Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To study the prevalence of different causes of anaemia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and their associations with immunological and clinical parameters and to evaluate the contribution of erythropoietin (Epo) and anti-erythropoietin (anti-Epo) autoantibodies to the development of SLE anaemia. METHODS—132 SLE patients with anaemia (defined as haemoglobin of 12 g/dl or less for women and 13.5 g/dl or less for men) from among a total of 345 consecutive SLE patients were prospectively enrolled into the study. Standard haematological and immunological tests were performed and serum Epo and anti-Epo antibodies were assayed. RESULTS—The identified causes were anaemia of chronic disease (ACD) n=49 (37.1%), iron deficiency anaemia (IDA) n=47 (35.6%), autoimmune haemolytic anaemia (AHA) n=19 (14.4%) and other causes n=17 (12.9%). There was significant heterogeneity in the severity of anaemia between the four groups (p<0.01) with AHA cases being on average more severe. The proportion of patients with anticardiolipin antibodies, low complement levels and anti-dsDNA differed significantly among the four groups; these markers were particularly common in patients with AHA, and uncommon in patients with IDA. Twenty one of 100 tested patients had anti-Epo antibodies. Such antibodies were seen practically only in patients with ACD (odds ratio 3.1, p=0.041) and in patients with high lupus activity (ECLAM) scores (odds ratio 1.27 per point, p=0.055). Epo response was inadequate in 42.4% and 41.2% of patients with ACD and AHA, respectively. CONCLUSIONS—Anaemia in SLE usually takes the form of ACD and IDA, however autoimmune haemolysis is not uncommon. SLE patients with different causes of anaemia differ in regard to several immunological parameters. Epo response is blunted in anaemic SLE patients, particularly those with ACD and AHA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (147.5 KB).
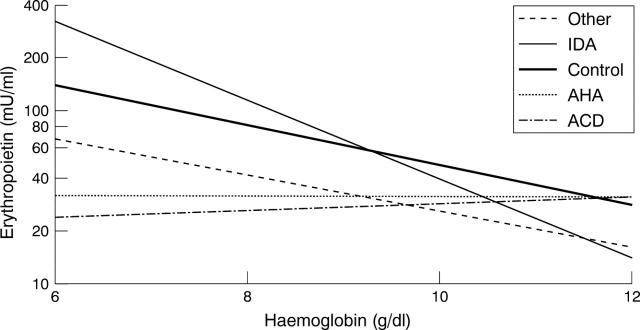
Figure 1 .
Relation of the log10 serum erythropoietin concentration to haemoglobin concentrations. In patients with ACD and AHA, the slope of the regression (b=0.024, p=0.53 and b=−0.002, p=0.97 respectively) was lower than in the controls (b=−0.110, p=0.003) who included 20 patients with uncomplicated iron deficiency anaemia. ACD: anaemia of chronic disease; AHA: autoimmune haemolytic anaemia; IDA: iron deficiency anaemia.
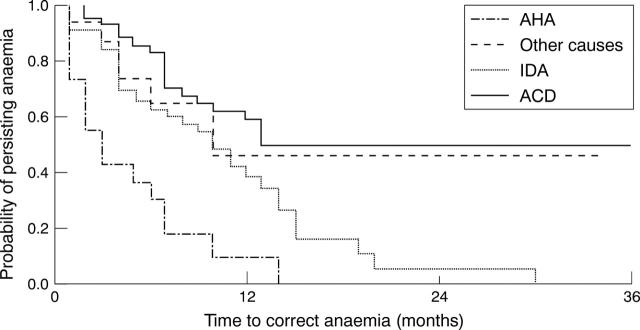
Figure 2 .
Kaplan-Meier plots for the time to correction of anaemia for different causes. Abbreviations as in figure 1.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvieux J., Roussel B., Ponard D., Colomb M. G. Reactivity patterns of anti-phospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus sera in relation to erythrocyte binding and complement activation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):466–471. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey F. A., Lilly M., Bertoli L. F., Ball G. V. An antibody that inhibits in vitro bone marrow proliferation in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and aplastic anemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):901–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barosi G. Inadequate erythropoietin response to anemia: definition and clinical relevance. Ann Hematol. 1994 May;68(5):215–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01737420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguin Y., Clemons G. K., Pootrakul P., Fillet G. Quantitative assessment of erythropoiesis and functional classification of anemia based on measurements of serum transferrin receptor and erythropoietin. Blood. 1993 Feb 15;81(4):1067–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budman D. R., Steinberg A. D. Hematologic aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus. Current concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Feb;86(2):220–229. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-2-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caligaris-Cappio F., Bergui L., Tesio L., Ziano R., Camussi G. HLA-Dr+ T cells of the Leu 3 (helper) type infiltrate the kidneys of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jan;59(1):185–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R., Johnson C. S., Weiner J. M. Pernicious anemia in Latin Americans is not a disease of the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Nov;147(11):1995–1996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmel R. Prevalence of undiagnosed pernicious anemia in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1996 May 27;156(10):1097–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadevall N., Dupuy E., Molho-Sabatier P., Tobelem G., Varet B., Mayeux P. Autoantibodies against erythropoietin in a patient with pure red-cell aplasia. N Engl J Med. 1996 Mar 7;334(10):630–633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199603073341004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello C., Abdelaal M., Coomes E. N. Pernicious anemia and systemic lupus erythematosus in a young woman. J Rheumatol. 1985 Aug;12(4):798–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delezé M., Alarcón-Segovia D., Oria C. V., Sánchez-Guerrero J., Fernández-Dominguez L., Gomez-Pacheco L., Ponce de León S. Hemocytopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol. 1989 Jul;16(7):926–930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faquin W. C., Schneider T. J., Goldberg M. A. Effect of inflammatory cytokines on hypoxia-induced erythropoietin production. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):1987–1994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond A., Rudge A. C., Loizou S., Bowcock S. J., Walport M. J. Reduced numbers of complement receptor type 1 on erythrocytes are associated with increased levels of anticardiolipin antibodies. Findings in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Mar;32(3):259–264. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazeltine M., Rauch J., Danoff D., Esdaile J. M., Tannenbaum H. Antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence of an association with positive Coombs' and hypocomplementemia. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jan;15(1):80–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V. Don't ignore low serum cobalamin (vitamin B12) levels. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Aug;148(8):1705–1707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama M., Kohgo Y., Kondo H., Shintani N., Fujikawa K., Sasaki K., Kato J., Niitsu Y. Regulation of iron metabolism in HepG2 cells: a possible role for cytokines in the hepatic deposition of iron. Hepatology. 1993 Oct;18(4):874–880. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840180420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Balderas F. J., Morales-Polanco M. R., Gutierrez L. Acute sideroblastic anemia in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1994 Jun;3(3):157–159. doi: 10.1177/096120339400300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongen-Lavrencic M., Peeters H. R., Vreugdenhil G., Swaak A. J. Interaction of inflammatory cytokines and erythropoeitin in iron metabolism and erythropoiesis in anaemia of chronic disease. Clin Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;14(5):519–525. doi: 10.1007/BF02208148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juncà J., Cuxart A., Tural C., Marti S. Systemic lupus erythematosus and pernicious anemia in an 82-year-old woman. J Rheumatol. 1991 Dec;18(12):1924–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Spivak J. L. Systemic lupus erythematosus and myelofibrosis. Am J Med. 1986 Nov;81(5):935–938. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90373-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeling D. M., Isenberg D. A. Haematological manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Blood Rev. 1993 Dec;7(4):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(93)90006-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Soto A., Cervera R., Font J., Bové A., Reverter J. C., Muñoz F. J., Miret C., Espinosa G., Ordinas A., Ingelmo M. Isotype distribution and clinical significance of antibodies to cardiolipin, phosphatidic acid, phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidylserine in systemic lupus erythematosus: prospective analysis of a series of 92 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997 Mar-Apr;15(2):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamus S. W., Beck-Schroeder S., Zanjani E. D. Suppression of normal human erythropoiesis by gamma interferon in vitro. Role of monocytes and T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1496–1503. doi: 10.1172/JCI111853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoussakis M. N., Tzioufas A. G., Silis M. P., Pange P. J., Goudevenos J., Moutsopoulos H. M. High prevalence of anti-cardiolipin and other autoantibodies in a healthy elderly population. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Sep;69(3):557–565. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means R. T., Jr, Dessypris E. N., Krantz S. B. Inhibition of human erythroid colony-forming units by interleukin-1 is mediated by gamma interferon. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jan;150(1):59–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means R. T., Jr, Krantz S. B. Inhibition of human erythroid colony-forming units by gamma interferon can be corrected by recombinant human erythropoietin. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2564–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means R. T., Jr, Krantz S. B. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of the anemia of chronic disease. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1639–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. J., Hoffman R., Zanjani E. D. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia and periodic pure red cell aplasia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1978 Aug;65(2):342–345. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90829-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesher G., Hanna V. E., Moore T. L., Hersh M., Osborn T. G. Thrombotic microangiographic hemolytic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Dec;24(3):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(94)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg R., Nived O., Sturfelt G., Unander M., Arfors L. Anticardiolipin and complement activation: relation to clinical symptoms. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossent J. C., Swaak A. J. Prevalence and significance of haematological abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1991 Jul;80(291):605–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago M. B., Gaburo N., Jr, de Oliveira R. M., Cossermelli W. Complement activation by anticardiolipin antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1991 Apr;50(4):249–250. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.4.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley J. C., Kullgren B., Allison A. C. Inhibition by interleukin-1 of the action of erythropoietin on erythroid precursors and its possible role in the pathogenesis of hypoplastic anaemias. Br J Haematol. 1987 Sep;67(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears D. A. Anemia of chronic disease. Med Clin North Am. 1992 May;76(3):567–579. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30340-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipsas N. V., Kokori S. I., Ioannidis J. P., Kyriaki D., Tzioufas A. G., Kordossis T. Circulating autoantibodies to erythropoietin are associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1-related anemia. J Infect Dis. 1999 Dec;180(6):2044–2047. doi: 10.1086/315156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sthoeger Z., Sthoeger D., Green L., Geltner D. The role of anticardiolipin autoantibodies in the pathogenesis of autoimmune hemolytic anemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1993 Dec;20(12):2058–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzioufas A. G., Kokori S. I., Petrovas C. I., Moutsopoulos H. M. Autoantibodies to human recombinant erythropoietin in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: correlation with anemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Dec;40(12):2212–2216. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzioufas A. G., Manoussakis M. N., Drosos A. A., Silis G., Gharavi A. E., Moutsopoulos H. M. Enzyme immunoassays for the detection of IgG and IgM anti-dsDNA antibodies: clinical significance and specificity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1987 Jul-Sep;5(3):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bencivelli W., Isenberg D. A., Smolen J. S., Snaith M. L., Sciuto M., Neri R., Bombardieri S. Disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: report of the Consensus Study Group of the European Workshop for Rheumatology Research. II. Identification of the variables indicative of disease activity and their use in the development of an activity score. The European Consensus Study Group for Disease Activity in SLE. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Sep-Oct;10(5):541–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlachoyiannopoulos P. G., Karassa F. B., Karakostas K. X., Drosos A. A., Moutsopoulos H. M. Systemic lupus erythematosus in Greece. Clinical features, evolution and outcome: a descriptive analysis of 292 patients. Lupus. 1993 Oct;2(5):303–312. doi: 10.1177/096120339300200505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. F., Hui P. K., Chan J. K., Chan Y. W., Ha S. Y. The acute lupus hemophagocytic syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Mar 1;114(5):387–390. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-5-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]