Abstract
OBJECTIVES—To determine the validity of the histological-histochemical grading system (HHGS) for osteoarthritic (OA) articular cartilage. METHODS—Human articular cartilage was obtained from macroscopically normal (n = 13) and OA (n = 21) knee joints. Sections of central and peripheral regions of normal samples were produced. Sections of regions containing severe, moderate, and mild OA changes were produced from each OA sample. A total of 89 sections were graded by means of the HHGS (0-14) twice by three observers. RESULTS—Average scores for regions designated severe (8.64) and moderate (5.83) OA were less than the expected (10-14 and 6-9, respectively) according to the HHGS, whereas average scores for the region designated mild (5.29) OA and central and peripheral regions (2.19) of normal cartilage were higher than expected (2-5 and 0-1, respectively). The HHGS was capable of differentiating between articular cartilage from macroscopically normal and OA joints and between the region designated severe OA and other regions. However, the HHGS did not adequately differentiate between regions designated mild and moderate OA. Values for sensitivity, specificity, and efficiency for all regions varied considerably. CONCLUSION—The HHGS is valid for normal and severe OA cartilage, but does not permit distinction between mild and moderate OA changes in articular cartilage. Keywords: histopathology; osteoarthritis; reliability; validity
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (120.9 KB).
Figure 1 .
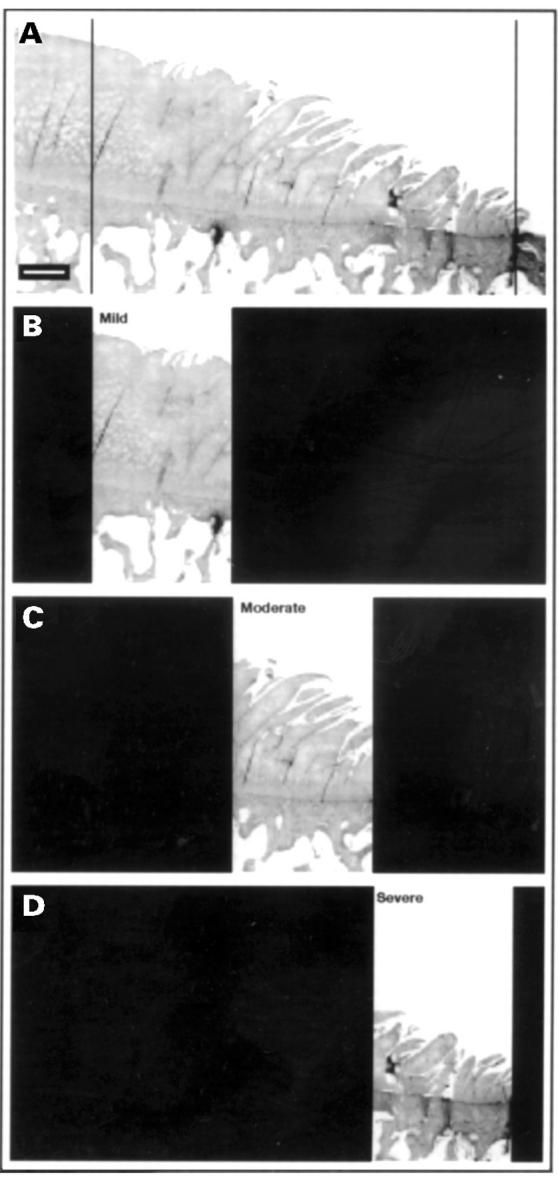
Section of osteoarthritic articular cartilage. OA articular cartilage and adjacent subchondral bone from a 79 years old woman. (A) The section includes a region of denuded bone and a shoulder of residual cartilage ending in a region of articular cartilage that on macroscopic examination appears intact. The shoulder of residual cartilage is divided into regions designated mild (B), moderate (C), and severe (D) OA changes as shown in the figure. Deparaffinised section stained with haematoxylin and eosin (bar marker: 800 µm).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aigner T., Bertling W., Stöss H., Weseloh G., von der Mark K. Independent expression of fibril-forming collagens I, II, and III in chondrocytes of human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):829–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI116303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baici A., Hörler D., Lang A., Merlin C., Kissling R. Cathepsin B in osteoarthritis: zonal variation of enzyme activity in human femoral head cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Apr;54(4):281–288. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.4.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulstra S. K., Buurman W. A., Walenkamp G. H., Van der Linden A. J. Metabolic characteristics of in vitro cultured human chondrocytes in relation to the histopathologic grade of osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989 May;(242):294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS D. H., McELLIGOTT T. F. Sulphate (35SO4) uptake by chondrocytes in relation to histological changes in osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1960 Dec;19:318–330. doi: 10.1136/ard.19.4.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan Y. General principles of grading lesions in diagnostic histopathology. Pathol Res Pract. 1989 Nov;185(5):539–543. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80189-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. D., Martel-Pelletier J., Pelletier J. P., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Evidence for metalloproteinase and metalloproteinase inhibitor imbalance in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):678–685. doi: 10.1172/JCI114215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dew T. L., Martin R. A. Functional, radiographic, and histologic assessment of healing of autogenous osteochondral grafts and full-thickness cartilage defects in the talus of dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1992 Nov;53(11):2141–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M. G., Armstrong A. L., Treadwell B. V., Mankin H. J. Degradative enzyme systems in cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986 Dec;(213):62–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahunia H. K., Lemaire C., Cross A. R., Babyn P., Kessler M. J., Pritzker K. P. Osteoarthritis in rhesus macaques: assessment of cartilage matrix quality by quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Agents Actions Suppl. 1993;39:255–259. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7442-7_31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Holbert C., Read R., Armstrong S. Hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan) in experimental osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995 Feb;43:155–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwasser M., Astley T., van der Rest M., Glorieux F. H. Analysis of the type of collagen present in osteoarthritic human cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Jul;(167):296–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. B., Lee J., Smith R. L., Csongradi J. C., Fornasier V. L. Mechanical overload of a single compartment induces early degenerative changes in the rabbit knee: a preliminary study. J Invest Surg. 1991;4(2):161–170. doi: 10.3109/08941939109140776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander A. P., Pidoux I., Reiner A., Rorabeck C., Bourne R., Poole A. R. Damage to type II collagen in aging and osteoarthritis starts at the articular surface, originates around chondrocytes, and extends into the cartilage with progressive degeneration. J Clin Invest. 1995 Dec;96(6):2859–2869. doi: 10.1172/JCI118357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. K., Moran M. E., Salter R. B. The potential for regeneration of articular cartilage in defects created by chondral shaving and subchondral abrasion. An experimental investigation in rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991 Oct;73(9):1301–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiviranta I., Tammi M., Jurvelin J., Sämänen A. M., Helminen H. J. Fixation, decalcification, and tissue processing effects on articular cartilage proteoglycans. Histochemistry. 1984;80(6):569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapadula G., Iannone F., Zuccaro C., Grattagliano V., Covelli M., Patella V., Lo Bianco G., Pipitone V. Integrin expression on chondrocytes: correlations with the degree of cartilage damage in human osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997 May-Jun;15(3):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippiello L., Hall D., Mankin H. J. Collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):593–600. doi: 10.1172/JCI108676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovász G., Llinás A., Benya P., Bodey B., McKellop H. A., Luck J. V., Jr, Sarmiento A. Effects of valgus tibial angulation on cartilage degeneration in the rabbit knee. J Orthop Res. 1995 Nov;13(6):846–853. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100130607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicourt D. H., Druetz-Van Egeren A., Haazen L., Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C. Effects of tenoxicam and aspirin on the metabolism of proteoglycans and hyaluronan in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1113–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17111.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Dorfman H., Lippiello L., Zarins A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Apr;53(3):523–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Johnson M. E., Lippiello L. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteoarthritic human hips. III. Distribution and metabolism of amino sugar-containing macromolecules. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Jan;63(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeag D., Smith B. W., Edminster R., Laird T., Clark J., Herron S. Estimating the severity of osteoarthritis with magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;21(4):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(92)90053-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Németh-Csóka M., Mészáros T. Minor collagens in arthrotic human cartilage. Change in content of 1 alpha, 2 alpha, 3 alpha and M-collagen with age and in osteoarthrosis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1983 Aug;54(4):613–619. doi: 10.3109/17453678308992898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Whiteside L. A., Andersen D. A. The intra-articular effect of various postoperative managements following knee ligament repair: an experimental study in dogs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980 Jul-Aug;(150):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Shinmei M., Tanaka O., Naka K., Kimura A., Nakanishi I., Bayliss M. T., Iwata K., Nagase H. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) in osteoarthritic cartilage and synovium. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):680–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard K., Petersen J., Andersen C. B., Bendtzen K., Salter D. M. Histologic/histochemical grading system for osteoarthritic articular cartilage: reproducibility and validity. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Oct;40(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Cloutier J. M., Woessner J. F., Jr Proteoglycan-degrading acid metalloprotease activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage, and the effect of intraarticular steroid injections. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 May;30(5):541–548. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J., Howell D. S., Ghandur-Mnaymneh L., Enis J. E., Woessner J. F., Jr Collagenase and collagenolytic activity in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Jan;26(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J. P., Martel-Pelletier J. Protective effects of corticosteroids on cartilage lesions and osteophyte formation in the Pond-Nuki dog model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;32(2):181–193. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizkalla G., Reiner A., Bogoch E., Poole A. R. Studies of the articular cartilage proteoglycan aggrecan in health and osteoarthritis. Evidence for molecular heterogeneity and extensive molecular changes in disease. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2268–2277. doi: 10.1172/JCI116113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu J., Treadwell B. V., Mankin H. J. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jan;27(1):49–57. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Tsuji H., Matsui H., Katoh Y., Sano A. Morphometric analysis of subchondral bone of the tibial condyle in osteoarthrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993 Aug;(293):229–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshima R., Treadwell B. V., Trahan C. A., Mankin H. J. Comparative rates of proteoglycan synthesis and size of proteoglycans in normal and osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1225–1230. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle C. A., Hung H. H., Bonassar L. J., Treadwell B. V., Mangham D. C. Detection of interleukin-1 in the cartilage of patients with osteoarthritis: a possible autocrine/paracrine role in pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997 Sep;5(5):293–300. doi: 10.1016/s1063-4584(97)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluijs J. A., Geesink R. G., van der Linden A. J., Bulstra S. K., Kuyer R., Drukker J. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992 Jan;10(1):58–61. doi: 10.1002/jor.1100100107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


