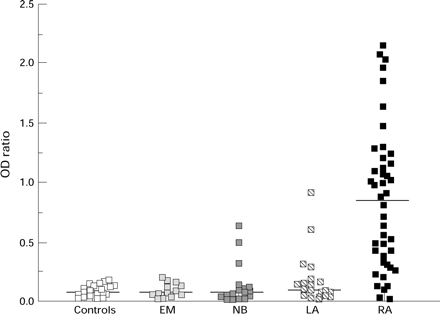
IgA RF concentration in controls and patients with erythema migrans (EM), neuroborreliosis (NB), Lyme arthritis (LA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Bar represents median value.
Figure 2 .

IgM RF concentration in controls and patients with EM, NB, LA and RA. Bar represents median value. Abbreviations as in figure 1.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axford J. S., Watts R. A., Long A. A., Isenberg D. A., Steere A. C. Expression of public idiotypes in patients with Lyme arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Mar;52(3):199–205. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.3.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Whalen J. A., Reinhardt B. N., Steere A. C. Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):392–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel K. M., Krause A., Neurath F. Acquired transient autoimmune reactions in Lyme arthritis: correlation between rheumatoid factor and disease activity. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:314–317. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jónsson T., Thorsteinsson J., Kolbeinsson A., Jónasdóttir E., Sigfússon N., Valdimarsson H. Population study of the importance of rheumatoid factor isotypes in adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jul;51(7):863–868. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.7.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jónsson T., Valdimarsson H. Is measurement of rheumatoid factor isotypes clinically useful? Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Feb;52(2):161–164. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalish R. A., Leong J. M., Steere A. C. Association of treatment-resistant chronic Lyme arthritis with HLA-DR4 and antibody reactivity to OspA and OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2774–2779. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2774-2779.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujala G. A., Steere A. C., Davis J. S., 4th IgM rheumatoid factor in Lyme disease: correlation with disease activity, total serum IgM, and IgM antibody to Borrelia burgdorferi. J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;14(4):772–776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengl-Janssen B., Strauss A. F., Steere A. C., Kamradt T. The T helper cell response in Lyme arthritis: differential recognition of Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A in patients with treatment-resistant or treatment-responsive Lyme arthritis. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2069–2078. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackworth-Young C. G., Harris E. N., Steere A. C., Rizvi F., Malawista S. E., Hughes G. R., Gharavi A. E. Anticardiolipin antibodies in Lyme disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1052–1056. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mageed R. A., Dearlove M., Goodall D. M., Jefferis R. Immunogenic and antigenic epitopes of immunoglobulins. XVII--Monoclonal antibodies reactive with common and restricted idiotopes to the heavy chain of human rheumatoid factors. Rheumatol Int. 1986;6(4):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00541285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mageed R. A., Goodall D. M., Jefferis R. A highly conserved conformational idiotope on human IgM rheumatoid factor paraproteins of the Wa cross-reactive idiotype family defined by a monoclonal antibody. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(2):57–63. doi: 10.1007/BF02274784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mageed R. A., MacKenzie L. E., Stevenson F. K., Yuksel B., Shokri F., Maziak B. R., Jefferis R., Lydyard P. M. Selective expression of a VHIV subfamily of immunoglobulin genes in human CD5+ B lymphocytes from cord blood. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):109–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocton J. J., Dressler F., Rutledge B. J., Rys P. N., Persing D. H., Steere A. C. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in synovial fluid from patients with Lyme arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 27;330(4):229–234. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401273300401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope R. M., McDuffy S. J. IgG rheumatoid factor. Relationship to seropositive rheumatoid arthritis and absence in seronegative disorders. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Sep;22(9):988–998. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Takemori T. Genetics, expression, and function of idiotypes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:569–607. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. H., Axford J. S. Lyme arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Sep;53(9):553–556. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.9.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesier M., Haas G., Wolff-Vorbeck G., Melchers I., Peter H. H. Autoreactive T cells in rheumatic disease (1). Analysis of growth frequencies and autoreactivity of T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Lyme disease. J Autoimmun. 1989 Feb;2(1):31–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokri F., Mageed R. A., Jefferis R. A quantitative ELISA for measurement of rheumatoid factor associated cross-reactive idiotypes in serum from patients with rheumatic diseases. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Oct;32(10):862–869. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.10.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokri F., Mageed R. A., Maziak B. R., Jefferis R. Expression of VHIII-associated cross-reactive idiotype on human B lymphocytes. Association with staphylococcal protein A binding and Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I stimulation. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):936–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal L. H. Cross-reactivity between Borrelia burgdorferi flagellin and a human axonal 64,000 molecular weight protein. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1372–1378. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Dwyer E., Winchester R. Association of chronic Lyme arthritis with HLA-DR4 and HLA-DR2 alleles. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):219–223. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Levin R. E., Molloy P. J., Kalish R. A., Abraham J. H., 3rd, Liu N. Y., Schmid C. H. Treatment of Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jun;37(6):878–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitsson I., Valdimarsson H. Use of monoclonal antibodies and F(ab')2 enzyme conjugates in ELISA for IgM, IgA and IgG rheumatoid factors. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jul 6;71(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. M., Garcia Monco J. C., Benach J. L., Golightly M. G., Habicht G. S., Steere A. C. Nonprotein antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):665–674. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth B. P., Lanchbury J. S., Sakkas L. I., Welsh K. I., Panayi G. S., Bell J. I. HLA-DR4 subtype frequencies in rheumatoid arthritis indicate that DRB1 is the major susceptibility locus within the HLA class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., van der Voort E. A., Breedveld F. C. Clinical significance of rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of a follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1029–1035. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


