Abstract
OBJECTIVE—To investigate further the influence of the autonomic nervous system on chronic rheumatic diseases. METHODS—The density and affinity of β2 adrenergic receptors (β2R) on CD19+ lymphocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and systemic sclerosis (SSc), as well as intracellular cAMP levels in patients with RA and SLE, were determined. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were separated from venous blood of patients and healthy controls by Ficoll-Hypaque density centrifugation. CD19+ lymphocytes were purified by magnetic cell sorting, and β2R were determined by a radioligand binding assay with [125I]iodocyanopindolol. Intracellular cAMP levels and β2R agonist induced cell death were measured by a radioimmunoassay and flow cytometry using annexin-V binding, respectively. Systemic disease activity of the patients was evaluated using multifactorial scoring systems. RESULTS—The density of β2R on peripheral CD19+ lymphocytes was significantly decreased in patients with RA, SLE, and SSc compared with healthy controls. In patients with RA and SSc β2R density was negatively correlated with systemic disease activity. Furthermore, although basal intracellular cAMP levels were raised in patients with RA and SLE, the increase of cAMP upon stimulation of β2R was significantly reduced in these patients compared with control subjects. Preliminary data suggest that β2R agonist induced cell death is diminished in patients with RA exhibiting decreased β2R densities. CONCLUSIONS—The results of this study show a reduction of β2R densities on B lymphocytes mirrored by an impaired intracellular cAMP generation in patients with chronic rheumatic diseases, indicating a decreased influence of the autonomic nervous system on B cells in these conditions.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (168.4 KB).
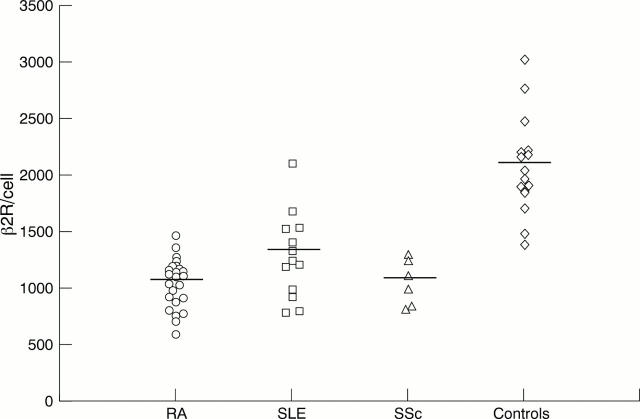
Figure 1 .
Density of β2 adrenergic receptors (β2R) on CD19+ lymphocytes. The density of β2R on CD19+ cells is significantly reduced in patients with chronic rheumatic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis (RA, n=24), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, n=13), systemic sclerosis (SSc, n=6) compared with healthy control subjects (controls, n=16) (p<0.001; one way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's procedure; RA, SLE, or SSc v controls). No significant difference is seen between the three patient groups. Data are presented as plots of the receptor numbers of individual subjects, the bar representing the mean.
Figure 2 .
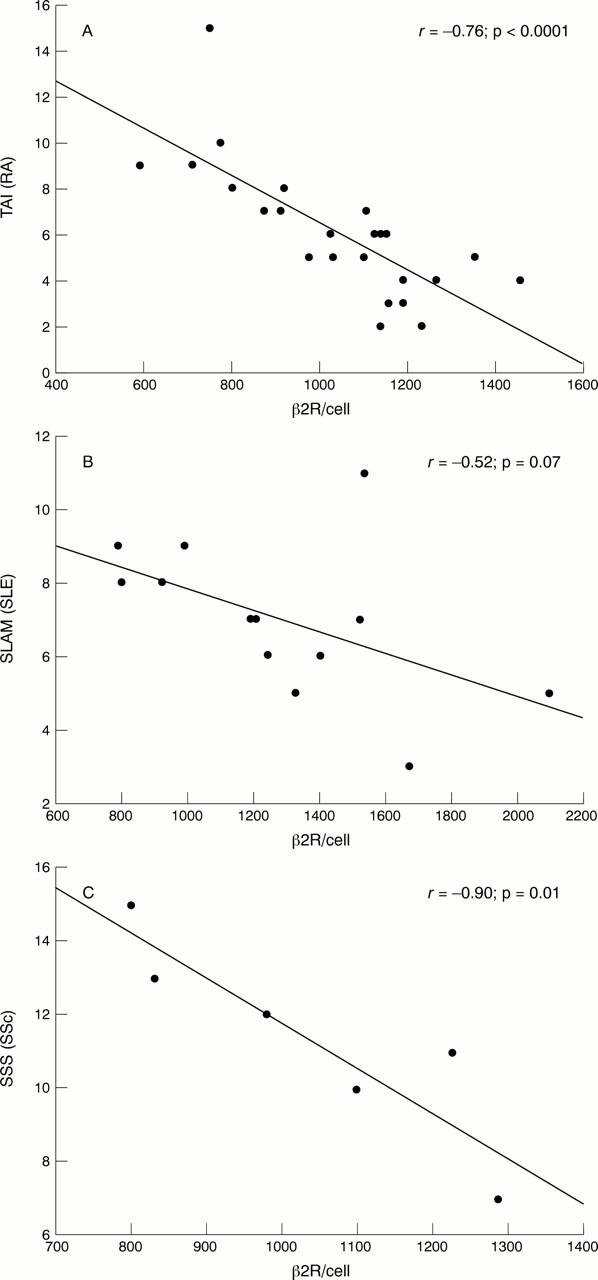
Correlation of the density of β2 adrenergic receptors (β2R) with disease activity. In patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic sclerosis (SSc) a significant negative correlation could be seen between systemic activity scores and the density of β2R on CD19+ lymphocytes. Correlation between β2R and disease activity just missed the significance level in the group with SLE: (A) β2R v the total disease activity score (TAI) in patients with RA; (B) β2R v the SLE activity measure (SLAM) in patients with SLE; (C) β2R v the SSc score (SSS) in patients with SSc. Correlation between β2R and the values obtained by the different scoring systems used in this study (TAI, SLAM, SSS) was calculated by the Pearson product moment correlation test.
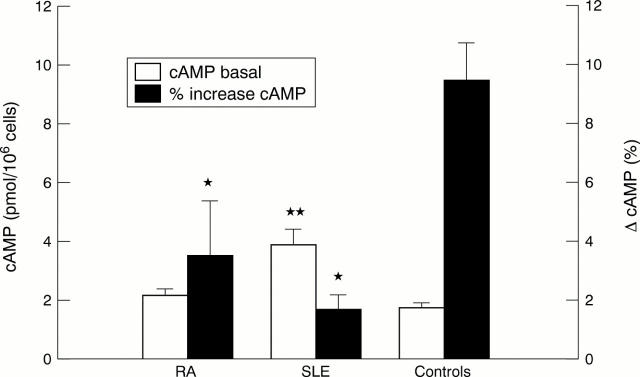
Figure 3 .
Intracellular cAMP levels. Basal cAMP levels (cAMP basal) were significantly raised in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) compared with control subjects. The relative increase of cAMP (% increase cAMP) above basal levels after isoprenaline stimulation was markedly decreased in both patient groups compared with the control group (* p<0.05, ** p<0.001; one way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's procedure; RA, SLE v control).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew E. M., Plater-Zyberk C., Brown C. M., Williams D. G., Maini R. N. The potential role of B-lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1991;30 (Suppl 1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhäupl T., Liebl B., Trunk E., Träger K., Ensinger H., Georgieff M. Evidence for inverse regulation of high and low affinity binding sites for (-)125iodocyanopindolol in human mononuclear leucocytes during epinephrine infusion. J Recept Res. 1993;13(1-4):355–367. doi: 10.3109/10799899309073666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerwald C. G., Laufenberg M., Specht T., von Wichert P., Burmester G. R., Krause A. Impaired sympathetic influence on the immune response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis due to lymphocyte subset-specific modulation of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Dec;36(12):1262–1269. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.12.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerwald C., Graefe C., Muhl C., Von Wichert P., Krause A. Beta 2-adrenergic receptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with rheumatic diseases. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;22 (Suppl 1):42–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerwald C., Graefe C., von Wichert P., Krause A. Decreased density of beta-adrenergic receptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992 Feb;19(2):204–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Kühn H., Weyand I., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional desensitization of the isolated beta-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: potential role of an analog of the retinal protein arrestin (48-kDa protein). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8879–8882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E., Brinkmann M., Schemuth R., O'Hara N., Daul A. Terbutaline-induced desensitization of human lymphocyte beta 2-adrenoceptors. Accelerated restoration of beta-adrenoceptor responsiveness by prednisone and ketotifen. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1096–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI112063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cases A., Bono M., Gaya J., Jimenez W., Calls J., Esforzado N., Rivera F., Revert L. Reversible decrease of surface beta 2-adrenoceptor number and response in lymphocytes of patients with pheochromocytoma. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1995 Apr;17(3):537–549. doi: 10.3109/10641969509037423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Z., McGuire J. C., Leach K. L., Cambier J. C. Transmembrane signaling through B cell MHC class II molecules: anti-Ia antibodies induce protein kinase C translocation to the nuclear fraction. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2345–2352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikanza I. C., Petrou P., Kingsley G., Chrousos G., Panayi G. S. Defective hypothalamic response to immune and inflammatory stimuli in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Nov;35(11):1281–1288. doi: 10.1002/art.1780351107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. O., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted high affinity state of the beta-adrenergic receptor in human neutrophils: modulation by corticosteroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Oct;53(4):703–708. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-4-703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr M., Kendall M. J., Young D. W., Meynell M. J., Hawkins C. F. Assessment of rheumatoid activity based on clinical features and blood and synovial fluid analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Apr;35(2):163–167. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L. Direct innervation of lymphoid organs: substrate for neurotransmitter signaling of cells of the immune system. Neuropsychobiology. 1993;28(1-2):110–112. doi: 10.1159/000119011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felten D. L., Felten S. Y., Bellinger D. L., Carlson S. L., Ackerman K. D., Madden K. S., Olschowki J. A., Livnat S. Noradrenergic sympathetic neural interactions with the immune system: structure and function. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:225–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00534.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs B. A., Albright J. W., Albright J. F. Beta-adrenergic receptors on murine lymphocytes: density varies with cell maturity and lymphocyte subtype and is decreased after antigen administration. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jul;114(2):231–245. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert K. M., Hoffmann M. K. cAMP is an essential signal in the induction of antibody production by B cells but inhibits helper function of T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2084–2089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Middleton E., Jr Lymphocyte blast transformation. I. Demonstration of adrenergic receptors in human peripheral lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Dec;1(6):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichsen H., Barth J., Ferstl R., Kirch W. Changes of immunoregulatory cells induced by acoustic stress in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis, and in healthy controls. Eur J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;19(4):372–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1989.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. L., Ashmore R. C., Gordon M. A. Effects of beta-adrenergic agents on the murine lymphocyte response to mitogen stimulation. J Immunopharmacol. 1981;3(2):205–219. doi: 10.3109/08923978109026427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Khan I. U., Malemud C. J. Deficient type I protein kinase A isozyme activity in systemic lupus erythematosus T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):422–430. doi: 10.1172/JCI117340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. M., Sansoni P., Silverman E. D., Engleman E. G., Melmon K. L. Beta-adrenergic receptors on human suppressor, helper, and cytolytic lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 1;35(7):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Buskila D., Gladman D., Bruser B., Malkin A. Cortisol catabolism by lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jan;17(1):30–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. A., Johnson G. D., Gordon J. Distribution of cAMP in secondary follicles and its expression in B cell apoptosis and CD40-mediated survival. Int Immunol. 1993 Sep;5(9):1085–1091. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.9.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korichneva I. L., Tkachuk V. A. Alterations in beta-adrenoceptor density on T-lymphocytes upon activation with interleukin-2 and phytohaemagglutinin. Biomed Sci. 1990 Jan;1(1):84–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause A., Henrich A., Beckh K. H., Von Wichert P., Baerwald C. Correlation between density of beta 2-adrenergic receptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptors in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;22 (Suppl 1):47–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause A., Steitz A., von Wichert P., Baerwald C. Influence of cytokines on the density of beta 2-adrenergic receptors on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Cytokine. 1995 Apr;7(3):273–276. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1995.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landmann R. Beta-adrenergic receptors in human leukocyte subpopulations. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;22 (Suppl 1):30–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang M. H., Socher S. A., Larson M. G., Schur P. H. Reliability and validity of six systems for the clinical assessment of disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Sep;32(9):1107–1118. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lømo J., Blomhoff H. K., Beiske K., Stokke T., Smeland E. B. TGF-beta 1 and cyclic AMP promote apoptosis in resting human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1634–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisel A. S., Fowler P., Rearden A., Motulsky H. J., Michel M. C. A new method for isolation of human lymphocyte subsets reveals differential regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by terbutaline treatment. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Oct;46(4):429–439. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miltenyi S., Müller W., Weichel W., Radbruch A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry. 1990;11(2):231–238. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. Adrenergic receptors in man: direct identification, physiologic regulation, and clinical alterations. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):18–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki T., Kontula K., Härkönen M. The beta-adrenergic system in man: physiological and pathophysiological response. Regulation of receptor density and functioning. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1990;201:25–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell M. K., VanderWall J., Beard K. S., Freed J. H. Ligation of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules mediates apoptotic cell death in resting B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10459–10463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigley K. P., Callard R. E. Inhibition of B cell proliferation with anti-CD19 monoclonal antibodies: anti-CD19 antibodies do not interfere with early signaling events triggered by anti-IgM or interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):535–540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie D. M., Boyle J. A., McInnes J. M., Jasani M. K., Dalakos T. G., Grieveson P., Buchanan W. W. Clinical studies with an articular index for the assessment of joint tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1968 Jul;37(147):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders V. M., Powell-Oliver F. E. Beta 2-adrenoceptor stimulation increases the number of antigen-specific precursor B lymphocytes that differentiate into IgM-secreting cells without affecting burst size. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1822–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders V. M. The role of adrenoceptor-mediated signals in the modulation of lymphocyte function. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1995;5(3):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0960-5428(95)00019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souvannavong V., Lemaire C., Andréau K., Brown S., Adam A. Age-associated modulation of apoptosis and activation in murine B lymphocytes. Mech Ageing Dev. 1998 Jul 15;103(3):285–299. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(98)00051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman C., Chelvarajan R. L., Cambier J. C., Bondada S. Interleukin-4 overcomes the negative influence of cyclic AMP accumulation on antigen receptor stimulated B lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 1998 Oct;35(14-15):997–1014. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(98)00068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H., Wang L., Huang C. S., Ju G. Plasticity of GAP-43 innervation of the spleen during immune response in the mouse. Evidence for axonal sprouting and redistribution of the nerve fibers. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1998 Jan-Apr;5(1-2):53–60. doi: 10.1159/000026326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoukos Y., Leonard J. P., Thomaides T., Thompson A. J., Cuzner M. L. beta-Adrenergic receptor density and function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells are increased in multiple sclerosis: a regulatory role for cortisol and interleukin-1. Ann Neurol. 1992 Jun;31(6):657–662. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]