Abstract
BACKGROUND—Treatment of reactive arthritis (ReA) with antibiotics has so far remained controversial. Eradication of the causative microbe appears logical, but short term antibiotic treatment has no beneficial effect on the outcome of ReA. OBJECTIVE—To evaluate the effect of a three month course of ciprofloxacin on ReA. METHODS—In a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial, between December 1992 and February 1996, 71 patients with acute ReA triggered by a gastrointestinal or a urogenital infection were randomly assigned to receive ciprofloxacin 500 mg or placebo twice daily for three months. Patients were assessed at study entry, at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months. Sixty two patients were valid for the efficacy analysis. The primary outcome measures were erythrocyte sedimentation rate, number of swollen joints, patients self assessment, and complete recovery. RESULTS—Adverse events were mostly mild and occurred in both treatment groups. There were no statistically significant differences in any of the primary or secondary efficacy variables between the study groups at baseline or during the 12 month follow up. All primary outcome measures indicated that the condition of the patients improved during the study. CONCLUSION—Both groups tended to recover. Ciprofloxacin, given as a three month course, had no advantage over placebo treatment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.3 KB).
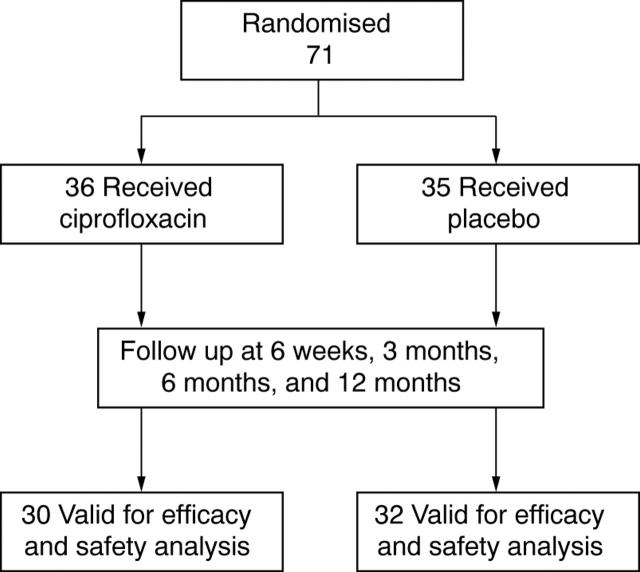
Figure 1 .
Trial profile.
Figure 2 .
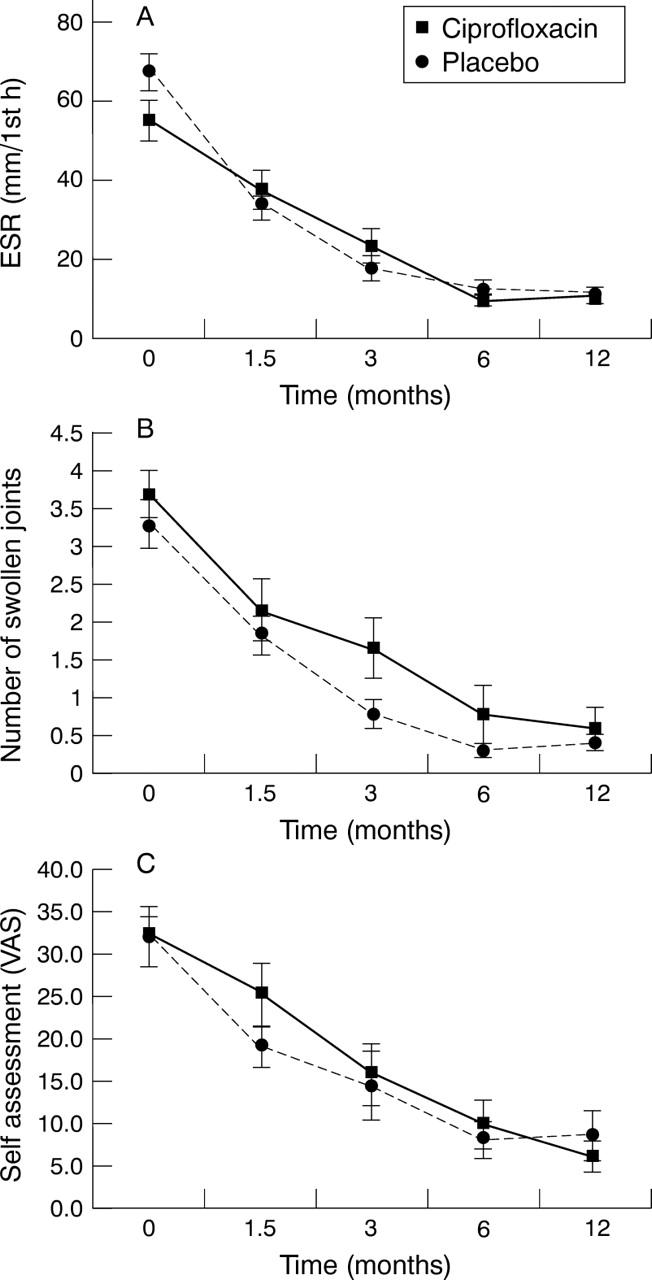
Changes in (A) erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), (B) number of swollen joints, and (C) patient global assessment in patients treated with ciprofloxacin (n=30) or placebo (n=32). Values are means (SEM). Differences between groups over time were not significant.
Figure 3 .
Cumulative proportion of patients in persistent complete remission after treatment with ciprofloxacin (n=30) or placebo (n=32). Differences between groups over time were not significant.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardin T., Enel C., Cornelis F., Salski C., Jorgensen C., Ward R., Lathrop G. M. Antibiotic treatment of venereal disease and Reiter's syndrome in a Greenland population. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;35(2):190–194. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C., Ayers L. W., Gerlach E. H., Sommers H. M. Antibacterial activities of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, oxolinic acid, cinoxacin, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):633–637. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Reda D. J., Weisman M. H., Cush J. J., Vasey F. B., Schumacher H. R., Jr, Budiman-Mak E., Balestra D. J., Blackburn W. D., Cannon G. W. Comparison of sulfasalazine and placebo in the treatment of reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome). A Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Dec;39(12):2021–2027. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn M. P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G and M antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):848–852. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.848-852.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydén A., Bengtsson A., Foberg U., Svenungsson B., Castor B., Kärnell A., Schvarcz R., Lindblom B., Kihlström E. Early antibiotic treatment of reactive arthritis associated with enteric infections: clinical and serological study. BMJ. 1990 Dec 8;301(6764):1299–1302. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6764.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., Lindberg A. A., Mäki-Ikola O., von Essen R., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Isomäki H., Saario R., Arnold W. J., Toivanen A. Salmonella lipopolysaccharide in synovial cells from patients with reactive arthritis. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):685–688. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90804-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Jalkanen S., Toivanen P., Koski J., Lindberg A. A. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide in synovial fluid cells in Shigella triggered reactive arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;19(3):500–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Ståhlberg T. H., Toivanen A. Comparison of bacteria with and without plasmid-encoded proteins as antigens for measurement of immunoglobulin M, G, and A antibodies to Yersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):583–585. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.583-585.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Toivanen A. IgA-anti-yersinia antibodies in yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Jul;45(7):561–565. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.7.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granfors K., Viljanen M., Tiilikainen A., Toivanen A. Persistence of IgM, IgG, and IgA antibodies to Yersinia in yersinia arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):424–429. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M., Nettelnbreker E., Hopf S., Schmitz E., Pörschke K., Zeidler H. Chlamydial rRNA in the joints of patients with Chlamydia-induced arthritis and undifferentiated arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Jan-Feb;10(1):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrlinger J. D., Asmussen J. U. Long term prognosis in yersinia arthritis: clinical and serological findings. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Dec;51(12):1332–1334. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.12.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A. Antibiotics in Yersinia enterocolitica infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jul;20(1):123–131. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A., de Koning J., Heesemann J. Persistence of Yersinia enterocolitica in man. Infection. 1988 Mar-Apr;16(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF01644307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomäki O., Vuento R., Granfors K. Serological diagnosis of salmonella infections by enzyme immunoassay. Lancet. 1989 Jun 24;1(8652):1411–1414. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalliomäki J. L., Leino R. Follow-up studies of joint complications in yersiniosis. Acta Med Scand. 1979;205(6):521–525. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1979.tb06095.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keat A. Reiter's syndrome and reactive arthritis in perspective. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 29;309(26):1606–1615. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312293092604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Foberg U., Bengtsson A., Frydén A., Svenungsson B., Schvarcz R., Lindblom B., Castor B. Intestinal symptoms and serological response in patients with complicated and uncomplicated Yersinia enterocolitica infections. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992;24(1):57–63. doi: 10.3109/00365549209048401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosunen T. U., Rautelin H., Pitkänen T., Pönkä A., Pettersson T. Antibodies against an acid extract from a single campylobacter strain in hospitalized campylobacter patients. Infection. 1983 Jul-Aug;11(4):189–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01641193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Granfors K., Isomäki H., Toivanen A. Yersinia specific immune complexes in the synovial fluid of patients with yersinia triggered reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jul;46(7):510–514. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.7.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Granfors K., Toivanen A. Detection of circulating Yersinia-immunoglobulin complexes by enzyme immunoassay (EIA). J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauhio A., Leirisalo-Repo M., Lähdevirta J., Saikku P., Repo H. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of three-month treatment with lymecycline in reactive arthritis, with special reference to Chlamydia arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jan;34(1):6–14. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauhio A., Sorsa T., Lindy O., Suomalainen K., Saari H., Golub L. M., Konttinen Y. T. The anticollagenolytic potential of lymecycline in the long-term treatment of reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Feb;35(2):195–198. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirisalo-Repo M., Helenius P., Hannu T., Lehtinen A., Kreula J., Taavitsainen M., Koskimies S. Long-term prognosis of reactive salmonella arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Sep;56(9):516–520. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.9.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht H., Kihlström E., Lindström F. D. Reactive arthritis after Salmonella among medical doctors--study of an outbreak. J Rheumatol. 1993 May;20(5):845–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue H. C., Wu M. H., Wang J. K., Wu F. F., Wu Y. N. Long-term outcome of patients with rheumatic fever receiving benzathine penicillin G prophylaxis every three weeks versus every four weeks. J Pediatr. 1994 Nov;125(5 Pt 1):812–816. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(94)70082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanagara R., Li F., Beutler A., Hudson A., Schumacher H. R., Jr Alteration of Chlamydia trachomatis biologic behavior in synovial membranes. Suppression of surface antigen production in reactive arthritis and Reiter's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;38(10):1410–1417. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sairanen E., Paronen I., Mähönen H. Reiter's syndrome: a follow-up study. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Jan-Feb;185(1-2):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb07298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Jr, Magge S., Cherian P. V., Sleckman J., Rothfuss S., Clayburne G., Sieck M. Light and electron microscopic studies on the synovial membrane in Reiter's syndrome. Immunocytochemical identification of chlamydial antigen in patients with early disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):937–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J., Brandt J., Miksits K., Heesemann J., Laitko S., Sörensen H., Distler A., Kingsley G. Pathogenetic role of Chlamydia, Yersinia and Borrelia in undifferentiated oligoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;19(8):1236–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Fendler C., Laitko S., Sörensen H., Gripenberg-Lerche C., Hiepe F., Alten R., Keitel W., Groh A., Uksila J. No benefit of long-term ciprofloxacin treatment in patients with reactive arthritis and undifferentiated oligoarthritis: a three-month, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jul;42(7):1386–1396. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199907)42:7<1386::AID-ANR12>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Levin R. E., Molloy P. J., Kalish R. A., Abraham J. H., 3rd, Liu N. Y., Schmid C. H. Treatment of Lyme arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jun;37(6):878–888. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Yli-Kerttula T., Luukkainen R., Merilahti-Palo R., Granfors K., Seppälä J. Effect of antimicrobial treatment on chronic reactive arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993 May-Jun;11(3):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V., Leirisalo M., Pentikäinen P. J., Räsänen T., Seppälä I., Larinkari U., Ranki M., Koskimies S., Malkamäki M., Mäkelä P. H. Triggering infections in reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jun;44(6):399–405. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.6.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yli-Kerttula T., Möttönen T., Toivanen A. Different course of reactive arthritis in two HLA-B27 positive brothers with fatal outcome in one. J Rheumatol. 1997 Oct;24(10):2047–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yli-Kerttula T., Tertti R., Toivanen A. Ten-year follow up study of patients from a Yersinia pseudotuberculosis III outbreak. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1995 May-Jun;13(3):333–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Gripenberg-Lerche C., Söderström K. O., Toivanen A., Toivanen P. Antibiotic prophylaxis and treatment of reactive arthritis. Lessons from an animal model. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1238–1243. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Toivanen A., Toivanen P. Experimental Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: effect of a 3-week course of ciprofloxacin. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 May;36(5):541–546. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]