Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate polymorphisms of both codon 54 allele and promoter variants of the mannose binding lectin (MBL) gene in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (SS). METHODS—Polymorphisms of codon 54 allele and promoter variants of the MBL gene in 104 patients with SS and 143 healthy controls were determined by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism and allele specific polymerase chain reaction respectively. RESULTS—The allele frequency of the wild type of MBL codon 54 was significantly higher in patients with SS than in controls (0.836 v 0.741; p=0.011), and the frequency of the homozygous wild type of MBL codon 54 was significantly higher in patients with SS than in controls (0.692 v 0.539; p=0.024). On the other hand, the allele frequencies of the MBL promoter gene did not differ between patients and controls (χ2=4.01, df=2, p=0.135). CONCLUSION—The polymorphism of the MBL gene may be one of the genetic factors that determines susceptibility to SS.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (150.1 KB).
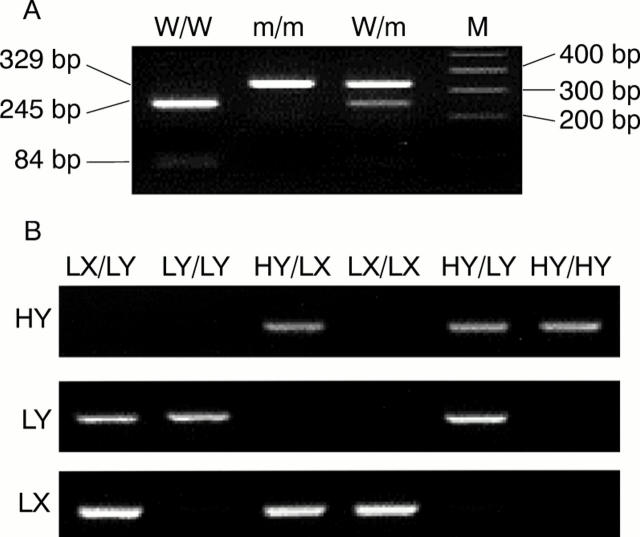
Figure 1 .
(A) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for the codon 54 allele of the mannose binding lectin (MBL) gene. PCR products were digested with BamI, and three genotypes of MBL codon 54 were determined. W/W, wild/wild; W/m, wild/mutant; m/m, mutant/mutant; M, marker. (B) Allele specific PCR analysis for promoter genotypes of the MBL gene. PCR products of HY, LY, and LX alleles are visualised separately by staining with ethidium bromide in 2% agarose gel, and promoter genotypes were determined according to positive bands. Representative LY/LX, LY/LY, HY/LX, LX/LX, LY/HY, and HY/HY genotypes are shown.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies E. J., Snowden N., Hillarby M. C., Carthy D., Grennan D. M., Thomson W., Ollier W. E. Mannose-binding protein gene polymorphism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Jan;38(1):110–114. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer P. B., Ellermann-Eriksen S., Thiel S., Jensenius J. C., Mogensen S. C. Mannan-binding protein and bovine conglutinin mediate enhancement of herpes simplex virus type 2 infection in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1994 May;39(5):439–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred P., Harboe M., Oettinger T., Koch C., Svejgaard A. Dual role of mannan-binding protein in infections: another case of heterosis? Eur J Immunogenet. 1994 Apr;21(2):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1994.tb00183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred P., Madsen H. O., Balslev U., Hofmann B., Pedersen C., Gerstoft J., Svejgaard A. Susceptibility to HIV infection and progression of AIDS in relation to variant alleles of mannose-binding lectin. Lancet. 1997 Jan 25;349(9047):236–240. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)08440-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garred P., Madsen H. O., Halberg P., Petersen J., Kronborg G., Svejgaard A., Andersen V., Jacobsen S. Mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms and susceptibility to infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2145–2152. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2145::AID-ANR15>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graudal N. A., Homann C., Madsen H. O., Svejgaard A., Jurik A. G., Graudal H. K., Garred P. Mannan binding lectin in rheumatoid arthritis. A longitudinal study. J Rheumatol. 1998 Apr;25(4):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley J. B., Alexander E. L., Bias W. B., Fox O. F., Provost T. T., Reichlin M., Yamagata H., Arnett F. C. Anti-Ro (SS-A) and anti-La (SS-B) in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Feb;29(2):196–206. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip W. K., Chan S. Y., Lau C. S., Lau Y. L. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with promoter polymorphisms of the mannose-binding lectin gene. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Sep;41(9):1663–1668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itescu S., Brancato L. J., Buxbaum J., Gregersen P. K., Rizk C. C., Croxson T. S., Solomon G. E., Winchester R. A diffuse infiltrative CD8 lymphocytosis syndrome in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: a host immune response associated with HLA-DR5. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jan 1;112(1):3–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlman M., Joiner K., Ezekowitz R. A. The human mannose-binding protein functions as an opsonin. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1733–1745. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai S., Kanagawa S., Morinobu A., Takada M., Nakamura K., Sugai S., Maruya E., Saji H. Association of a new allele of the TAP2 gene, TAP2*Bky2 (Val577), with susceptibility to Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1685–1692. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. L., Lau C. S., Chan S. Y., Karlberg J., Turner M. W. Mannose-binding protein in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Apr;39(4):706–708. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe R. J., Sumiya M., Hill A. V., Lau Y. L., Levinsky R. J., Summerfield J. A., Turner M. W. High frequencies in African and non-African populations of independent mutations in the mannose binding protein gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Dec;1(9):709–715. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.9.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J. H., Thiel S., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Reid K. B. Binding of the pentamer/hexamer forms of mannan-binding protein to zymosan activates the proenzyme C1r2C1s2 complex, of the classical pathway of complement, without involvement of C1q. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2287–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen H. O., Garred P., Kurtzhals J. A., Lamm L. U., Ryder L. P., Thiel S., Svejgaard A. A new frequent allele is the missing link in the structural polymorphism of the human mannan-binding protein. Immunogenetics. 1994;40(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00163962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen H. O., Garred P., Thiel S., Kurtzhals J. A., Lamm L. U., Ryder L. P., Svejgaard A. Interplay between promoter and structural gene variants control basal serum level of mannan-binding protein. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 15;155(6):3013–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariette X., Agbalika F., Daniel M. T., Bisson M., Lagrange P., Brouet J. C., Morinet F. Detection of human T lymphotropic virus type I tax gene in salivary gland epithelium from two patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Oct;36(10):1423–1428. doi: 10.1002/art.1780361015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M., Fujita T. Activation of the classical complement pathway by mannose-binding protein in association with a novel C1s-like serine protease. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1497–1502. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita M., Hijikata M., Ohta Y., Iwata K., Matsumoto M., Nakao K., Kanai K., Yoshida N., Baba K., Mishiro S. Hepatitis C virus infection and mutations of mannose-binding lectin gene MBL. Arch Virol. 1998;143(4):645–651. doi: 10.1007/s007050050320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinobu A., Kanagawa S., Koshiba M., Sugai S., Kumagai S. Association of the glutathione S-transferase M1 homozygous null genotype with susceptibility to Sjögren's syndrome in Japanese individuals. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Dec;42(12):2612–2615. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199912)42:12<2612::AID-ANR15>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlotsky J. M., Roudot-Thoraval F., Simmonds P., Mellor J., Ben Yahia M. B., André C., Voisin M. C., Intrator L., Zafrani E. S., Duval J. Extrahepatic immunologic manifestations in chronic hepatitis C and hepatitis C virus serotypes. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Feb 1;122(3):169–173. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-3-199502010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Servenius B., Compton T., Fox R. I. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction in blood and tissue biopsies from patients with Sjogren's syndrome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2191–2198. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth S. J., Donn R. P., Hassall A., Dawes P., Ollier W., Snowden N. Absence of an association between mannose-binding lectin polymorphism and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 Feb;37(2):186–188. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. E., Wooten C., Goldman D., Petri M. Mannose-binding protein genetic polymorphisms in black patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Dec;39(12):2046–2051. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiya M., Super M., Tabona P., Levinsky R. J., Arai T., Turner M. W., Summerfield J. A. Molecular basis of opsonic defect in immunodeficient children. Lancet. 1991 Jun 29;337(8757):1569–1570. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93263-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield J. A., Sumiya M., Levin M., Turner M. W. Association of mutations in mannose binding protein gene with childhood infection in consecutive hospital series. BMJ. 1997 Apr 26;314(7089):1229–1232. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7089.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Super M., Thiel S., Lu J., Levinsky R. J., Turner M. W. Association of low levels of mannan-binding protein with a common defect of opsonisation. Lancet. 1989 Nov 25;2(8674):1236–1239. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel S., Vorup-Jensen T., Stover C. M., Schwaeble W., Laursen S. B., Poulsen K., Willis A. C., Eggleton P., Hansen S., Holmskov U. A second serine protease associated with mannan-binding lectin that activates complement. Nature. 1997 Apr 3;386(6624):506–510. doi: 10.1038/386506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitali C., Bombardieri S., Moutsopoulos H. M., Balestrieri G., Bencivelli W., Bernstein R. M., Bjerrum K. B., Braga S., Coll J., de Vita S. Preliminary criteria for the classification of Sjögren's syndrome. Results of a prospective concerted action supported by the European Community. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Mar;36(3):340–347. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. W., Provost T. T., Bias W. B., Alexander E. L., Edlow D. W., Hochberg M. C., Stevens M. B., Arnett F. C. Sjögren's syndrome. Influence of multiple HLA-D region alloantigens on clinical and serologic expression. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Nov;27(11):1245–1253. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]