Abstract
OBJECTIVES—To study the pathogenesis of pneumomediastinum in polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM). PATIENTS AND METHODS—The clinical records of 48 patients with PM/DM were reviewed, focusing mainly on the presence of pneumomediastinum and cutaneous vasculopathy, and the chest radiographic changes. A patient with pneumomediastinum with a characteristic change in his bronchus is described in detail. Case reports of pneumomediastinum in PM/DM in English publications are reviewed. RESULTS—Among the 48 patients with PM/DM, pneumomediastinum was observed as a complication in four patients with DM and none of the patients with PM. Three of the four patients with pneumomediastinum, but only six of the 44 patients without this complication, had associated cutaneous vasculopathy. There was a significant association of pneumomediastinum with cutaneous vasculopathy (p = 0.02) and younger age (p = 0.04), but not with the prevalence of lung disease. A 30 year old man (patient 1) with DM, who had interstitial pneumonitis and skin ulceration due to vasculopathy, developed pneumomediastinum. Fibreoptic bronchoscopy showed white plaques on the bronchial mucosa, which were confirmed by microscopic examination as representing subepithelial necrosis. A literature review showed 13 cases of DM but no patient with PM with pneumomediastinum. CONCLUSIONS—In patient 1, bronchial necrosis due to vasculopathy was strongly suspected as being responsible for the pneumomediastinum. The results suggest that pneumomediastinum was associated not with interstitial pneumonitis but with the complication of vasculopathy appearing as skin lesions in DM.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (155.7 KB).
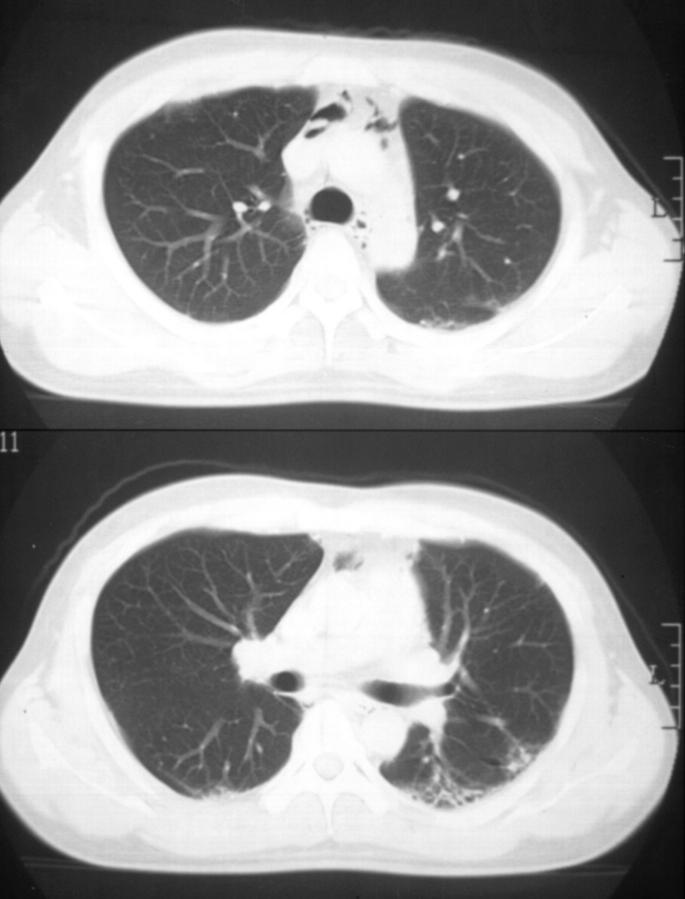
Figure 1 .
Computed tomograms of the chest (patient 1), showing air around the trachea and in the anterior mediastinum. A honeycomb pattern is also seen in the posterior bases of the lungs.
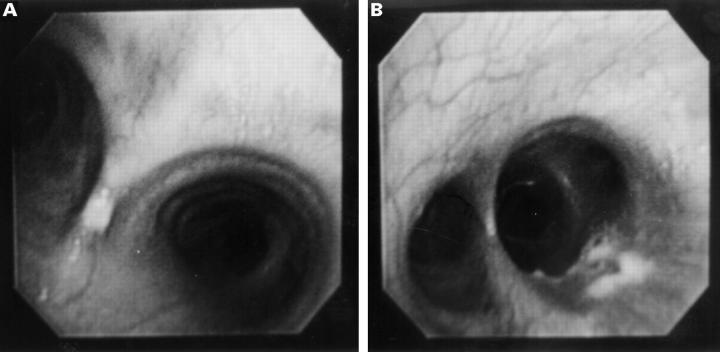
Figure 2 .
A fibreoptic bronchoscopy, showing studded white plaques on the bronchial mucosa at the carina (A) and the main (B), lobar and segmental bronchi of both lungs.
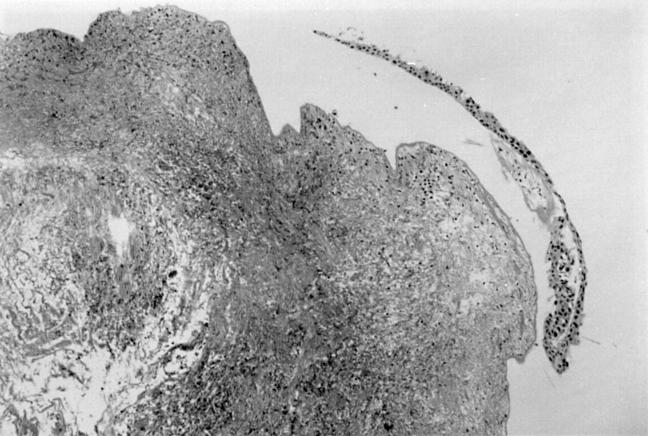
Figure 3 .
Biopsy of the plaque at the carina (original magnification ×60, haematoxylin and eosin staining) showing subepithelial necrosis of the bronchial wall with epithelial squamatisation.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohan A., Peter J. B. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Feb 13;292(7):344–347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197502132920706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet E., Rolland Y., Bon E., Cantagrel A., Tubery M., Murris M., Didier A., Maziéres B. Pneumomediastinum, a rare complication of dermatomyositis. Report of a case. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1996 Jun;63(6):457–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley J. D. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum in adult dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Sep;45(9):780–782. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.9.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmody E., McNicholl J., Chadwick G., Bresnihan B., Fitzgerald M. X. Prolonged spontaneous pneumomediastinum in adult dermatomyositis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jul;46(7):566–566. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. L., Yao Y. T., Wang N. S., Lee Y. C. Segmental necrosis of small bronchi after prolonged intakes of Sauropus androgynus in Taiwan. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Feb;157(2):594–598. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.2.9704040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicuttini F. M., Fraser K. J. Recurrent pneumomediastinum in adult dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol. 1989 Mar;16(3):384–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Arahata K. Mononuclear cells in myopathies: quantitation of functionally distinct subsets, recognition of antigen-specific cell-mediated cytotoxicity in some diseases, and implications for the pathogenesis of the different inflammatory myopathies. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jul;17(7):704–721. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. B., Waldstein G., Hernandez J. A., Fan L. L. Necrotizing tracheobronchitis. An ischemic lesion. Am J Dis Child. 1988 Oct;142(10):1094–1098. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1988.02150100088034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfer R. S., Nakao S. K., Cernea S. S. Dermatomyositis associated with pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous cellular tissue emphysema. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Nov;33(11):1092–1092. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.11.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang K. A., Kim S. H., Choi J. H., Sung K. J., Moon K. C., Koh J. K. Subcutaneous emphysema with spontaneous pneumomediastinum and pneumothorax in adult dermatomyositis. J Dermatol. 1999 Feb;26(2):125–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1999.tb03524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen T. L., Barrera P., van Engelen B. G., Cox N., Laan R. F., van de Putte L. B. Dermatomyositis with subclinical myositis and spontaneous pneumomediastinum with pneumothorax: case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 Nov-Dec;16(6):733–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayser K., Wiebel M., Schulz V., Gabius H. J. Necrotizing bronchitis, angiitis, and amyloidosis associated with chronic Q fever. Respiration. 1995;62(2):114–116. doi: 10.1159/000196404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissel J. T., Mendell J. R., Rammohan K. W. Microvascular deposition of complement membrane attack complex in dermatomyositis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 6;314(6):329–334. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602063140601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamaze R., Tréchot P., Martinet Y. Bronchial necrosis and granuloma induced by the aspiration of a tablet of ferrous sulphate. Eur Respir J. 1994 Sep;7(9):1710–1711. doi: 10.1183/09031936.94.07091710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Tomii M., Kashiwazaki S. Fatal pneumomediastinum in dermatomyositis without creatine kinase elevation. Intern Med. 1993 Aug;32(8):643–647. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.32.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunder R. J., Pierson D. J., Hudson L. D. Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med. 1984 Jul;144(7):1447–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoud T. C., Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A. Diffuse infiltrative lung disease: a new scheme for description. Radiology. 1983 Nov;149(2):353–363. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.2.6622676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta A. C., Dweik R. A. Necrosis of the bronchus. Role of radiation. Chest. 1995 Nov;108(5):1462–1466. doi: 10.1378/chest.108.5.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Ishikawa O., Miyachi Y. Pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema associated with fatal interstitial pneumonia in dermatomyositis. J Dermatol. 1997 Jul;24(7):482–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.1997.tb02825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago M. B., Chalhoub M., Pereira S. T. Amyopathic dermatomyositis complicated by interstitial pulmonary disease and pneumomediastinum. J Rheumatol. 1998 Oct;25(10):2042–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Viggiano R. W., Pickersgill J., Colby T. V. Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clinical features and prognosis as correlated with histologic findings. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Mar;141(3):727–733. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.3.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis W. D., Hoffman G. S., Leavitt R. Y., Pass H. I., Fauci A. S. Surgical pathology of the lung in Wegener's granulomatosis. Review of 87 open lung biopsies from 67 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991 Apr;15(4):315–333. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199104000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi Y., Maeda H., Konishi F., Hiyama K., Yamana S., Ishioka S., Yamakido M. Dermatomyositis associated with rapidly progressive fatal interstitial pneumonitis and pneumomediastinum. Scand J Rheumatol. 1999;28(1):58–61. doi: 10.1080/03009749950155805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]