Abstract
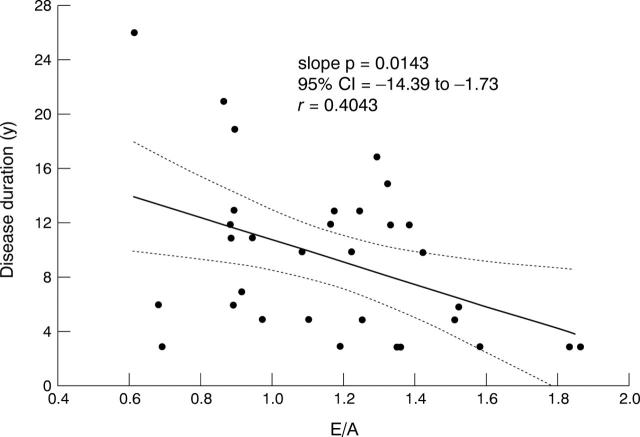
OBJECTIVE—The aim of this study was to evaluate left ventricular filling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), analysing transmitral flow and pulmonary venous flow, with special regard to age and disease duration. METHODS—32 patients affected by RA according to ARA criteria were selected, without evidence of cardiac disease, and compared with matched control subjects. All patients and the control group were submitted to M-mode, two dimensional, Doppler and colour Doppler (continuous and pulsed wave) echocardiography. The following diastolic parameters were evaluated: transmitralic flow (E/A ratio), pulmonary venous flow (S/D ratio), a-Pw, IVRT and DT. RESULTS—In RA patients left ventricular filling abnormalities were found characterised by a reduced E/A ratio (mean (SD) 1.16 (0.31) v controls 1.37 (0.32); p =0.02) and an increased S/D ratio (1.43 (0.40) v controls 1.22 (0.29); p = 0.017). In the group of patients a relation was found between E/A ratio and disease duration (r= 0.40, p =0.01 Spearman rank correlation). CONCLUSIONS—At present, it is concluded that RA patients, in absence of clinical evidence of heart disease, show diastolic dysfunction characterised by impaired E/A and S/D ratio. The relation between transmitral flow alteration and disease duration suggests a sub-clinical myocardial involvement.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (113.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
Scatterplot of the relation between mitral E/A wave velocity ratio and disease duration.