Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate the incidence of retinopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to clarify its significance in relation to other clinical manifestations. METHODS—A cross sectional study on lupus retinopathy was made in 69 patients with SLE. One expert ophthalmologist examined the ocular fundi of the lupus patients without any information of their disease state. Clinical and laboratory findings in the patients with retinopathy and those without were compared. RESULTS—Retinopathy was found in 7/69 (10%) patients. The findings included haemorrhages, vasculitis, cotton wool spots, and hard exudates, all of which were considered to reflect vascular damage. Retinopathy was found to be associated with the presence of anticardiolipin antibody (p<0.05) and with central nervous system lupus (p<0.01). The patients with retinopathy had higher levels of serum creatinine than the patients without retinopathy (p<0.01). The disease activity of lupus, as assessed by the maximum SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) score of the patients, was also significantly higher in the patients with retinopathy (p<0.03). CONCLUSION—Incidence of retinopathy in SLE was similar to that in previous reports and it may reflect tissue microangiopathy, particularly associated with vasculitis or anticardiolipin antibodies, or both.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (121.3 KB).
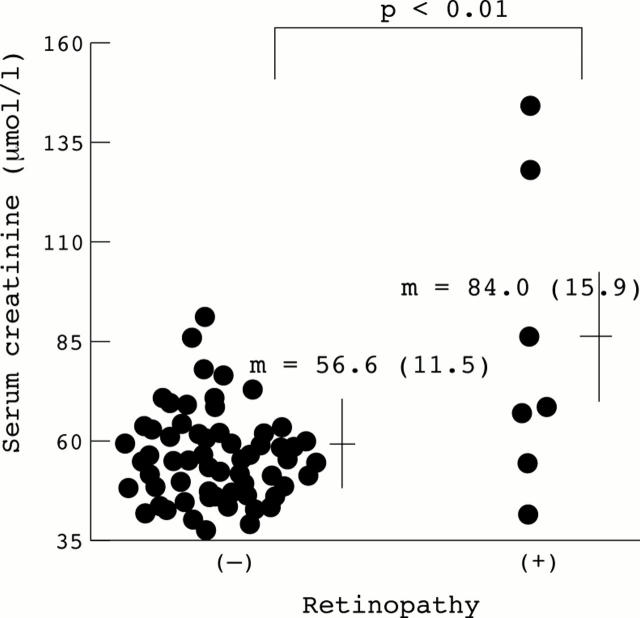
Figure 1 .
Serum creatinine concentrations in the patients with or without retinopathy.
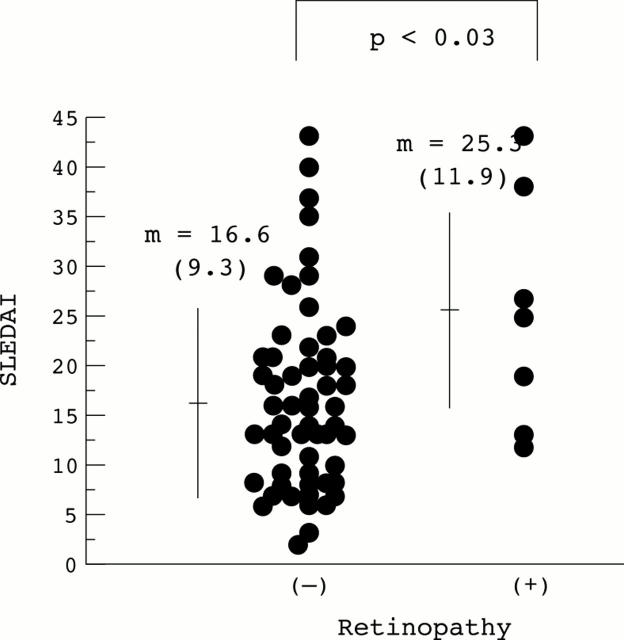
Figure 2 .
Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) scores in the patients with or without retinopathy. The maximum SLEDAI score for each patient is shown.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Delezé M., Oria C. V., Sánchez-Guerrero J., Gómez-Pacheco L., Cabiedes J., Fernández L., Ponce de León S. Antiphospholipid antibodies and the antiphospholipid syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus. A prospective analysis of 500 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1989 Nov;68(6):353–365. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198911000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigo M. C., Garcia-Torres R., Robles M., Bochicchio T., Reyes P. A. Renal involvement in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1992 Aug;19(8):1181–1185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. J., Ordoñez N. G., Diddie K. R., Ernest J. T. Immune-complex deposition in the eye in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Nov;139(11):1312–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atsumi T., Khamashta M. A., Haworth R. S., Brooks G., Amengual O., Ichikawa K., Koike T., Hughes G. R. Arterial disease and thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome: a pathogenic role for endothelin 1. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 May;41(5):800–807. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199805)41:5<800::AID-ART5>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. N., Gharavi A. E., Boey M. L., Patel B. M., Mackworth-Young C. G., Loizou S., Hughes G. R. Anticardiolipin antibodies: detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 1983 Nov 26;2(8361):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herranz M. T., Rivier G., Khamashta M. A., Blaser K. U., Hughes G. R. Association between antiphospholipid antibodies and epilepsy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Apr;37(4):568–571. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii Y., Nagasawa K., Mayumi T., Niho Y. Clinical importance of persistence of anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Jun;49(6):387–390. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.6.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpik A. G., Schwartz M. M., Dickey L. E., Streeten B. W., Roberts J. L. Ocular immune reactants in patients dying with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Jun;35(3):295–312. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie J. T., Kobayashi S., Tokano Y., Hashimoto H. Systemic and cerebral vasculitis coexisting with disseminated coagulopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 1995 Nov;22(11):2173–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford-Brady F. J., Urowitz M. B., Gladman D. D., Easterbrook M. Lupus retinopathy. Patterns, associations, and prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toubi E., Khamashta M. A., Panarra A., Hughes G. R. Association of antiphospholipid antibodies with central nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1995 Oct;99(4):397–401. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)80188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]