Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (7.0 MB).
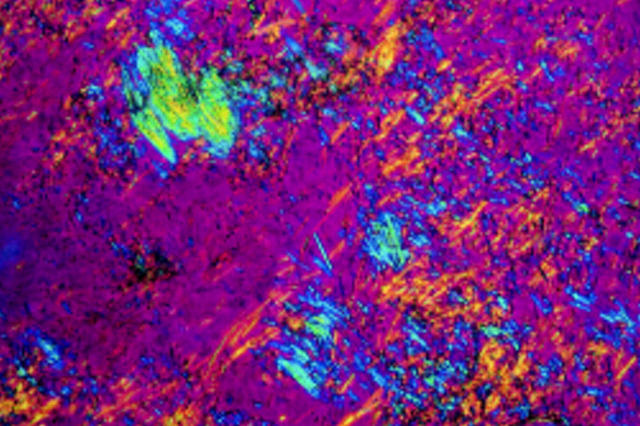
Figure 1 .
Monosodium urate monohydrate crystals from a gouty tophus viewed under polarised light. Note the strong birifringence, needle shaped morphology and "flaring" that help distinguish them from other crystals.
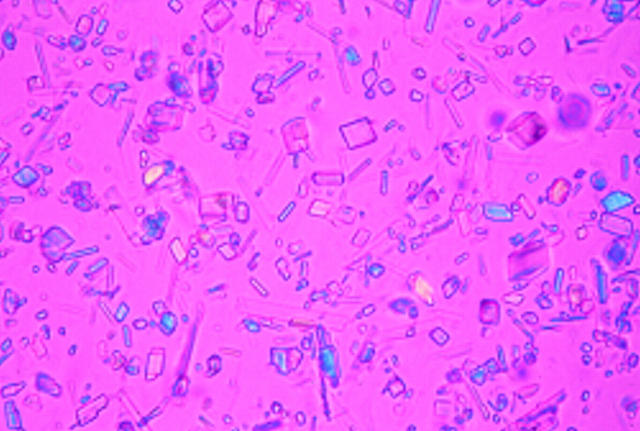
Figure 2 .
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals extracted from the synovial fluid of a patient with pseudogout viewed under polarised light microscopy. Note the variation in size and morphology of the crystals, and the fact that some of the particles do not appear to exhibit birifringence.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bjelle A., Crocker P., Willoughby D. Ultra-microcrystals in pyrophosphate arthropathy. Crystal identification and case report. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(1-2):89–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg J. M., Schumacher H. R., Davidson P. K., Kaufmann L. Usefulness of synovial fluid analysis in the evaluation of joint effusions. Use of threshold analysis and likelihood ratios to assess a diagnostic test. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Apr;144(4):715–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., Swan A., Dieppe P. Detection of crystals in synovial fluids by light microscopy: sensitivity and reliability. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Sep;48(9):737–742. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.9.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher P. Variation in synovial fluid analysis by hospital laboratories. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jun;30(6):637–642. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig S., Gorevic P., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Crystal deposition disease. Diagnosis by electron microscopy. Am J Med. 1977 Jul;63(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill N. W., York H. F. Reproducibility of synovial fluid examination for crystals. Aust N Z J Med. 1991 Oct;21(5):710–713. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1991.tb01374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill N., Dieppe P. A., Bowden M., Gardiner D. J., Hall M. Identification of pathological mineral deposits by Raman microscopy. Lancet. 1991 Jan 12;337(8733):77–78. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90738-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe K., Pattrick M., Doherty M. Complications resulting from misdiagnosing pseudogout as sepsis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 16;293(6544):440–441. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6544.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Broderick T. W. Bony proliferation of terminal toe phalanges in psoriasis: the "ivory" phalanx. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1977 Sep;28(3):187–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Jr, Sieck M. S., Rothfuss S., Clayburne G. M., Baumgarten D. F., Mochan B. S., Kant J. A. Reproducibility of synovial fluid analyses. A study among four laboratories. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Jun;29(6):770–774. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan A., Chapman B., Heap P., Seward H., Dieppe P. Submicroscopic crystals in osteoarthritic synovial fluids. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Jul;53(7):467–470. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.7.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]