Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate systemic and intrathecal production of proinflammatory cytokines in relation to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) nitric oxide (NO) release in patients with neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus (NPLE). METHODS—Thirty patients with NPLE rated as mild, moderate, or severe were studied and CSF was obtained from 21 of these. Cytokine mRNA expressing cells were detected by in situ hybridisation. Soluble cytokines were assessed by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Nitrite and nitrate were determined by capillary electrophoresis. RESULTS—Patients with NPLE had high numbers of lymphocytes expressing mRNA for tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα), interferon γ, and interleukin 10 in blood. The number of peripheral blood TNFα mRNA positive cells correlated strongly with the level of NO metabolites in the CSF (r2=0.69). Both the number of peripheral blood mononuclear cells expressing mRNA for TNFα as well as the CSF level of NO metabolites correlated with NPLE disease severity. CONCLUSION—These data suggest that increased peripheral production of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα may contribute both to an increased production of NO in the central nervous system and to generation of clinical NPLE. The data also support the possibility that measurements of NO metabolites in CSF may be of value in the diagnosis of neurological symptoms related to SLE.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (106.7 KB).
Figure 1 .
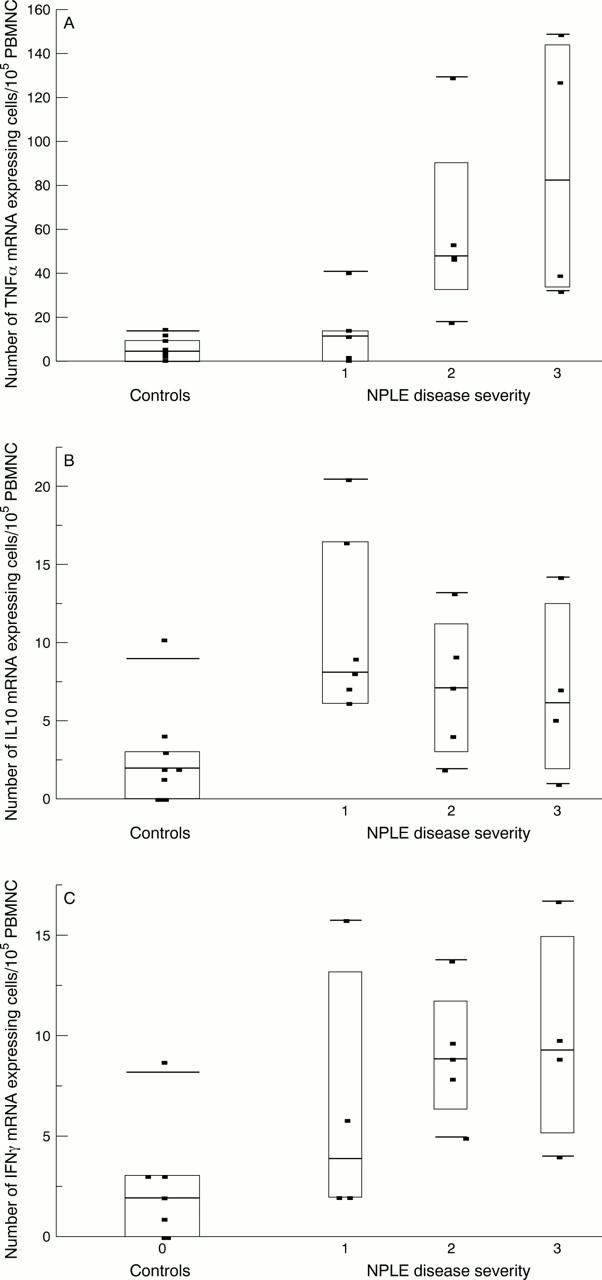
Box plot showing 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, and 90th centile distribution of the number of peripheral blood cells (PBMNC) expressing mRNA for (A) tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα), (B) interleukin 10 (IL10), and (C) interferon γ (IFNγ) in 11 healthy controls and 16 patients with mild (1), moderate (2), or severe (3) neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus (NPLE). Patients with moderate and severe disease had more TNFα expressing cells than controls; p<0.001 for both groups.
Figure 2 .
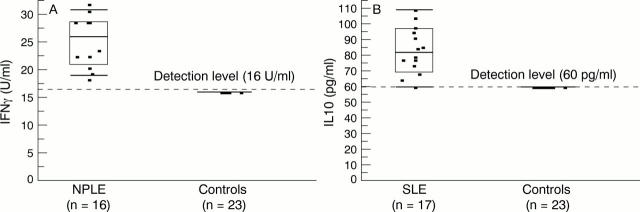
Box plot showing 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, and 90th centiles for (A) soluble interferon γ (IFNγ) and (B) soluble interleukin 10 (IL10) in the cerebrospinal fluid of 16 patients with neuropsychiatric lupus and 23 healthy controls who all had levels under the detection level (dashed line). Patients v controls: IFNγ, p<0.001; IL10, p<0.0001 by Fisher's exact test evaluated at detection level.
Figure 3 .
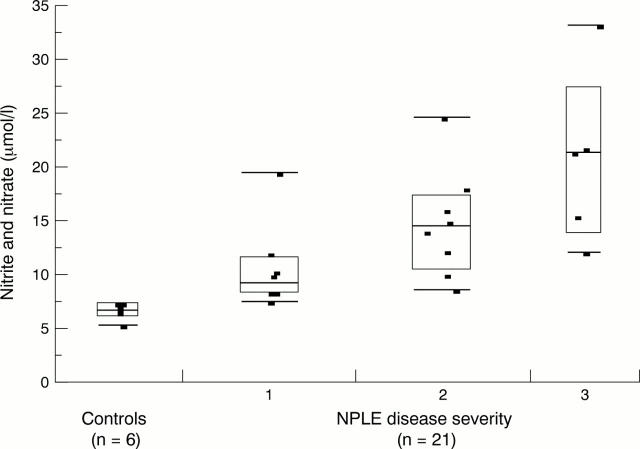
Box plot showing 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, and 90th centiles of cerebrospinal fluid concentration of nitric oxide oxidation products nitrite and nitrate in six healthy controls and 21 patients with mild (1), moderate (2), or severe (3) neuropsychiatric lupus. p<0.004 for each patient group compared with healthy controls. The group with mild disease differed significantly from the group with severe disease (p<0.04).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Wysenbeek A., Engelmann H., Cope A. P., Brennan F., Molad Y., Hornik V., Levo Y., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Correlation between serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1111–1120. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcocer-Varela J., Aleman-Hoey D., Alarcon-Segovia D. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 activities are increased in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with CNS lupus erythematosus and correlate with local late T-cell activation markers. Lupus. 1992 Feb;1(2):111–117. doi: 10.1177/096120339200100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alosachie I. J., Terryberry J. W., Mevorach D., Chapman Y., Lorber M., Torre D., Youinou P., Peter J. B., Shoenfeld Y. Central nervous system (CNS) involvement in SLE. The diagnostic role of antibodies to neuronal antigens. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 1998 Fall;16(3):275–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02737637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arditi M., Manogue K. R., Caplan M., Yogev R. Cerebrospinal fluid cachectin/tumor necrosis factor-alpha and platelet-activating factor concentrations and severity of bacterial meningitis in children. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):139–147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Golombek S. J., Kaufman L. D., Skelly S., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. B. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Battistini L., Raine C. S., Dickson D. W., Casadevall A., Lee S. C. Reactive nitrogen intermediates in human neuropathology: an overview. Dev Neurosci. 1994;16(3-4):152–161. doi: 10.1159/000112102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundin L., Svenungsson E., Morcos E., Andersson M., Olsson T., Lundberg I., Wiklund N. P. Central nervous system nitric oxide formation in cerebral systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Neurol. 1998 Oct;44(4):704–706. doi: 10.1002/ana.410440421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J., Cohen-Armon M., Shoenfeld Y., Korczyn A. D. Antiphospholipid antibodies permeabilize and depolarize brain synaptoneurosomes. Lupus. 1999;8(2):127–133. doi: 10.1191/096120399678847524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinn R. J., Wilkinson I. D., Hall-Craggs M. A., Paley M. N., Shortall E., Carter S., Kendall B. E., Isenberg D. A., Newman S. P., Harrison M. J. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and cerebral proton spectroscopy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Jan;40(1):36–46. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg S. D., Behmann S. A., Carbotte R. M., Denburg J. A. Lymphocyte antigens in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship of lymphocyte antibody specificities to clinical disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Mar;37(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkeson G., Cannon C., Oates J., Reilly C., Goldman D., Petri M. Correlation of serum measures of nitric oxide production with lupus disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1999 Feb;26(2):318–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L. O., Link H., Sandlund L., Einarsson R. Oligoclonal IgG in cerebrospinal fluid detected by isoelectric focusing using PhastSystem. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1993 Aug;53(5):487–492. doi: 10.1080/00365519309092544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig B., Fiehn C., Brockhaus M., Gallati H., Pezzutto A., Hunstein W. Evaluation of soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors and TNF receptor antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematodes, progressive systemic sclerosis, and mixed connective tissue disease. J Clin Immunol. 1993 Sep;13(5):321–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00920240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirohata S., Miyamoto T. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and central nervous system involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):644–649. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in autoimmunity: pretty girl or old witch? Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):122–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90107-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacki J. K., Leszczynski P., Kelemen J., Müller W., Mackiewicz S. H. Cytokine concentration in serum of lupus erythematosus patients: the effect on acute phase response. J Med. 1997;28(1-2):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacki J. K., Samborski W., Mackiewicz S. H. Interleukin-10 and interleukin-6 in lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, correlations with acute phase proteins. Clin Rheumatol. 1997 May;16(3):275–278. doi: 10.1007/BF02238963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Dickson D. W., Liu W., Brosnan C. F. Induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in human astrocytes by interleukin-1 beta and interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Dickson D. W., Liu W., Brosnan C. F. Induction of nitric oxide synthase activity in human astrocytes by interleukin-1 beta and interferon-gamma. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leone A. M., Francis P. L., Rhodes P., Moncada S. A rapid and simple method for the measurement of nitrite and nitrate in plasma by high performance capillary electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Apr 29;200(2):951–957. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link J., Söderström M., Olsson T., Höjeberg B., Ljungdahl A., Link H. Increased transforming growth factor-beta, interleukin-4, and interferon-gamma in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994 Sep;36(3):379–386. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorente L., Richaud-Patin Y., Fior R., Alcocer-Varela J., Wijdenes J., Fourrier B. M., Galanaud P., Emilie D. In vivo production of interleukin-10 by non-T cells in rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus. A potential mechanism of B lymphocyte hyperactivity and autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Nov;37(11):1647–1655. doi: 10.1002/art.1780371114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malide D., Russo P., Bendayan M. Presence of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in renal mesangial cells of lupus nephritis patients. Hum Pathol. 1995 May;26(5):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maury C. P., Teppo A. M. Tumor necrosis factor in the serum of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;32(2):146–150. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohga S., Gondo K., Nomura A., Onoe Y., Matsuzaki A., Hara T. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokine concentrations in a patient with lupus meningoencephalitis: differences from cytokine profiles in central nervous system infections. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Jan;37(1):111–112. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pistiner M., Wallace D. J., Nessim S., Metzger A. L., Klinenberg J. R. Lupus erythematosus in the 1980s: a survey of 570 patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;21(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(91)90057-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos P. C., Mendez M. J., Ames P. R., Khamashta M. A., Hughes G. R. Pulse cyclophosphamide in the treatment of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996 May-Jun;14(3):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolla G., Brussino L., Bertero M. T., Colagrande P., Converso M., Bucca C., Polizzi S., Caligaris-Cappio F. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1997 Jun;24(6):1066–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Kuroki Y., Kim M., Hirohata S., Ogino T. Interferon-alpha in lupus psychosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Apr;35(4):417–422. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toubi E., Khamashta M. A., Panarra A., Hughes G. R. Association of antiphospholipid antibodies with central nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1995 Oct;99(4):397–401. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)80188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. G., Emlen W., Wener M. H., Kotzin B. L. Neuropsychiatric lupus erythematosus: a 10-year prospective study on the value of diagnostic tests. Am J Med. 1995 Aug;99(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)80135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. G. Neuropsychiatric lupus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994 Feb;20(1):129–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. L., Rettori V., al-Shekhlee A., Bongiorno P. B., Canteros G., McCann S. M., Gold P. W., Licinio J. Inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in the brain during systemic inflammation. Nat Med. 1996 May;2(5):581–584. doi: 10.1038/nm0596-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Janadi M., al-Balla S., al-Dalaan A., Raziuddin S. Cytokine profile in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other rheumatic diseases. J Clin Immunol. 1993 Jan;13(1):58–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00920636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]