Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To evaluate plasma human cartilage glycoprotein (HC gp-39) as a possible marker for the presence and/or activity of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other inflammatory conditions. BACKGROUND—HC gp-39 is a secretory product of chondrocytes, synovial cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. HC gp-39, also described as YKL-40, was found to be a marker of joint disease and tissue injury in RA and various other diseases. METHODS—Levels of HC gp-39 were determined by a sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 47 patients with RA, 47 with osteoarthritis (OA), 24 with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 24 with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and in 47 healthy controls. A disease activity score was assessed in the patients with RA, SLE, and IBD. RESULTS—The plasma level of HC gp-39 in the RA patient group was significantly higher than in the other patient groups and healthy controls. The level in patients with OA, SLE, and IBD was also significantly higher than the HC gp-39 level found in the healthy control group. HC gp-39 levels in patients with RA correlated positively with the ESR and IgM rheumatoid factor level but not with other variables of disease activity. In the patients with SLE and IBD no correlation was found with the disease activity score. CONCLUSION—The plasma level of HC gp-39 is increased in inflammatory conditions with and without joint disease (SLE, IBD, OA, and RA). Thus increased levels of HC gp-39 do not only reflect joint disease but also reflect inflammation or tissue degradation in various conditions. Notably, the highest level of HC gp-39 was found in patients with RA. Only in the RA patient group was a correlation between HC gp-39 plasma levels and some laboratory variables of disease activity found.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (146.4 KB).
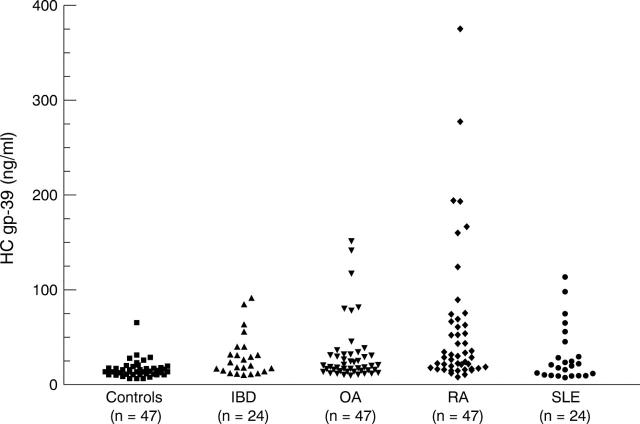
Figure 1 .
Human cartilage glycoprotein-39 (HC gp-39) levels in different patient groups. IBD = inflammatory bowel disease; OA = osteoarthritis; RA = rheumatoid arthritis; SLE = systemic lupus erythematosus.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best W. R., Becktel J. M., Singleton J. W., Kern F., Jr Development of a Crohn's disease activity index. National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos E. S., van der Doelen A. A., van Rooy N., Schuurs A. H. 3,3',5,5' - Tetramethylbenzidine as an Ames test negative chromogen for horse-radish peroxidase in enzyme-immunoassay. J Immunoassay. 1981;2(3-4):187–204. doi: 10.1080/15321818108056977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cintin C., Johansen J. S., Christensen I. J., Price P. A., Sørensen S., Nielsen H. J. Serum YKL-40 and colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 1999 Mar;79(9-10):1494–1499. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6690238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. A. The use of the disease activity score in the analysis of clinical trials in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1993 Nov;20(11):1863–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakala B. E., White C., Recklies A. D. Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25803–25810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Weisman M., O'Dell J., Scott T., Krusemeier M., Visor J., Swindlehurst C. Chondrex: new marker of joint disease. Clin Chem. 1998 Mar;44(3):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B., Bairoch A. New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1993 Aug 1;293(Pt 3):781–788. doi: 10.1042/bj2930781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu B., Trinh K., Figueira W. F., Price P. A. Isolation and sequence of a novel human chondrocyte protein related to mammalian members of the chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 9;271(32):19415–19420. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.32.19415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. S., Cintin C., Jørgensen M., Kamby C., Price P. A. Serum YKL-40: a new potential marker of prognosis and location of metastases of patients with recurrent breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A(9):1437–1442. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00196-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. S., Hvolris J., Hansen M., Backer V., Lorenzen I., Price P. A. Serum YKL-40 levels in healthy children and adults. Comparison with serum and synovial fluid levels of YKL-40 in patients with osteoarthritis or trauma of the knee joint. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Jun;35(6):553–559. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.6.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. S., Jensen H. S., Price P. A. A new biochemical marker for joint injury. Analysis of YKL-40 in serum and synovial fluid. Br J Rheumatol. 1993 Nov;32(11):949–955. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/32.11.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. S., Møller S., Price P. A., Bendtsen F., Junge J., Garbarsch C., Henriksen J. H. Plasma YKL-40: a new potential marker of fibrosis in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis? Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997 Jun;32(6):582–590. doi: 10.3109/00365529709025104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. S., Stoltenberg M., Hansen M., Florescu A., Hørslev-Petersen K., Lorenzen I., Price P. A. Serum YKL-40 concentrations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: relation to disease activity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Jul;38(7):618–626. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.7.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick R. B., Emery J. G., Connor J. R., Dodds R., Lysko P. G., Rosenberg M. Induction and expression of human cartilage glycoprotein 39 in rheumatoid inflammatory and peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1997 Nov 25;237(1):46–54. doi: 10.1006/excr.1997.3764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyirkos P., Golds E. E. Human synovial cells secrete a 39 kDa protein similar to a bovine mammary protein expressed during the non-lactating period. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):265–268. doi: 10.1042/bj2690265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijden G. F., Rijnders A. W., Bos E., Coenen-de Roo C. J., van Staveren C. J., Miltenburg A. M., Meijerink J. H., Elewaut D., de Keyser F., Veys E. Human cartilage glycoprotein-39 as a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Jun;40(6):1115–1125. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volck B., Price P. A., Johansen J. S., Sørensen O., Benfield T. L., Nielsen H. J., Calafat J., Borregaard N. YKL-40, a mammalian member of the chitinase family, is a matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1998 Jul-Aug;110(4):351–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolvers D. A., Coenen-de Roo C. J., Mebius R. E., van der Cammen M. J., Tirion F., Miltenburg A. M., Kraal G. Intranasally induced immunological tolerance is determined by characteristics of the draining lymph nodes: studies with OVA and human cartilage gp-39. J Immunol. 1999 Feb 15;162(4):1994–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van 't Hof M. A., van Riel P. L., Theunisse L. A., Lubberts E. W., van Leeuwen M. A., van Rijswijk M. H., van de Putte L. B. Judging disease activity in clinical practice in rheumatoid arthritis: first step in the development of a disease activity score. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Nov;49(11):916–920. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.11.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]