Abstract
OBJECTIVES—To compare the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthropathy (SpA), and osteoarthritis (OA) after exclusion of possible biases induced by disease duration or activity, or both. METHODS—Synovial biopsy specimens were obtained by needle arthroscopy in patients with early RA (n=16), late RA (n=14), early SpA (n=23), and OA (n=12). Macroscopic and microscopic features were scored on a four point scale and analysed as a function of disease duration (early versus late RA), local and systemic disease activity, and diagnosis. RESULTS—Except for the maximal synovial lining thickness, no significant differences were seen between early and late RA. For disease activity, synovial histology was only weakly correlated with C reactive protein in RA, but seemed to be strongly dependent on effusion of the biopsied joint in all disease groups. After stratification for local disease activity, no disease related differences were found in patients without joint effusion. In contrast, important differences were found between patients with RA and SpA with active joint effusion. Synovial vascularity was macroscopically increased in SpA versus RA (p=0.017). A straight vessel pattern was only seen in RA, while tortuous vessels were preferentially seen in SpA. Vascularity was also microscopically increased in SpA compared with RA (p=0.031), and correlated with the macroscopic vascularity (rs=0.36, p=0.036). CD3+ (p=0.008), CD4+ (p=0.008), and CD20+ (p=0.024) lymphocytes were overrepresented in RA compared with SpA. The integrin expression in RA was characterised by a decrease of αVβ3 in the synovial lining (p=0.006) and an increase of αVβ5 in the sublining (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS—The immune architecture of the synovial membrane is more dependent on local disease activity than on disease duration. Synovium obtained from clinically affected joints shows important histological differences between RA and SpA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (267.3 KB).
Figure 1 .
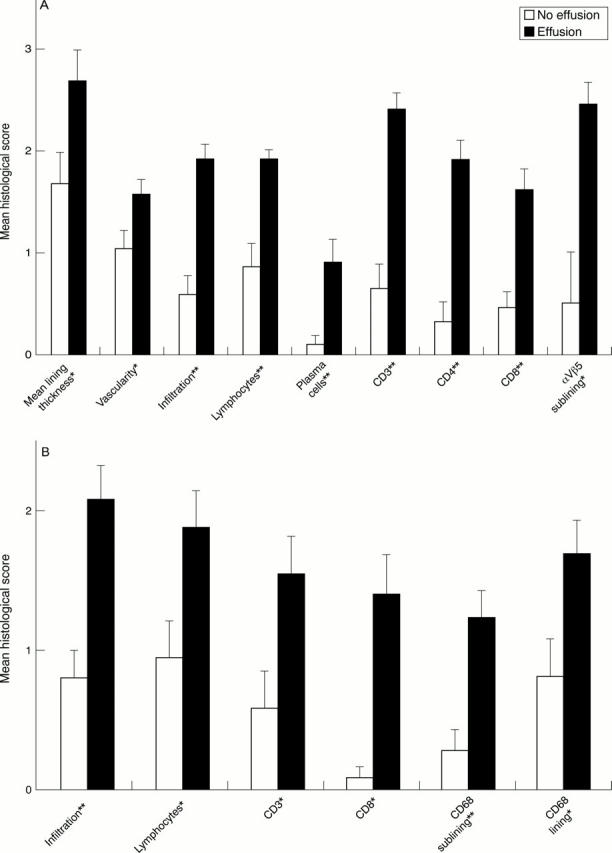
Comparison of the histological scores in patients with and without effusion of the biopsied joint. Mean (standard error of the mean). *p<0.05. **p<0.01. (A) Patients with rheumatoid arthritis with (n=18) and without joint effusion (n=12). (B) Patients with spondyloarthropathy with (n=13) and without joint effusion (n=10).
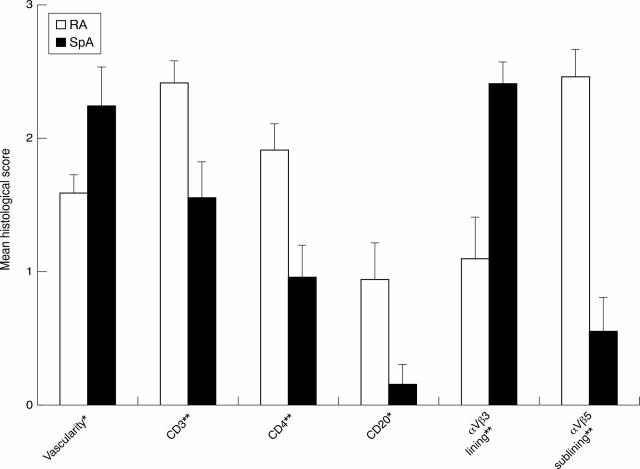
Figure 2 .
Comparison of the histological scores in 18 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 13 patients with spondyloarthropathy (SpA) with effusion of the biopsied joint. Mean (standard error of the mean). *p<0.05. **p<0.01.
Figure 3 .
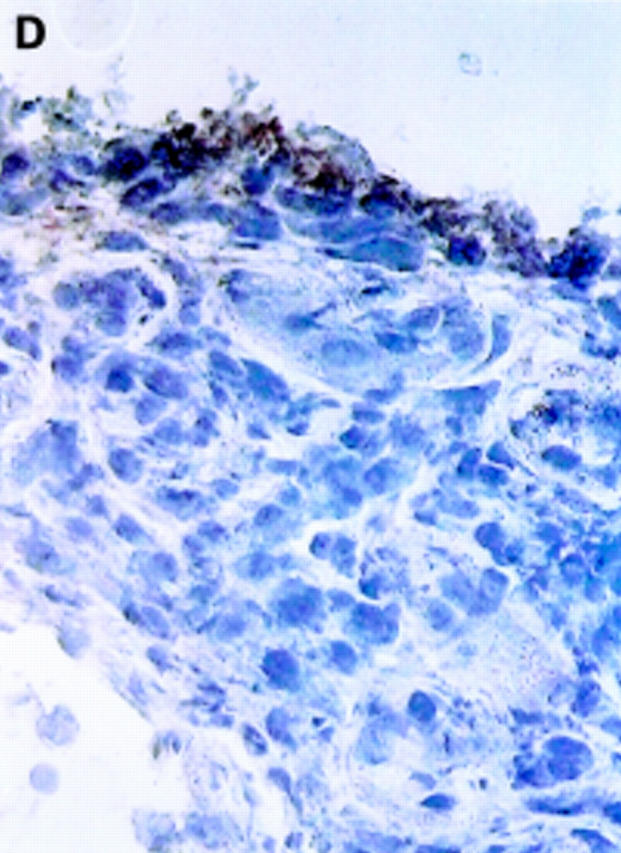
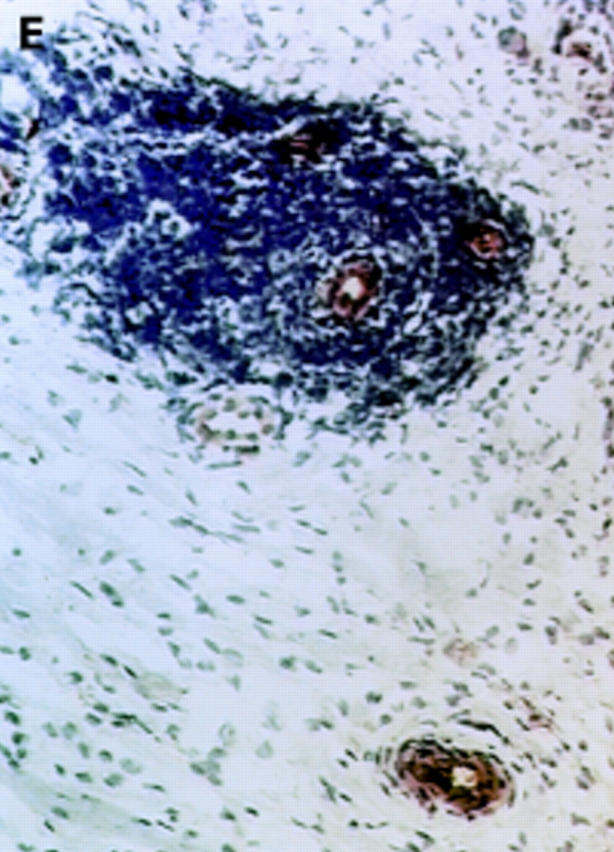
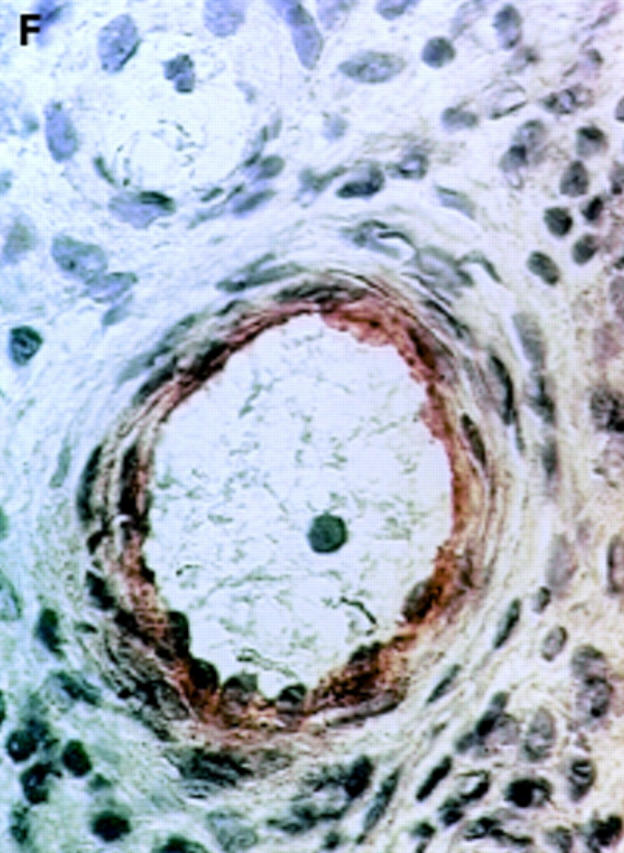
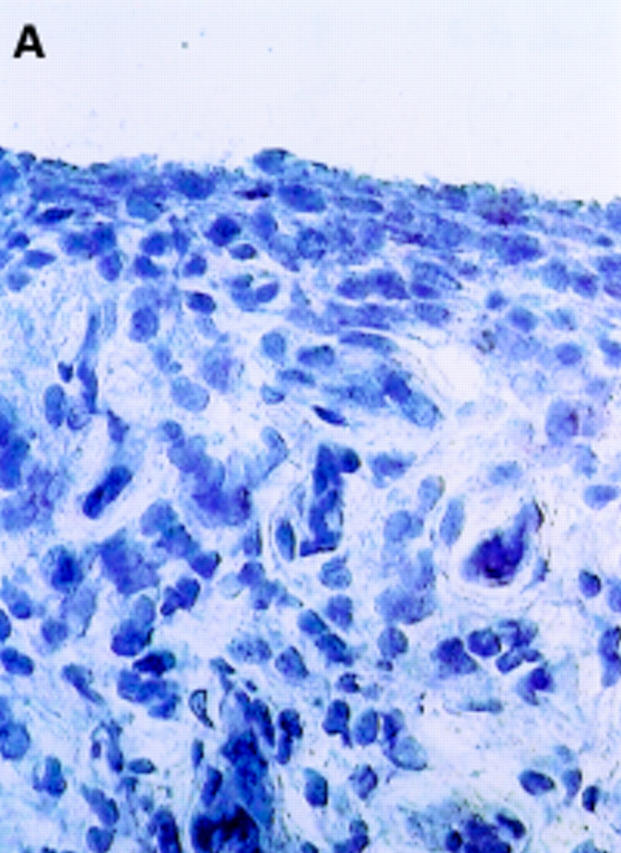
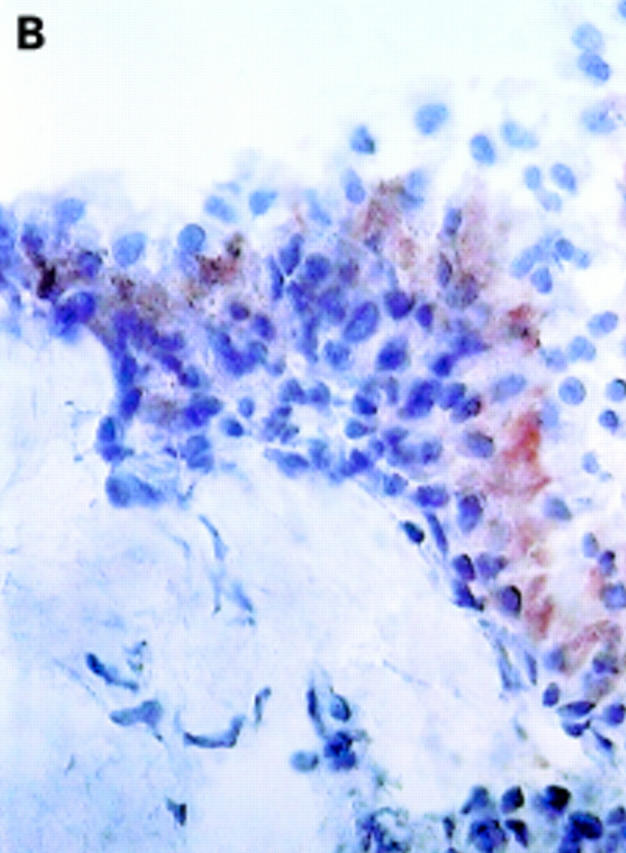
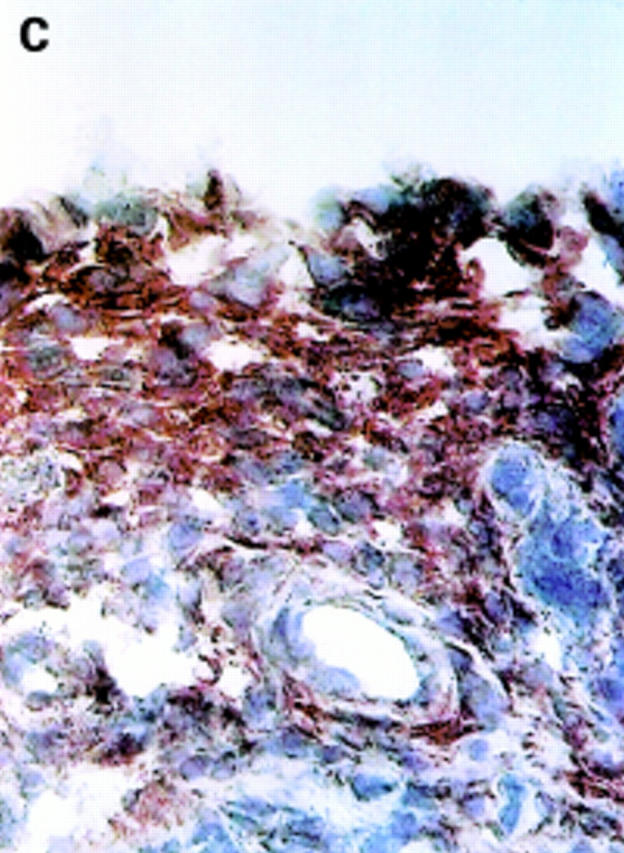
αV integrin expression in the synovial membrane. Frozen sections of synovial biopsy specimens from RA (A and C) and SpA (B and D) were stained immunohistochemically for αVβ3 (A and B) and αVβ5 (C and D). (A) αVβ3 expression in RA synovium: no staining of synovial lining cells. (B) αVβ3 expression in SpA synovium: staining of synovial lining cells. (C) αVβ5 expression in RA synovium: staining of superficial synovial lining cells and of sublining cells. (D) αVβ5 expression in SpA synovium: staining of superficial synovial lining cells, but not of sublining cells. (E) αVβ3 expression on endothelial cells in RA synovium. (F) αVβ3 expression on endothelial cells in SpA synovium.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten D., Van den Bosch F., Elewaut D., Stuer A., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Needle arthroscopy of the knee with synovial biopsy sampling: technical experience in 150 patients. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18(6):434–441. doi: 10.1007/s100670050134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Cunnane G., Youssef P., Yanni G., Fitzgerald O., Mulherin D. Microscopic measurement of synovial membrane inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: proposals for the evaluation of tissue samples by quantitative analysis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Jun;37(6):636–642. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.6.636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucht A., Oksenberg J. R., Lindblad S., Grönberg A., Steinman L., Klareskog L. Characterization of T-cell receptor alpha beta repertoire in synovial tissue from different temporal phases of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Feb;35(2):159–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb02846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceponis A., Konttinen Y. T., MacKevicius Z., Solovieva S. A., Hukkanen M., Tamulaitiene M., Matulis A., Santavirta S. Aberrant vascularity and von Willebrand factor distribution in inflamed synovial membrane. J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;23(11):1880–1886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnane G., Bresnihan B., FitzGerald O. Immunohistologic analysis of peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):180–182. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<180::AID-ART24>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolhain R. J., ter Haar N. T., Hoefakker S., Tak P. P., de Ley M., Claassen E., Breedveld F. C., Miltenburg A. M. Increased expression of interferon (IFN)-gamma together with IFN-gamma receptor in the rheumatoid synovial membrane compared with synovium of patients with osteoarthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jan;35(1):24–32. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elewaut D., De Keyser F., Van den Bosch F., Verbruggen G., Veys E. M. Broadening of the T cell receptor spectrum among rheumatoid arthritis synovial cell-lines in relation to disease duration. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Mar-Apr;18(2):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Echeverri F., Yeo M., Zvaifler N. J., Green D. R. Somatic mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 30;94(20):10895–10900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Yeo M., Zvaifler N. J. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1631–1638. doi: 10.1172/JCI118202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Zvaifler N. J. How important are T cells in chronic rheumatoid synovitis? Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Jun;33(6):768–773. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald O., Soden M., Yanni G., Robinson R., Bresnihan B. Morphometric analysis of blood vessels in synovial membranes obtained from clinically affected and unaffected knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Nov;50(11):792–796. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.11.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraoui B., Pelletier J. P., Cloutier J. M., Faure M. P., Martel-Pelletier J. Synovial membrane histology and immunopathology in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. In vivo effects of antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Feb;34(2):153–163. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton M. A., Taylor M. L., Arnett T. R., Helfrich M. H. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides and the anti-vitronectin receptor antibody 23C6 inhibit dentine resorption and cell spreading by osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):368–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. A., Haines G. K., Harlow L. A., Koch A. E. Adhesion molecule expression in human synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Feb;36(2):137–146. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. A., Haines G. K., Harlow L. A., Koch A. E. Adhesion molecule expression in human synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Feb;36(2):137–146. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd B. L., Moore K., Walters M. T., Smith J. L., Cawley M. I. Immunohistological features of synovitis in ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Feb;48(2):92–98. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E. Review: angiogenesis: implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jun;41(6):951–962. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199806)41:6<951::AID-ART2>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Versendaal H., Jonker M., Bresnihan B., Post W. J., t Hart B. A., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Asymptomatic synovitis precedes clinically manifest arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;41(8):1481–1488. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1481::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor P. A., Mapp P. I., Hall P. A., Revell P. A. Proliferative activity of cells in the synovium as demonstrated by a monoclonal antibody, Ki67. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7(5):183–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00541375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad S., Hedfors E. Intraarticular variation in synovitis. Local macroscopic and microscopic signs of inflammatory activity are significantly correlated. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Sep;28(9):977–986. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherin D., Fitzgerald O., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jan;39(1):115–124. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkari L., Haapasalmi K., Aho H., Torvinen A., Sheppard D., Larjava H., Heino J. Localization of the alpha v subfamily of integrins and their putative ligands in synovial lining cell layer. J Rheumatol. 1995 Jan;22(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleolog E. M. Angiogenesis: a critical process in the pathogenesis of RA--a role for VEGF? Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Oct;35(10):917–919. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potocnik A. J., Kinne R., Menninger H., Zacher J., Emmrich F., Kroczek R. A. Expression of activation antigens on T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Feb;31(2):213–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z., Garcia C. H., O'Rourke L. M., Planck S. R., Kohli M., Rosenbaum J. T. Local proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes contributes to synovial hyperplasia. Results of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin, c-myc, and nucleolar organizer region staining. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Feb;37(2):212–220. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Canete J. D., Parsons W. J., Emery P., Veale D. J. Distinct vascular patterns of early synovitis in psoriatic, reactive, and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jul;42(7):1481–1484. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199907)42:7<1481::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkissian M., Lafyatis R. Integrin engagement regulates proliferation and collagenase expression of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1999 Feb 1;162(3):1772–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seftor R. E., Seftor E. A., Gehlsen K. R., Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Brown P. D., Ruoslahti E., Hendrix M. J. Role of the alpha v beta 3 integrin in human melanoma cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1557–1561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J., Dolhain RJEM, Miltenburg A. M., de Kuiper R., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Poor expression of T cell-derived cytokines and activation and proliferation markers in early rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1998 Jul;88(1):84–90. doi: 10.1006/clin.1998.4525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J., Dolhain R. J., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Analysis of the cellular infiltrates and expression of cytokines in synovial tissue from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and reactive arthritis. J Pathol. 1998 Sep;186(1):75–81. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199809)186:1<75::AID-PATH142>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., O'Donnell J., Highton J., Palmer D. G., Rozenbilds M., Roberts-Thomson P. J. Immunohistochemical analysis of synovial membranes from inflammatory and non-inflammatory arthritides: scarcity of CD5 positive B cells and IL2 receptor bearing T cells. Pathology. 1992 Jan;24(1):19–26. doi: 10.3109/00313029209063615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soden M., Rooney M., Cullen A., Whelan A., Feighery C., Bresnihan B. Immunohistological features in the synovium obtained from clinically uninvolved knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;28(4):287–292. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.4.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivatsa S. S., Fitzpatrick L. A., Tsao P. W., Reilly T. M., Holmes D. R., Jr, Schwartz R. S., Mousa S. A. Selective alpha v beta 3 integrin blockade potently limits neointimal hyperplasia and lumen stenosis following deep coronary arterial stent injury: evidence for the functional importance of integrin alpha v beta 3 and osteopontin expression during neointima formation. Cardiovasc Res. 1997 Dec;36(3):408–428. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(97)00184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefansson S., Lawrence D. A. The serpin PAI-1 inhibits cell migration by blocking integrin alpha V beta 3 binding to vitronectin. Nature. 1996 Oct 3;383(6599):441–443. doi: 10.1038/383441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Hintzen R. Q., Teunissen J. J., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., van Lier R. A., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Swaak A. J., Breedveld F. C. Expression of the activation antigen CD27 in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Aug;80(2):129–138. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Kummer J. A., Hack C. E., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Erkelens G. W., Meinders A. E., Kluin P. M., Breedveld F. C. Granzyme-positive cytotoxic cells are specifically increased in early rheumatoid synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Dec;37(12):1735–1743. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Meijers K. A., Brand R., Meinders A. E., Breedveld F. C. Analysis of the synovial cell infiltrate in early rheumatoid synovial tissue in relation to local disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Feb;40(2):217–225. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Taylor P. C., Breedveld F. C., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Maini R. N. Decrease in cellularity and expression of adhesion molecules by anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1077–1081. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Thurkow E. W., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Smeets T. J., Meinders A. E., Breedveld F. C. Expression of adhesion molecules in early rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Dec;77(3):236–242. doi: 10.1006/clin.1995.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., van der Lubbe P. A., Cauli A., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Yanni G., Panayi G. S., Breedveld F. C. Reduction of synovial inflammation after anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;38(10):1457–1465. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi H., Iizuka H., Juji T., Nakagawa T., Yamamoto A., Miyazaki T., Koshihara Y., Oda H., Nakamura K., Tanaka S. Involvement of receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand/osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis from synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Feb;43(2):259–269. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<259::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. C., Peters A. M., Paleolog E., Chapman P. T., Elliott M. J., McCloskey R., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Reduction of chemokine levels and leukocyte traffic to joints by tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):38–47. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<38::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D. J., Reece R. J., Parsons W., Radjenovic A., O'Connor P. J., Orgles C. S., Berry E., Ridgway J. P., Mason U., Boylston A. W. Intra-articular primatised anti-CD4: efficacy in resistant rheumatoid knees. A study of combined arthroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, and histology. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Jun;58(6):342–349. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.6.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veale D., Yanni G., Rogers S., Barnes L., Bresnihan B., Fitzgerald O. Reduced synovial membrane macrophage numbers, ELAM-1 expression, and lining layer hyperplasia in psoriatic arthritis as compared with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jul;36(7):893–900. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssef P. P., Haynes D. R., Triantafillou S., Parker A., Gamble J. R., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J., Smith M. D. Effects of pulse methylprednisolone on inflammatory mediators in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1400–1408. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J., Firestein G. S. Pannus and pannocytes. Alternative models of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jun;37(6):783–789. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid arthritis. The multiple pathways to chronic synovitis. Lab Invest. 1995 Sep;73(3):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]