Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To assess organ involvement according to a modified Medsger severity scale and its relation to outcome and prognosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. METHODS—One hundred consecutive patients observed in Lund with systemic sclerosis were followed up for a period of 14 years. The mean follow up time was 7.7 years. Initial assessment and an annual evaluation was performed for each patient, with a mean visit frequency of 5.6 per patient. RESULTS—Age at referral, high total skin score, truncal skin involvement, low vital capacity, low static lung compliance, low Cr-EDTA clearance, and ECG abnormalities at the initial assessment predict poor outcome. A severity scoring system for five organ systems indicates a slow progression of organ dysfunction after recruitment into the study. The female: male ratio was 2:1, the mean age at onset of symptoms was 42.3 (range 3-82), and the mean age at recruitment was 47.2 years (range 17-82). Thirty patients died during the follow up period at the mean age of 61.3 years (range 33-85). The causes of death were directly related to systemic sclerosis in at least 10 patients, infections in six, cancers in nine, and other causes in four patients. The standardised mortality ratio was 3.5 and 3.7 for men and women, respectively. CONCLUSION—A high severity score for function of vital organs was shown to predict shortened survival. In this study a severity score based on simple clinical assessment variables was able to predict poor outcome from extensive skin changes, ECG changes, and compromised lung and renal function. Organ dysfunction mainly became manifest during the first five years of the disease, whereafter organ function remained largely stable.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (137.9 KB).
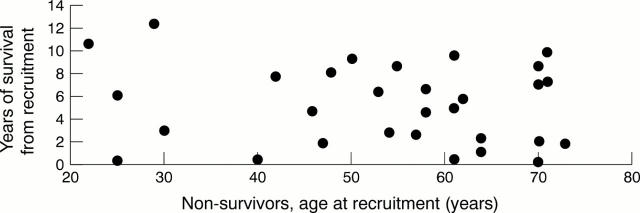
Figure 1 .
Survival time in non-survivors. Within six years from recruitment into the study 16 of 30 non-survivors died, 2/3 of them were over 50 years of age at the time of death.
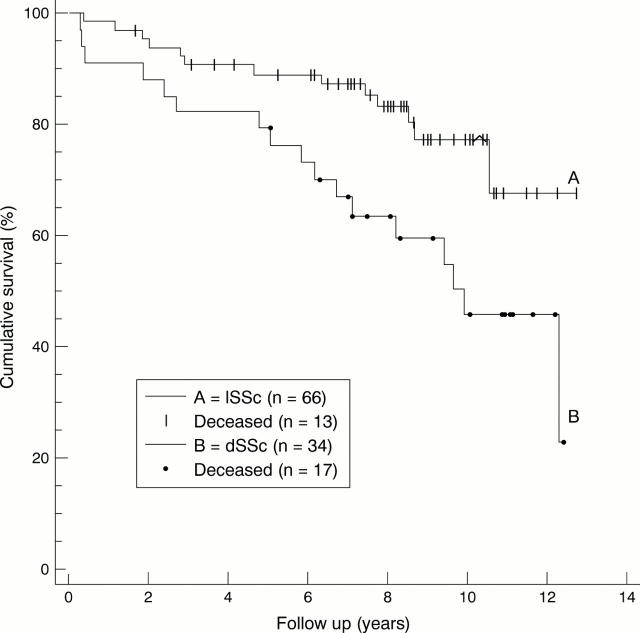
Figure 2 .
Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival plot. Skin involvement as a determinant of survival in systemic sclerosis. Improved survival for patients with limited systemic sclerosis (p=0.015).
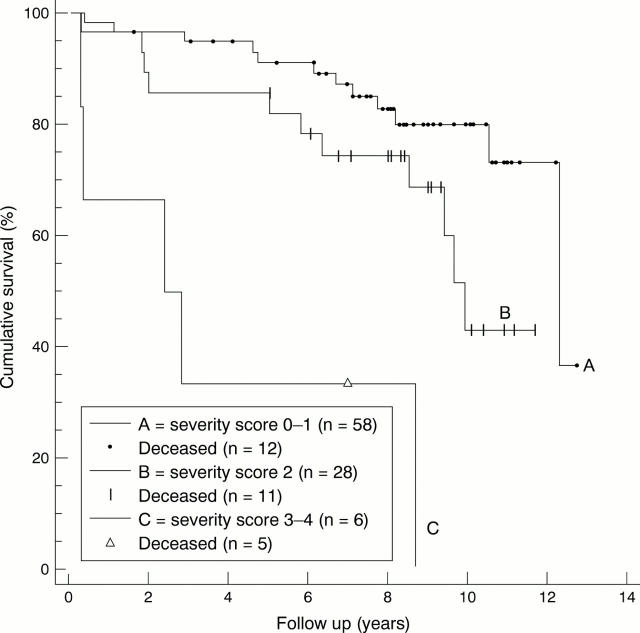
Figure 3 .
Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival plot. Renal function measured by Cr-EDTA clearance as a determinant of survival in systemic sclerosis, grouping of patients according to severity score 0-1, 2, and 3-4. There is a significantly improved survival for those with severity score of 0-1 compared with severity score 2 (p<0.001).
Figure 4 .
Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival plot. Haemoglobin as a determinant of survival in systemic sclerosis. There is a significantly improved survival for patients with severity score of 0-1 compared with severity score 2 (p= 0.0003).
Figure 5 .
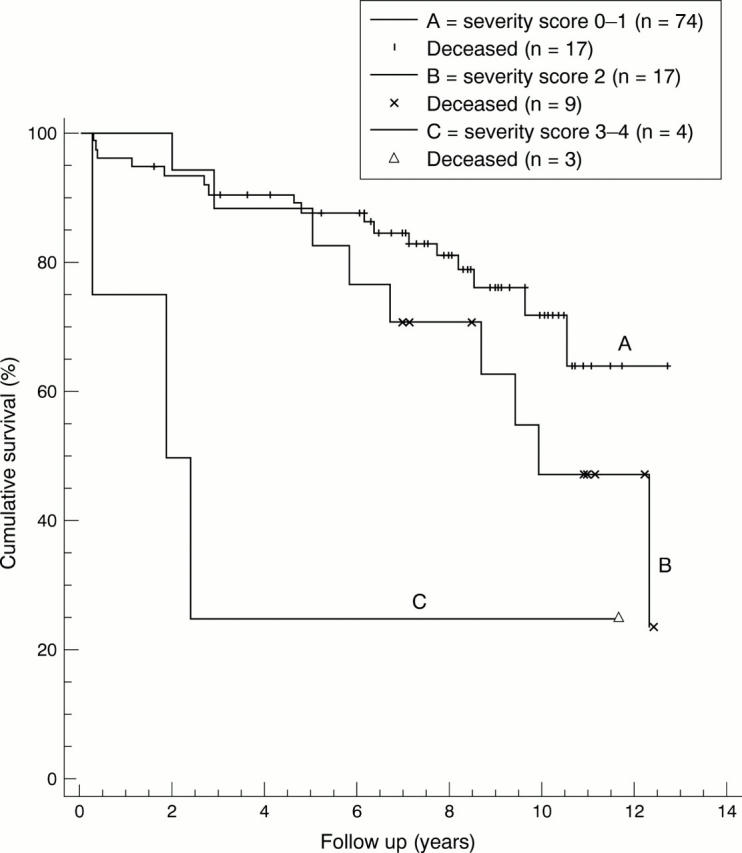
Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival plot. Lung function measured by vital capacity and static lung compliance as a determinant of survival in systemic sclerosis. Grouping of patients according to severity score 0-1, 2, and 3-4. Improved survival for those patients with severity score of 0-1 compared with severity scores 2 and 3-4 (p=0.0077).
Figure 6 .
Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival plot. Gastrointestinal function measured by cinematography and triolein test as a determinant of survival in systemic sclerosis. Grouping of patients according to severity score 0-1, 2, and 3-4, showing improved survival for patients with severity score of 0-1 compared with severity scores 2 and 3-4 (p<0.0001).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akesson A., Forsberg L., Hederström E., Wollheim F. Ultrasound examination of skin thickness in patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1986 Jan-Feb;27(1):91–94. doi: 10.1177/028418518602700117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akesson A., Scheja A., Lundin A., Wollheim F. A. Improved pulmonary function in systemic sclerosis after treatment with cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akesson A., Wollheim F. A. Organ manifestations in 100 patients with progressive systemic sclerosis: a comparison between the CREST syndrome and diffuse scleroderma. Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;28(4):281–286. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.4.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akesson B., Florén C. H. Use of the triolein breath test for the demonstration of fat malabsorption in coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 May;19(3):307–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R. D., Medsger T. A., Jr, Bloch D. A., Michel B. A. Predictors of survival in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Apr;34(4):403–413. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R., Bluestone R., Holt P. J., Bywaters E. G. Survival in scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Nov;30(6):581–588. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.6.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan C., Howard Y., Brennan P., Black C., Silman A. Survival following the onset of scleroderma: results from a retrospective inception cohort study of the UK patient population. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;35(11):1122–1126. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.11.1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER R. G., GIFFORD R. W., Jr, HINES E. A., Jr Prognostic significance of Raynaud's phenomenon and other clinical characteristics of systemic scleroderma. A study of 271 cases. Circulation. 1960 Jun;21:1088–1095. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.21.6.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follansbee W. P., Curtiss E. I., Medsger T. A., Jr, Steen V. D., Uretsky B. F., Owens G. R., Rodnan G. P. Physiologic abnormalities of cardiac function in progressive systemic sclerosis with diffuse scleroderma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):142–148. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geirsson A. J., Akesson A., Gustafson T., Elner A., Wollheim F. A. Cineradiography identifies esophageal candidiasis in progressive systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1989 Jan-Feb;7(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geirsson A. J., Danielsen R., Pétursson E. Left ventricular myocardial perfusion and function in systemic sclerosis before and after diltiazem treatment. Scand J Rheumatol. 1996;25(5):317–320. doi: 10.3109/03009749609104064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geirsson A. J., Steinsson K., Guthmundsson S., Sigurthsson V. Systemic sclerosis in Iceland. A nationwide epidemiological study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 Aug;53(8):502–505. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.8.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesselstrand R., Scheja A., Akesson A. Mortality and causes of death in a Swedish series of systemic sclerosis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Nov;57(11):682–686. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.11.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonson B. A method for determination of pulmonary elastic recoil and resistance at a regulated flow rate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1969 Sep;24(2):115–125. doi: 10.3109/00365516909080141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan A., Devaux J. Y., Amor B., Menkès C. J., Weber S., Nitenberg A., Venot A., Guérin F., Degeorges M., Roucayrol J. C. Nifedipine and thallium-201 myocardial perfusion in progressive systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 29;314(22):1397–1402. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605293142201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoy E. C., Black C., Fleischmajer R., Jablonska S., Krieg T., Medsger T. A., Jr, Rowell N., Wollheim F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1988 Feb;15(2):202–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medsger T. A., Jr, Masi A. T. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):714–721. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medsger T. A., Jr, Masi A. T., Rodnan G. P., Benedek T. G., Robinson H. Survival with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A life-table analysis of clinical and demographic factors in 309 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Sep;75(3):369–376. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medsger T. A., Jr, Silman A. J., Steen V. D., Black C. M., Akesson A., Bacon P. A., Harris C. A., Jablonska S., Jayson M. I., Jimenez S. A. A disease severity scale for systemic sclerosis: development and testing. J Rheumatol. 1999 Oct;26(10):2159–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Czirják L. Predictors of survival in 171 patients with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Clin Rheumatol. 1997 Sep;16(5):454–460. doi: 10.1007/BF02238937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 May;23(5):581–590. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silman A. J. Scleroderma--demographics and survival. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1997 May;48:58–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeon C. P., Armadans L., Fonollosa V., Vilardell M., Candell J., Tolosa C., Mearin F., Rodrigo M. J., Solans R., Lima J. Survival prognostic factors and markers of morbidity in Spanish patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 Dec;56(12):723–728. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.12.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen V. D., Conte C., Owens G. R., Medsger T. A., Jr Severe restrictive lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Sep;37(9):1283–1289. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen V. D., Medsger T. A., Jr Epidemiology and natural history of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990 Feb;16(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen V. D., Medsger T. A., Jr, Osial T. A., Jr, Ziegler G. L., Shapiro A. P., Rodnan G. P. Factors predicting development of renal involvement in progressive systemic sclerosis. Am J Med. 1984 May;76(5):779–786. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]