Abstract
OBJECTIVES—To develop an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using as substrate a synthetic 22-aminoacid peptide, corresponding to the ribosomal P0, P1 and P2 common epitope. To study the specificity and sensitivity of the method and evaluate the frequency and clinical associations of anti-P antibodies in two groups of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: (a) unselected SLE patients and (b) SLE patients with central nervous system (CNS) involvement. PATIENTS AND METHODS—The C-terminal 22 aminoacid peptide of the ribosomal P proteins (Lys-Lys-Glu-Glu-Lys-Lys-Glu-Glu-Lys-Ser-Glu-Glu-Glu-Asp-Glu-Asp-Met-Gly-Phe-Gly-Leu-Phe-Asp) was synthesised according to Merrifield's solid phase procedure. Purification of the peptide was performed by preparative high performance liquid chromatography and confirmed by amino acid analysis. Using this peptide, in a concentration 5 µg/ml, an ELISA was developed. The presence of anti-P antibodies was evaluated by western blot using purified ribosomal proteins from rat liver. Sera from 178 consecutive patients with SLE and 28 patients with SLE and CNS manifestations were tested. Sera from 58 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and 57 patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome were used as controls. The cut off point of the assay was defined using 124 normal sera. RESULTS—The specificity of the assay was evaluated by homologous inhibition. Pretreatment of positive sera with soluble 22mer peptide of the ribosomal P proteins resulted in 88% inhibition. The concordance between the peptide assay and western blot was found to be 83%. Thirty three of 178 (18.6%) of the unselected SLE patients had antibodies to P-protein common epitope. Their presence was associated with more active disease (European Consensus Lupus Activity Measurement, ECLAM scoring system) (p<0.001), higher levels of anti-ds DNA antibodies (p<0.05) and lower levels of the C4 component of complement (p<0.01). Eleven of 28 (39.3%) patients with SLE and active CNS involvement had antibodies to P-protein. The overall prevalence of anti-P antibodies in active CNS disease patients was statistically significantly higher, as compared with unselected SLE patients (χ2=6.04, p<0.05). These antibodies were found in a high proportion of patients without anticardiolipin antibodies (52.4%) and they were associated with diffuse CNS involvement (psychiatric disorders (71%) and epilepsy (75%)). CONCLUSIONS—A synthetic analogue of the common epitope of ribosomal P-proteins can be use as an antigen for the detection of anti-P antibodies. These antibodies are associated with active SLE and CNS involvement particularly in patients without anticardiolipin antibodies.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (165.9 KB).
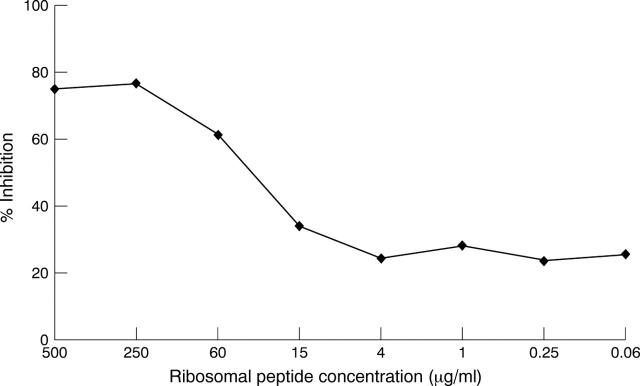
Figure 1 .
Inhibition of a serum positive for anti-ribosomal P antibodies with serial concentrations of soluble synthetic epitope analogue yielded a maximum inhibition of 78%.
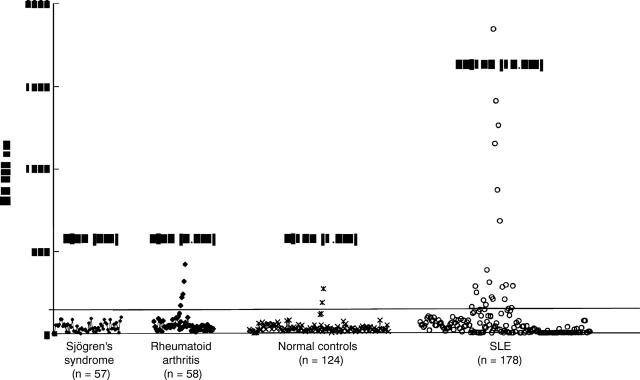
Figure 2 .
The prevalence of antibodies to ribosomal P synthetic epitope analogue in unselected patients with SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, primary Sjögren's syndrome and normal controls.
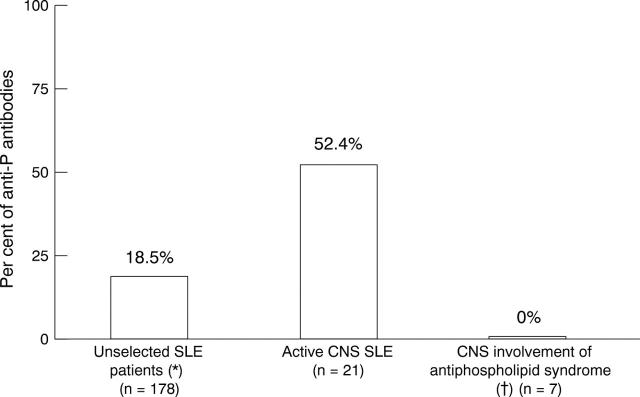
Figure 3 .
The prevalence of antibodies to ribosomal P synthetic epitope analogue in unselected patients with SLE, patients with SLE and active CNS involvement, and patients with antiphospholipid syndrome and CNS involvement. Patients with active CNS lupus, had more frequently anti-P antibodies as compared with unselected patients with SLE. * χ2= 6.04, p<0.05 and patients with antiphospholipid syndrome † χ2= 9.76, p<0.005.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Pérez-Vázquez M. E., Villa A. R., Drenkard C., Cabiedes J. Preliminary classification criteria for the antiphospholipid syndrome within systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Apr;21(5):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(92)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Reveille J. D., Moutsopoulos H. M., Georgescu L., Elkon K. B. Ribosomal P autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Frequencies in different ethnic groups and clinical and immunogenetic associations. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Nov;39(11):1833–1839. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Gaburo Júnior N., Tavares A. V., Cossermelli W. Comparison of five methods for the detection of antiribosomal P protein antibody. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994 Mar;27(3):637–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Golombek S. J., Kaufman L. D., Skelly S., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. B. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caponi L., Pegoraro S., Di Bartolo V., Rovero P., Revoltella R., Bombardieri S. Autoantibodies directed against ribosomal P proteins: use of a multiple antigen peptide as the coating agent in ELISA. J Immunol Methods. 1995 Feb 27;179(2):193–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)00285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. K., DelGiudice-Asch G., Zehetbauer J. B., Lawson J. L., Brot N., Weissbach H., Elkon K. B. Autoantigen-specific T cell proliferation induced by the ribosomal P2 protein in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):345–352. doi: 10.1172/JCI117328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Parnassa A. P., Foster C. L. Lupus autoantibodies target ribosomal P proteins. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):459–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K., Skelly S., Parnassa A., Moller W., Danho W., Weissbach H., Brot N. Identification and chemical synthesis of a ribosomal protein antigenic determinant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7419–7423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Peebles C. L., Heckman K. J., Lee J. C., Tan E. M. Identification of ribosomal protein autoantigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirohata S., Isshi K., Toyoshima S. Association between serum IgG antibodies to recombinant ribosomal P0 fusion protein and neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Apr;41(4):745–747. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199804)41:4<745::AID-ART27>3.0.CO;2-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isshi K., Hirohata S. Association of anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Sep;39(9):1483–1490. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoussakis M. N., Tzioufas A. G., Silis M. P., Pange P. J., Goudevenos J., Moutsopoulos H. M. High prevalence of anti-cardiolipin and other autoantibodies in a healthy elderly population. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):557–565. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meilof J. F., Bantjes I., De Jong J., Van Dam A. P., Smeenk R. J. The detection of anti-Ro/SS-A and anti-La/SS-B antibodies. A comparison of counterimmunoelectrophoresis with immunoblot, ELISA, and RNA-precipitation assays. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Oct 19;133(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90362-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima Y., Minota S., Yamada A., Takaku F., Aotsuka S., Yokohari R. Correlation of antibodies to ribosomal P protein with psychosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1053–1055. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press J., Palayew K., Laxer R. M., Elkon K., Eddy A., Rakoff D., Silverman E. D. Antiribosomal P antibodies in pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and psychosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Apr;39(4):671–676. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Uchiumi T., Ozawa T., Kikuchi M., Nakano M., Kominami R., Arakawa M. Autoantibodies against ribosomal proteins found with high frequency in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with active disease. J Rheumatol. 1991 Nov;18(11):1681–1684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneebaum A. B., Singleton J. D., West S. G., Blodgett J. K., Allen L. G., Cheronis J. C., Kotzin B. L. Association of psychiatric manifestations with antibodies to ribosomal P proteins in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1991 Jan;90(1):54–62. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90506-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh L. S., Bedwell A. E., Isenberg D. A., Gordon C., Emery P., Charles P. J., Harper M., Amos N., Williams B. D. Antibodies to protein P in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Apr;51(4):489–494. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.4.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh L. S., Isenberg D. A. Antiribosomal P protein antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. A reappraisal. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Mar;37(3):307–315. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh L. S., Lee M. K., Wang F., Manivasagar M., Charles P. J., Nicholson G. D., Hay E. M., Isenberg D. A., Amos N., Williams B. D. Antiribosomal P protein antibodies in different populations of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Aug;32(8):663–665. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.8.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzioufas A. G., Manoussakis M. N., Drosos A. A., Silis G., Gharavi A. E., Moutsopoulos H. M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of IgG and IgM anti-dsDNA antibodies: clinical significance and specificity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1987 Jul-Sep;5(3):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bencivelli W., Isenberg D. A., Smolen J. S., Snaith M. L., Sciuto M., Neri R., Bombardieri S. Disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: report of the Consensus Study Group of the European Workshop for Rheumatology Research. II. Identification of the variables indicative of disease activity and their use in the development of an activity score. The European Consensus Study Group for Disease Activity in SLE. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Sep-Oct;10(5):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bombardieri S., Moutsopoulos H. M., Balestrieri G., Bencivelli W., Bernstein R. M., Bjerrum K. B., Braga S., Coll J., de Vita S. Preliminary criteria for the classification of Sjögren's syndrome. Results of a prospective concerted action supported by the European Community. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Mar;36(3):340–347. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. G. Neuropsychiatric lupus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994 Feb;20(1):129–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshio T., Masuyama J. I., Minota S., Iwamoto M., Mimori A., Takeda A., Okazaki H., Kano S. Correlation of serum IgG antibodies to recombinant P0 fusion protein with IgG antibodies to carboxyl-terminal 22 synthetic peptides and carboxyl-terminal 22 amino acid-deleted recombinant P0 fusion protein in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Jul;40(7):1364–1365. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199707)40:7<1364::AID-ART24>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dam A., Nossent H., de Jong J., Meilof J., ter Borg E. J., Swaak T., Smeenk R. Diagnostic value of antibodies against ribosomal phosphoproteins. A cross sectional and longitudinal study. J Rheumatol. 1991 Jul;18(7):1026–1034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]