Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To study the prevalence of ultrasonic hip joint effusion and its relation with clinical, radiological and laboratory (ESR) findings in adults with hip pain. METHODS—Patients (n=224) aged 50 years or older with hip pain, referred by the general practitioner for radiological investigation, underwent a standardised examination. The distance between the ventral capsule and the femoral neck, an increase in which represents joint effusion, was measured sonographically. Joint effusion was defined in three different ways: "effusion" according to Koski's definition, "major effusion", and "asymmetrical effusion" based on only individual side differences. RESULTS—"Effusion" was present in 80 (38%), "major effusion" in 20 (9%), and "asymmetrical effusion" in 47 (22%) patients. Pain in the groin or medial thigh, pain aggravated by lying on the side, decreased extension/internal rotation/abduction/flexion, painful external rotation, and pain on palpation in the groin showed a significant relation (adjusted for age and radiological osteoarthritis of the hip) with ultrasonic hip joint effusion. "Major effusion" showed a significant relation with an increased ESR. When patients with bilateral pain and increased ESR were excluded, a side difference in the range of motion of extension of the hip was shown to be a good predictor for "asymmetrical effusion" (positive predictive value: 71%, negative predictive value: 80%). CONCLUSION—This study showed a relatively high prevalence of ultrasonic joint effusion in adults with hip pain in general practice. Furthermore the results indicate a relation between joint effusion and clinical signs.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (149.0 KB).
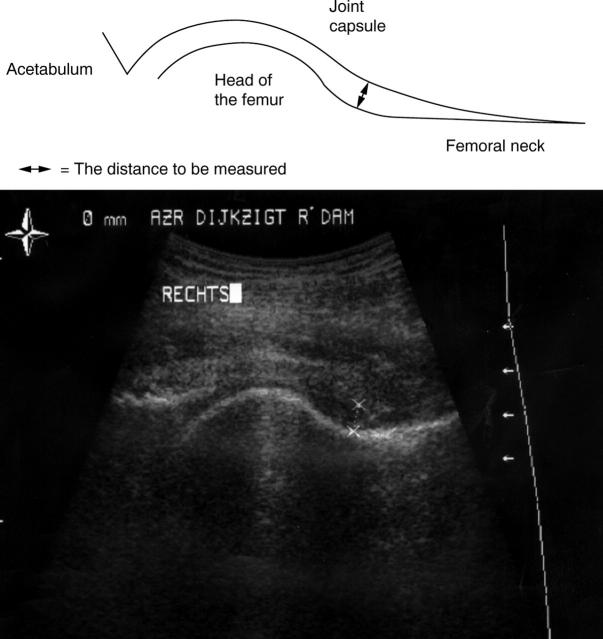
Figure 1 .
The hip joint as seen during sonographic examination (anterior view).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boone D. C., Azen S. P. Normal range of motion of joints in male subjects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979 Jul;61(5):756–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. D., Brandt K. D., Katz B. P., Kalasinski L. A., Ryan S. I. Treatment of knee osteoarthritis: relationship of clinical features of joint inflammation to the response to a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug or pure analgesic. J Rheumatol. 1992 Dec;19(12):1950–1954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYRING E. J., MURRAY W. R. THE EFFECT OF JOINT POSITION ON THE PRESSURE OF INTRA-ARTICULAR EFFUSION. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964 Sep;46:1235–1241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Földes K., Bálint P., Gaál M., Buchanan W. W., Bálint G. P. Nocturnal pain correlates with effusions in diseased hips. J Rheumatol. 1992 Nov;19(11):1756–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Ledingham J., Perry J. D. Intra-articular triamcinolone hexacetonide in knee osteoarthritis: factors influencing the clinical response. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 May;54(5):379–381. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.5.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard N. J., Gosling P. T. Intra-articular fluid pressure and pain in osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988 Jan;70(1):52–55. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.70B1.3339061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harcke H. T. Hip in infants and children. Clin Diagn Ultrasound. 1995;30:179–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H., LAWRENCE J. S. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957 Dec;16(4):494–502. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.4.494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang B., Zhu T. B., Du J. Y., Liu J. R., Chen R. Q., Huang J. H. Ultrasound diagnosis of effusion of the hip. J Tongji Med Univ. 1993;13(3):156–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02886507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M., Anttila P. J., Isomäki H. A. Ultrasonography of the adult hip joint. Scand J Rheumatol. 1989;18(2):113–117. doi: 10.3109/03009748909099926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M., Anttila P., Hämäläinen M., Isomäki H. Hip joint ultrasonography: correlation with intra-articular effusion and synovitis. Br J Rheumatol. 1990 Jun;29(3):189–192. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/29.3.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski J. M. Ultrasonographic evidence of hip synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 1989;18(3):127–131. doi: 10.3109/03009748909095409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD-ROBERTS G. C. The role of capsular changes in osteoarthritis of the hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953 Nov;35-B(4):627–642. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.35B4.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach K. E., Miles T. P. Normal hip and knee active range of motion: the relationship to age. Phys Ther. 1991 Sep;71(9):656–665. doi: 10.1093/ptj/71.9.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydholm U., Wingstrand H., Egund N., Elborg R., Forsberg L., Lidgren L. Sonography, arthroscopy, and intracapsular pressure in juvenile chronic arthritis of the hip. Acta Orthop Scand. 1986 Aug;57(4):295–298. doi: 10.3109/17453678608994395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sada P. N., Rajan P., Jeyaseelan L., Washburn M. C. Standards for ultrasonographic measurements of the hip joint in Indian adults. Skeletal Radiol. 1994 Feb;23(2):111–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00563203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Sue D., Miles-Elkousy N., Ford G., Trevelyan H. Active mobility of the extremities in older subjects. Phys Ther. 1984 Jun;64(6):919–923. doi: 10.1093/ptj/64.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. J., Green D. J., MacLarnon J. C. Arthrosonography of the painful hip. Clin Radiol. 1984 Jan;35(1):17–19. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(84)80219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingstrand H., Egund N., Forsberg L. Sonography and joint pressure in synovitis of the adult hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987 Mar;69(2):254–256. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.69B2.3546329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]